Your Essential Companion Planting Guide

Your Essential Companion Planting Guide
Welcome to the world of companion planting, where harmony reigns supreme in the garden.
Companion planting is a time-honoured practice that involves strategically placing plants together to maximize their growth, health, and productivity.
This holistic approach to gardening harnesses the natural relationships between different plant species, utilizing their unique qualities to benefit one another.
Whether you're a seasoned gardener or just starting, this comprehensive guide will illuminate the secrets of companion planting, helping you create a thriving ecosystem in your backyard.
Discover how companion planting can unlock your garden's full potential, from deterring pests and boosting pollination to enhancing flavour and nutrient uptake.
Join us on a journey of discovery as we delve into the fascinating world of plant partnerships and cultivate a greener, more vibrant garden together.
What Is Companion Planting?
A gardening practice known as companion planting entails carefully placing multiple plant species next to one another for mutual benefit.
The theory behind this technique is that certain plants naturally affinize or have antagonistic relationships with one another, which may be used to encourage better growth and higher harvests.
Certain plants, for instance, discharge compounds into the soil that deter pests or prevent weeds from growing.
Conversely, some entice advantageous insects that aid in flower pollination or serve as prey for detrimental pests.
Furthermore, companion planting can also enhance soil fertility and structure by promoting a diverse range of root depths and microbial activity.
Certain plants have deep roots that help break up compacted soil and draw nutrients from deeper layers, making them available to shallower-rooted plants nearby.
Furthermore, nitrogen-fixing bacteria live symbiotic relationships with leguminous plants like beans and peas, enriching the soil with nitrogen and benefiting nearby plants.
Gardeners can create a balanced ecosystem by carefully selecting which plants to grow together.
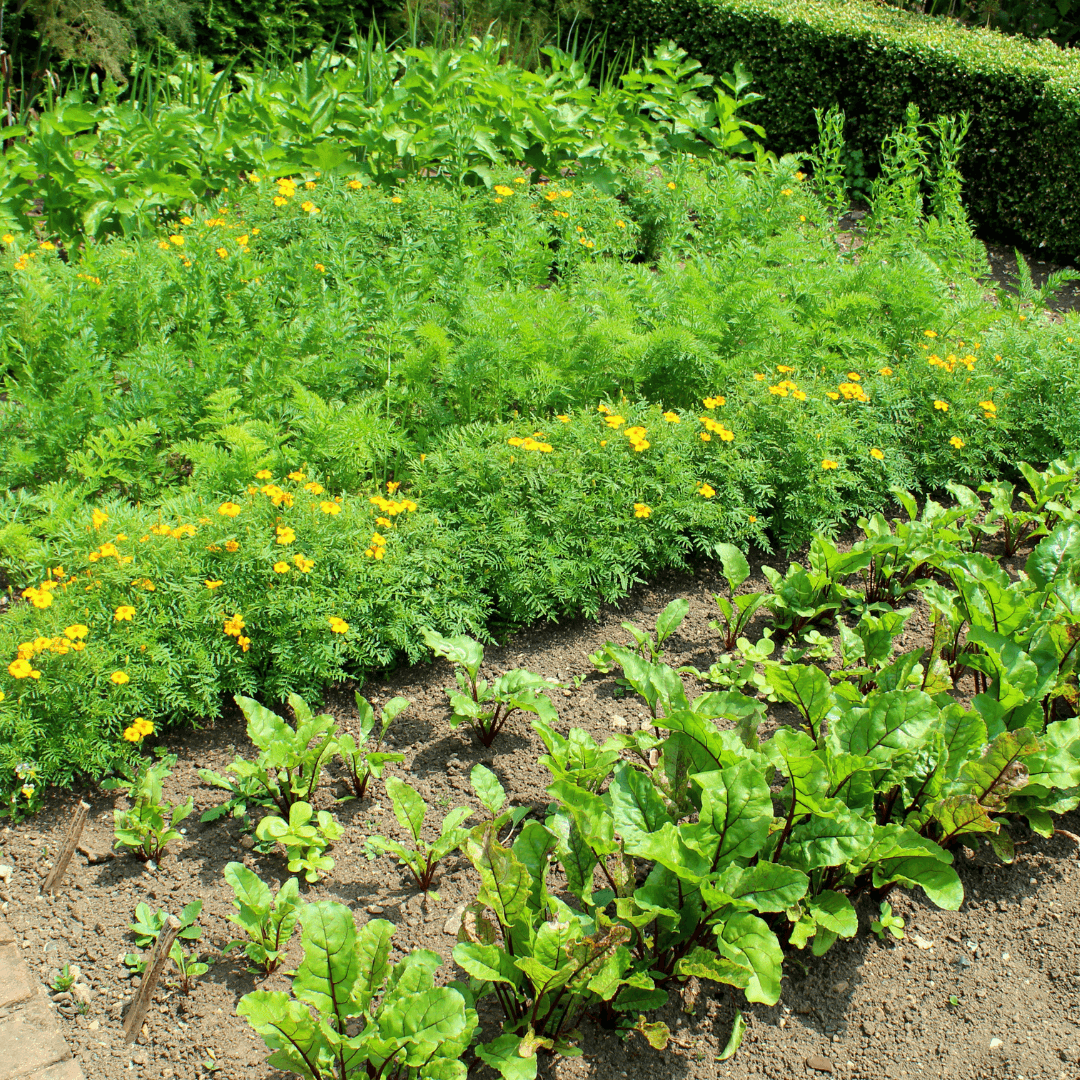

The Science Behind Companion Planting
Companion planting operates on various scientific principles rooted in ecology and plant biology.
One key aspect is allelopathy, where certain plants release biochemicals into the soil that affect the growth of neighbouring plants.
For instance, marigolds exude compounds that deter nematodes, while some herbs like basil produce aromatic oils that repel pests.
Understanding these chemical interactions enables gardeners to pair plants strategically for mutual benefit.
Moreover, companion planting leverages biodiversity to create a more resilient ecosystem. By diversifying plant species, gardeners can disrupt pest and disease cycles, as pests targeting one species may not thrive amidst various plants.
Another scientific basis for companion planting lies in the concept of ecological niches. Different plants have distinct requirements for nutrients, water, and sunlight, and by interplanting species with complementary needs, gardeners can maximize the use of available resources.
For example, tall, sun-loving plants like corn can provide shade and support for trailing crops like beans, which fix nitrogen in the soil.
Additionally, certain plants attract beneficial insects or birds that prey on pests, creating a natural form of pest control.
By exploiting these ecological niches, companion planting optimizes space and fosters a harmonious balance within the garden ecosystem.
Flowers As Companion Plants
Companion planting with flowers can be a wonderful way to enhance your garden's beauty while benefiting other plants.
Here are some common flowers used as companion plants and their benefits:
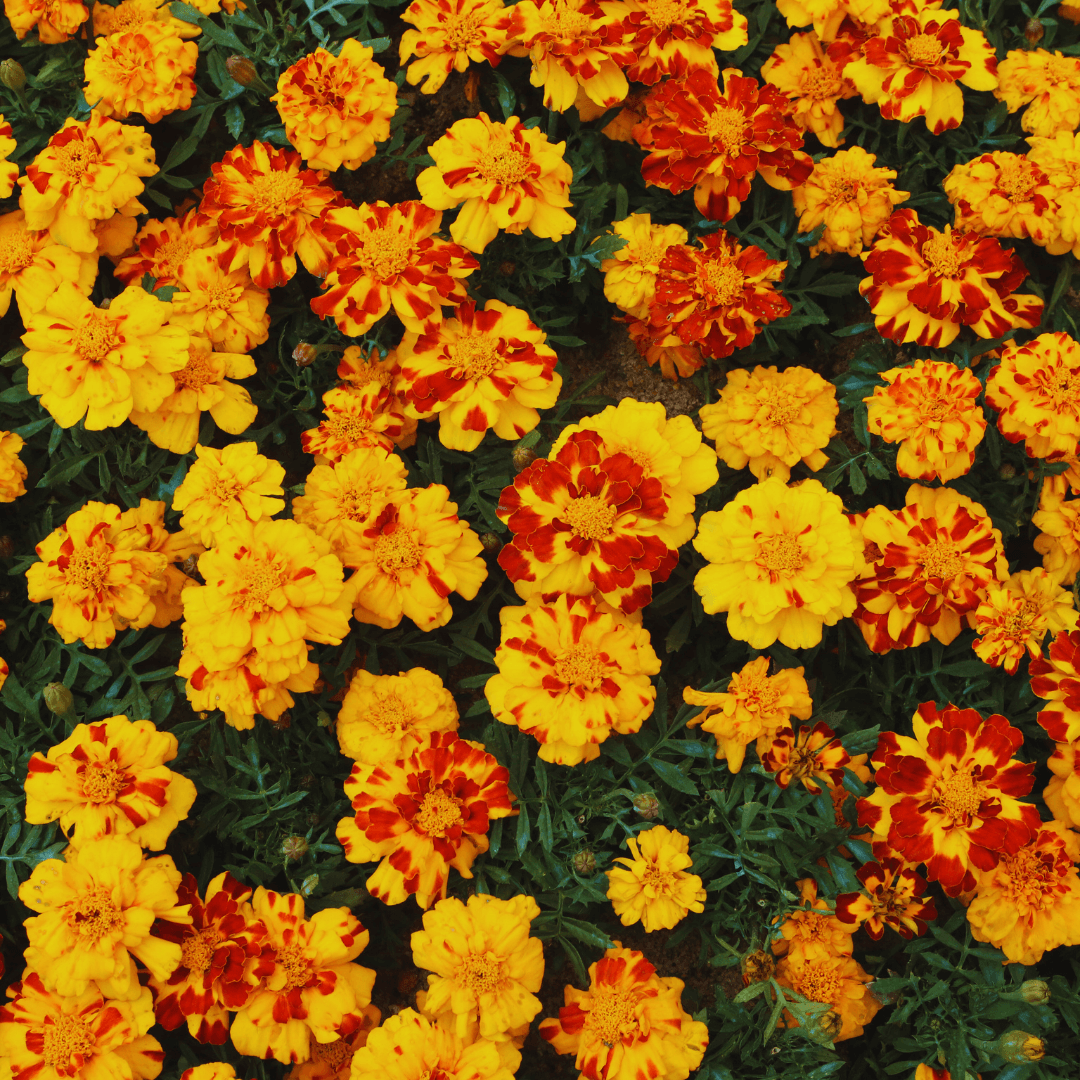

1. Marigolds As Companion Plants
Marigolds are invaluable as companion plants in the garden. Renowned for their nematode-repelling properties, they protect plant roots from these harmful pests.
Moreover, marigolds attract beneficial insects like ladybugs and hoverflies, essential for natural pest control.
These insects prey on common garden nuisances like aphids, fostering a healthier and more balanced ecosystem.
With their dual role in pest management and insect attraction, marigolds contribute significantly to the vitality and sustainability of the garden.
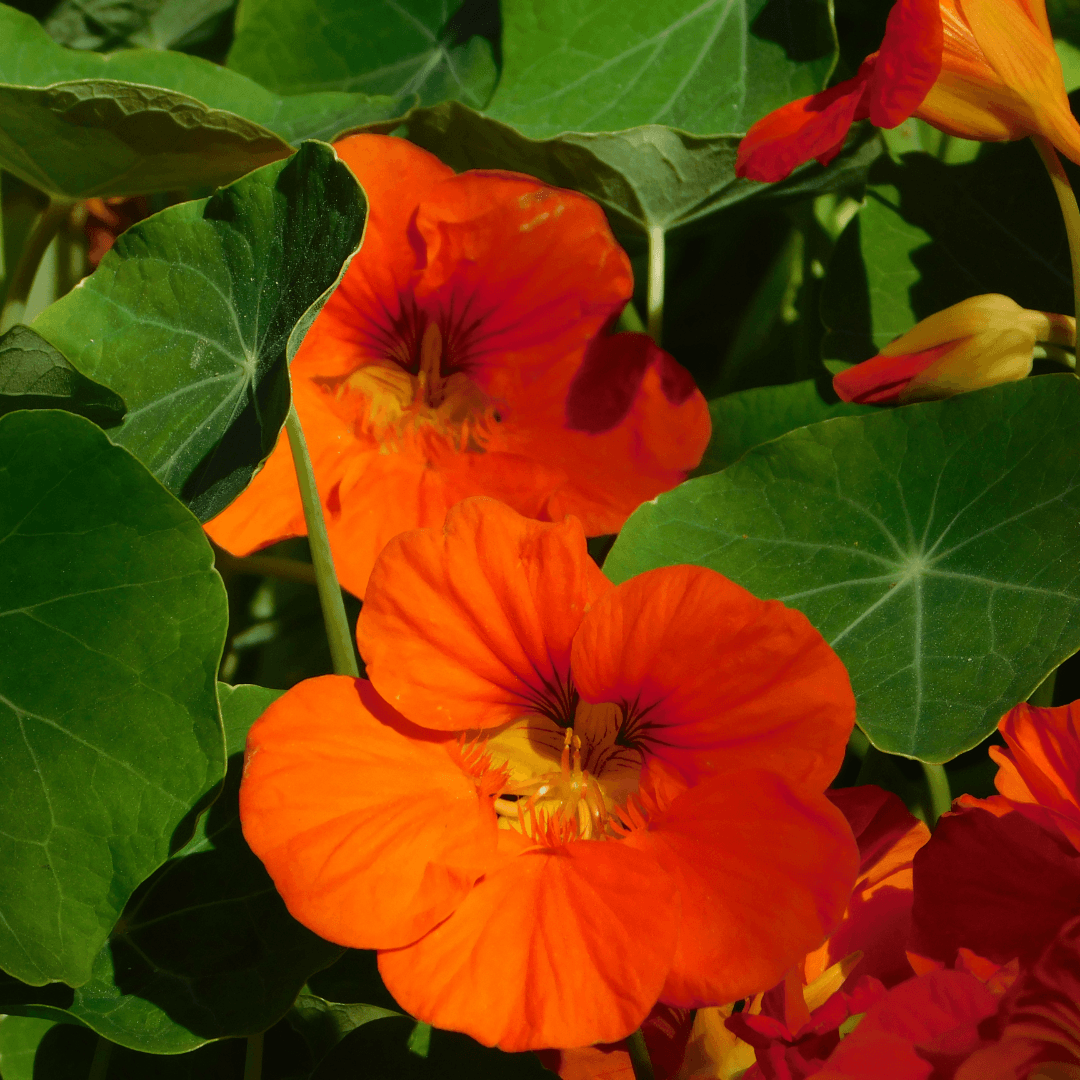
2. Nasturtiums As Companion Flowers
With their vibrant blooms, Nasturtiums offer more than just aesthetic appeal in the garden. They also act as a natural pest management tool, diverting aphids away from other plants, functioning as a sacrificial trap.
Moreover, these versatile flowers deter pests like whiteflies, squash bugs, and cucumber beetles, thus contributing to a healthier garden ecosystem.
Their dual role in pest control and ornamental beauty makes them an invaluable companion plant for any garden.
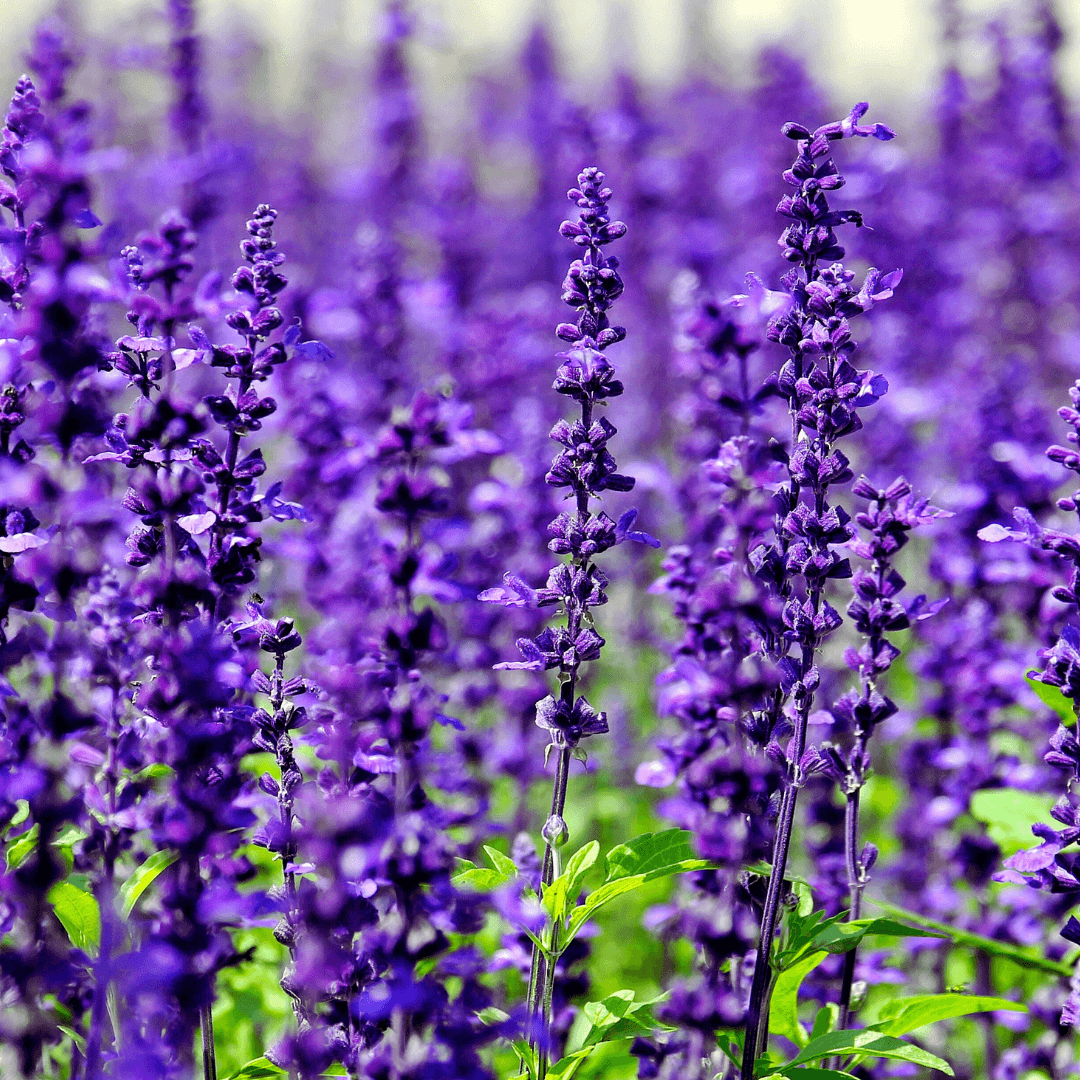

3. Lavender As Companion Flowers
Lavender is a prized companion plant in gardens for its aromatic fragrance and stunning purple blooms. Lavender's allure extends beyond aesthetics, drawing in essential pollinators like bees and butterflies.
Additionally, it is a natural deterrent to various pests, including moths, fleas, and mosquitoes, enhancing the overall health and tranquillity of the garden environment. Lavender is a valuable addition to any garden landscape because it attracts pollinators and repels pests.
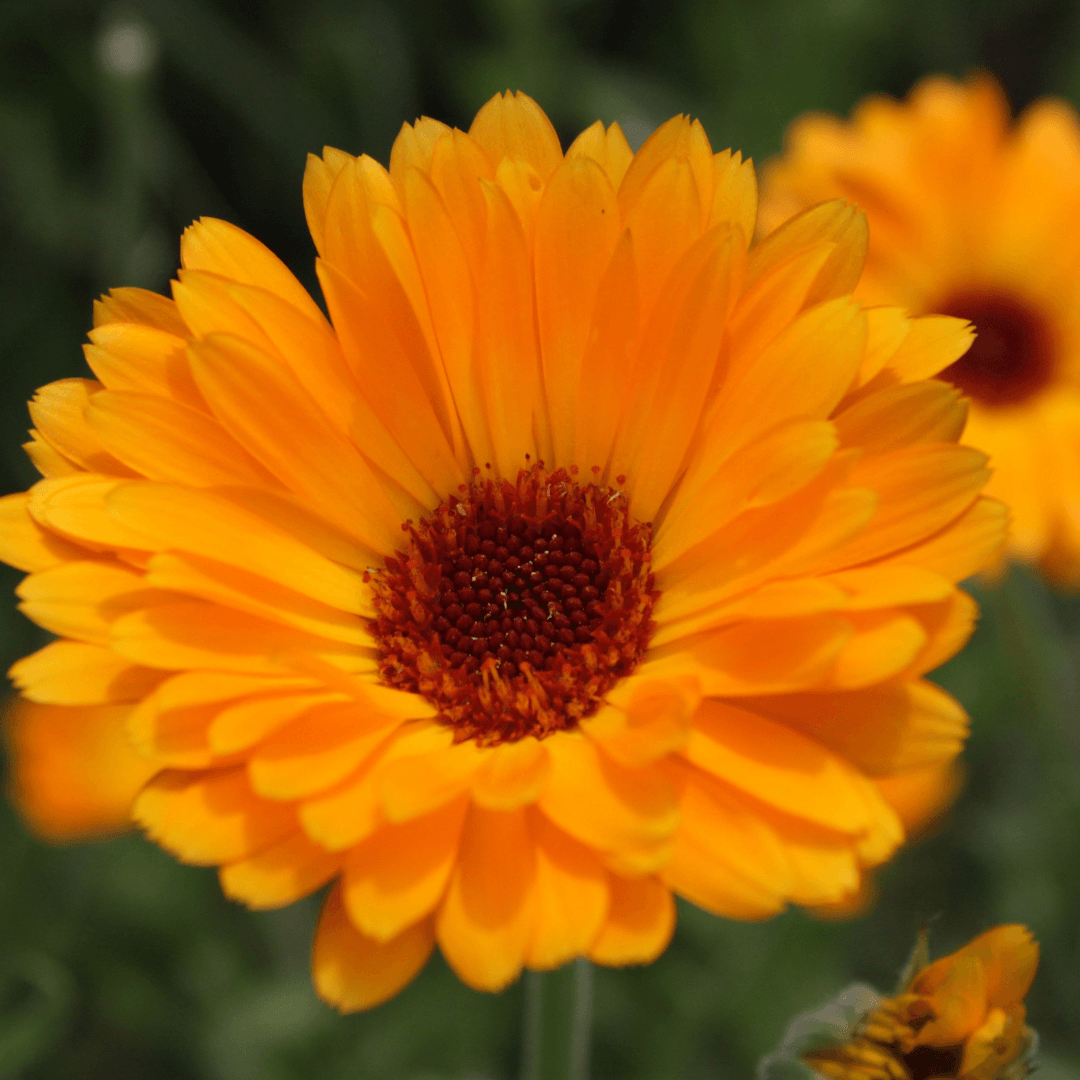

4. Calendula As Companion Flowers
Calendula, or pot marigold, offers more than just vibrant blooms in the garden. Its bright yellow or orange flowers attract essential pollinators and beneficial insects, aiding in the health and productivity of neighbouring plants.
Furthermore, calendula boasts anti-fungal properties, a natural defence against soil-borne diseases. By planting calendula alongside vegetation, gardeners can promote a thriving ecosystem while safeguarding plants from potential fungal threats, ensuring a bountiful and resilient garden environment.
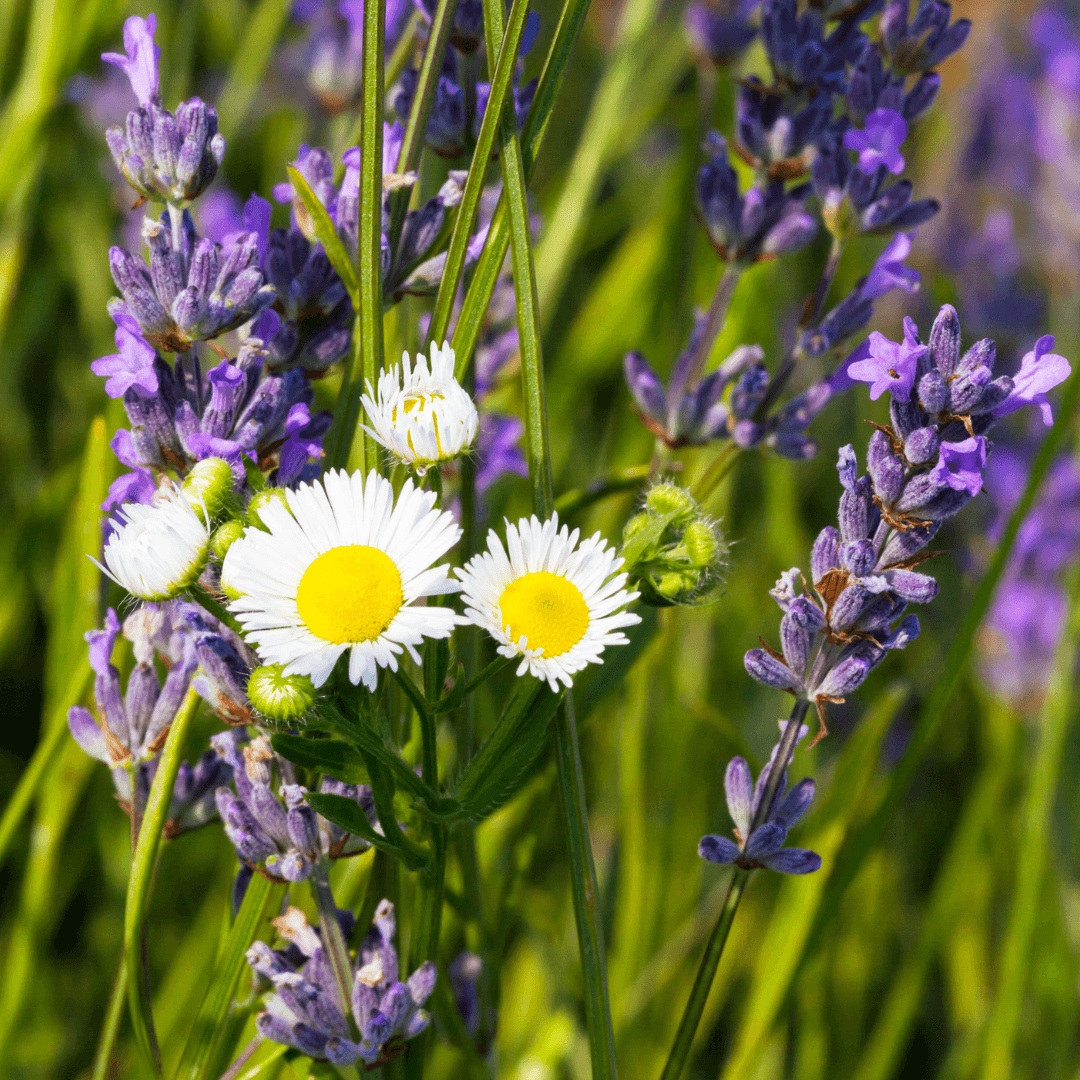

5. Chamomile
Chamomile, with its delicate daisy-like flowers, offers multiple benefits as a companion plant. Its blooms attract hoverflies, natural predators of aphids, aiding in pest control without the need for harmful pesticides.
Moreover, chamomile acts as a nutrient accumulator, enriching the soil with essential minerals like calcium, potassium, and sulphur as it grows.
These nutrients become more readily available to neighbouring plants, promoting their growth and overall health. Chamomile thus plays a vital role in fostering a thriving and balanced garden ecosystem.
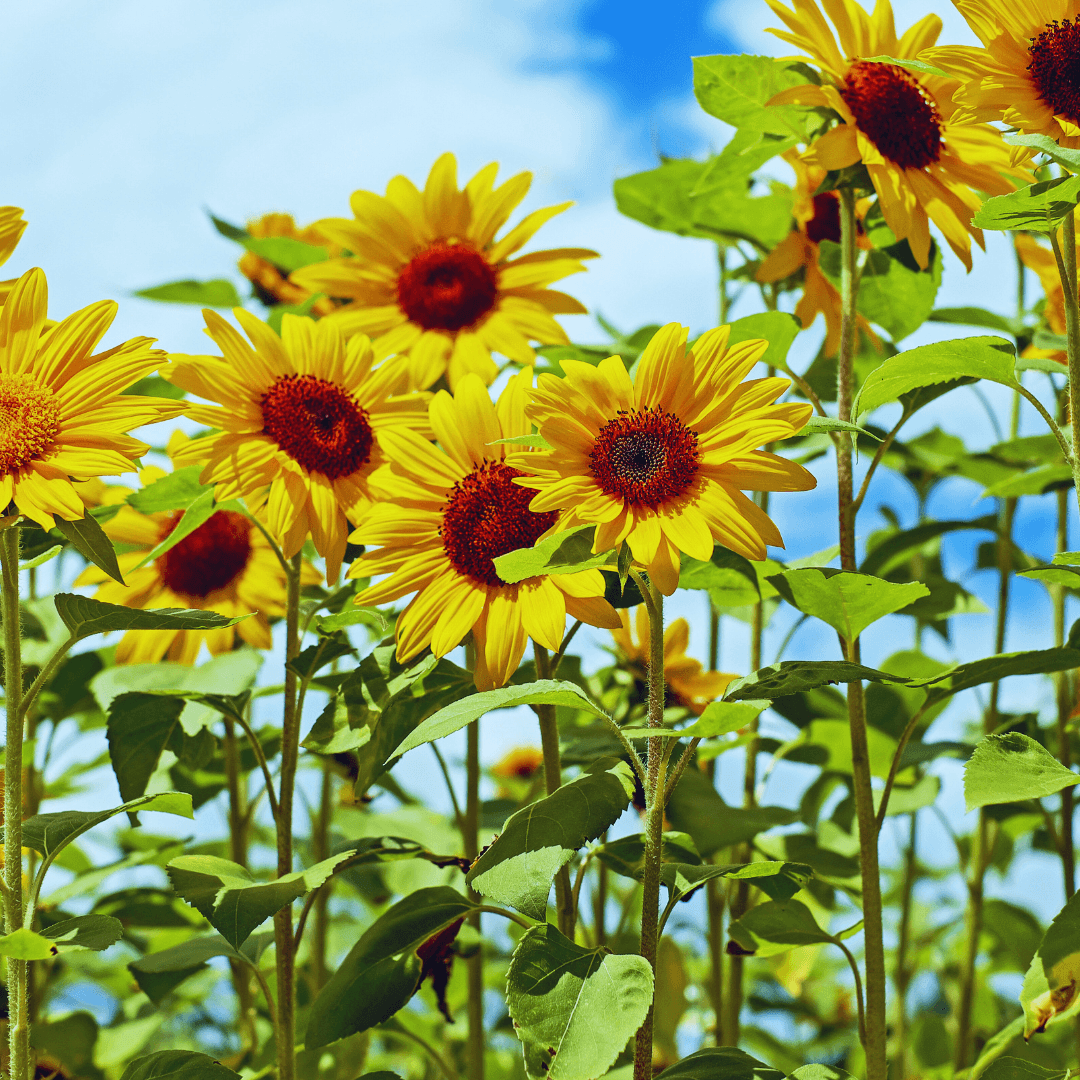

6. Sunflowers As Companion Flowers
Sunflowers are not just striking additions to the garden. They offer numerous benefits as companion plants.
Their towering presence attracts essential pollinators like bees and butterflies, promoting biodiversity and fruit set in nearby plants.
Additionally, sunflowers' tall stalks provide valuable shade and structural support, particularly beneficial for climbing vegetables like beans or cucumbers.
Sunflowers contribute to a thriving and harmonious garden ecosystem through their multifaceted roles, enhancing beauty and functionality.
Fruit Companion Plants
Companion planting with fruit plants involves strategically selecting companion plants that offer benefits such as pest control, improved pollination, soil enrichment, and space utilization.
Here are some common fruit companion plants and their benefits:
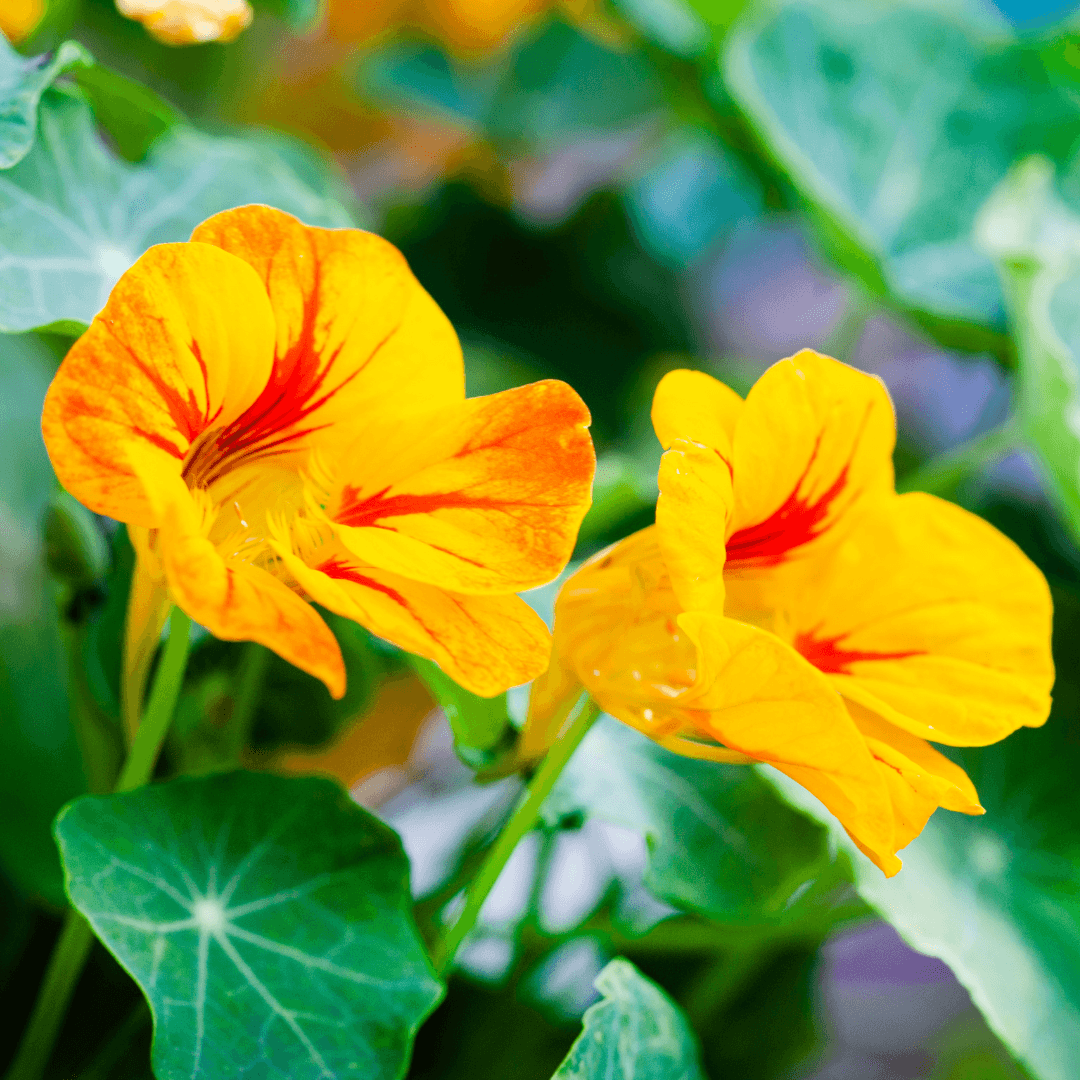

1. Nasturtiums
Nasturtiums are excellent companions for various fruit plants, including tomatoes, cucumbers, and squash. Their presence in the garden diverts aphids away from these fruit-bearing plants, effectively acting as decoys.
Moreover, nasturtiums possess natural repellent properties that deter pests like whiteflies and cucumber beetles, further safeguarding the health of fruit crops.
By attracting pests away from valuable plants and offering pest-repelling attributes, nasturtiums play a vital role in promoting the vitality and productivity of fruit gardens.
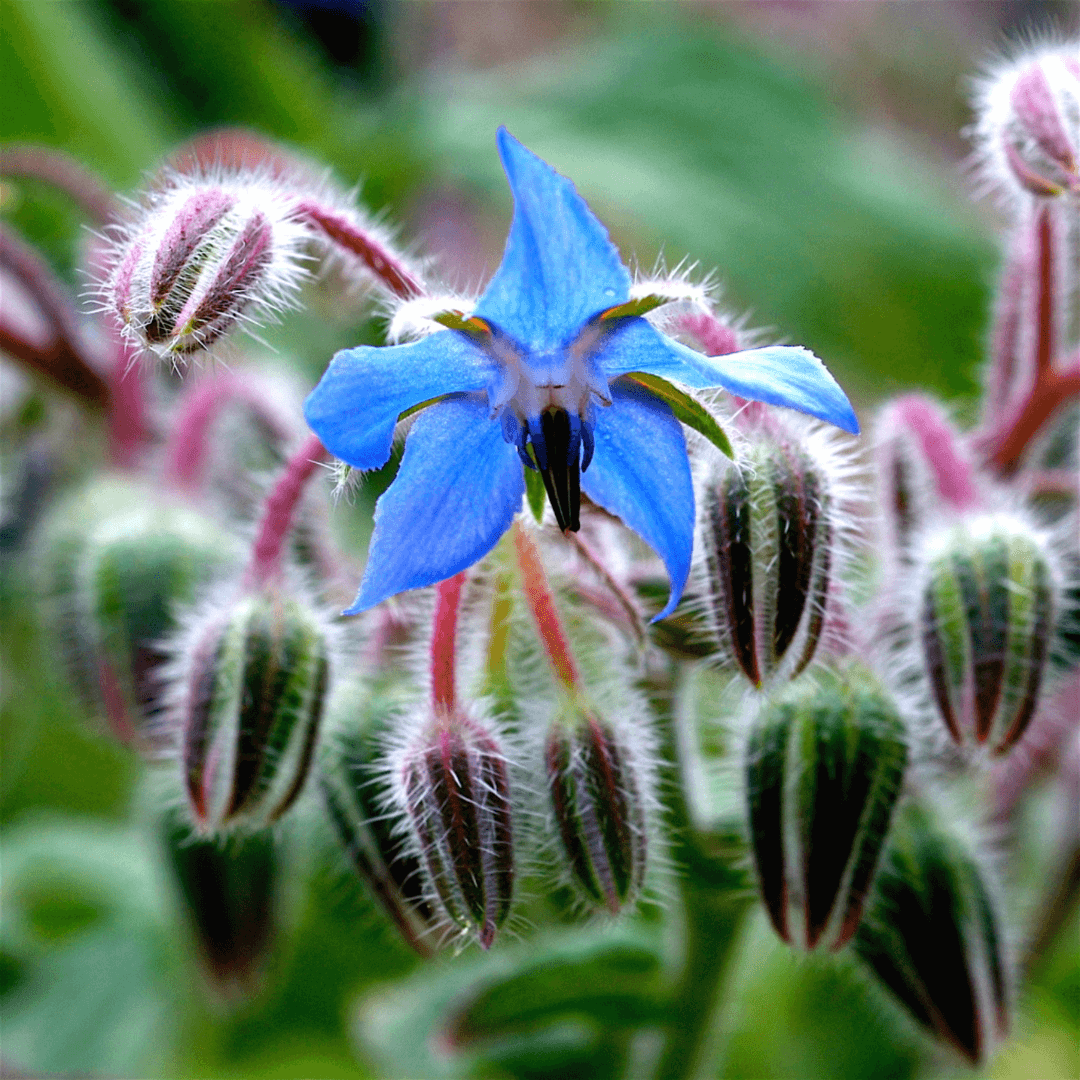

2. Borage
Borage is a beneficial companion to fruit-bearing plants like strawberries, tomatoes, and squash. Its vivid blue flowers attract crucial pollinators, notably bees, aiding fruit production.
Additionally, borage lures beneficial insects like parasitic wasps, pivotal for natural pest control against common garden threats such as tomato hornworms and cabbage worms.
With its dual role in pollination enhancement and pest management, borage significantly bolsters the garden's health and fruit crop yield.
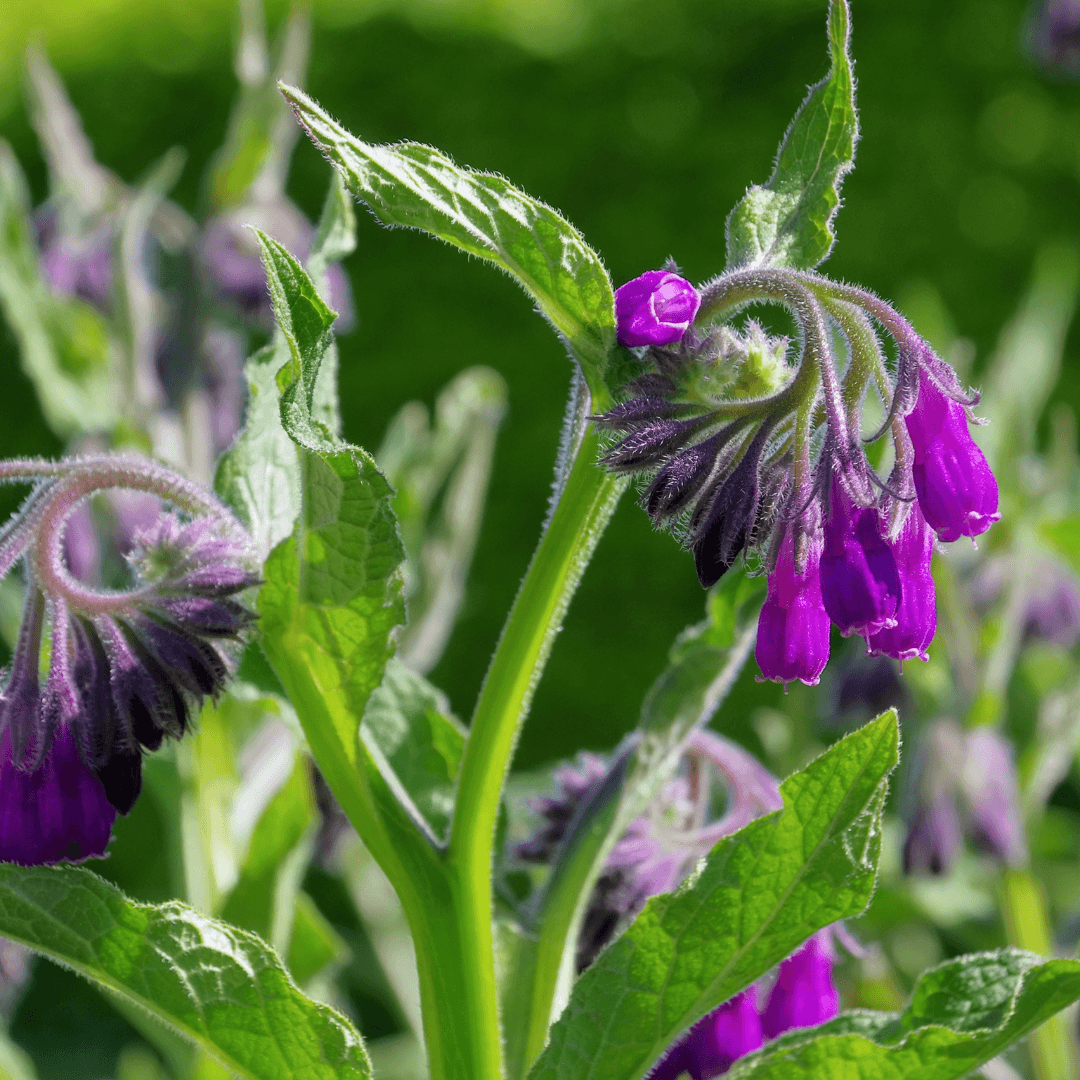

3. Comfrey
Comfrey is an invaluable companion plant for fruit trees and bushes due to its remarkable ability to accumulate energy dynamically.
By delving deep into the soil, comfrey extracts nutrients and minerals, enriching its foliage. As these leaves decompose, they release these essential nutrients into the surrounding soil, effectively nourishing nearby fruit plants.
This natural fertilization process enhances the health and vigour of fruit trees and bushes, promoting robust growth and abundant yields.
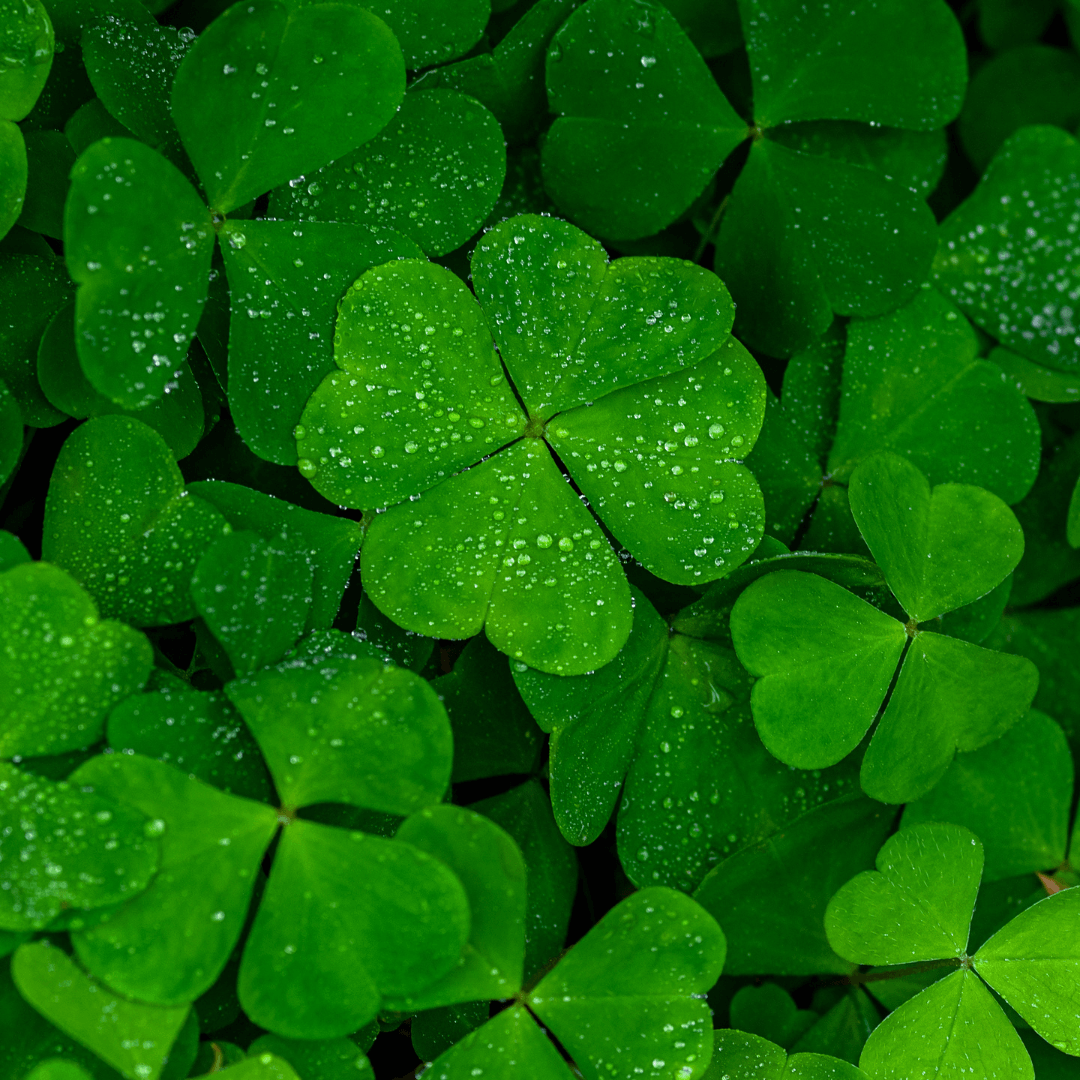

4. Clover
Clover proves advantageous as a companion plant for fruit trees and bushes. As a nitrogen-fixing plant, it enriches soil fertility with essential nutrients.
Additionally, clover serves as a living mulch, effectively suppressing weed growth and conserving soil moisture.
Through these dual functions, clover creates a conducive environment for fruit-bearing plants' healthy growth and development, ultimately fostering improved yields in the orchard or garden.
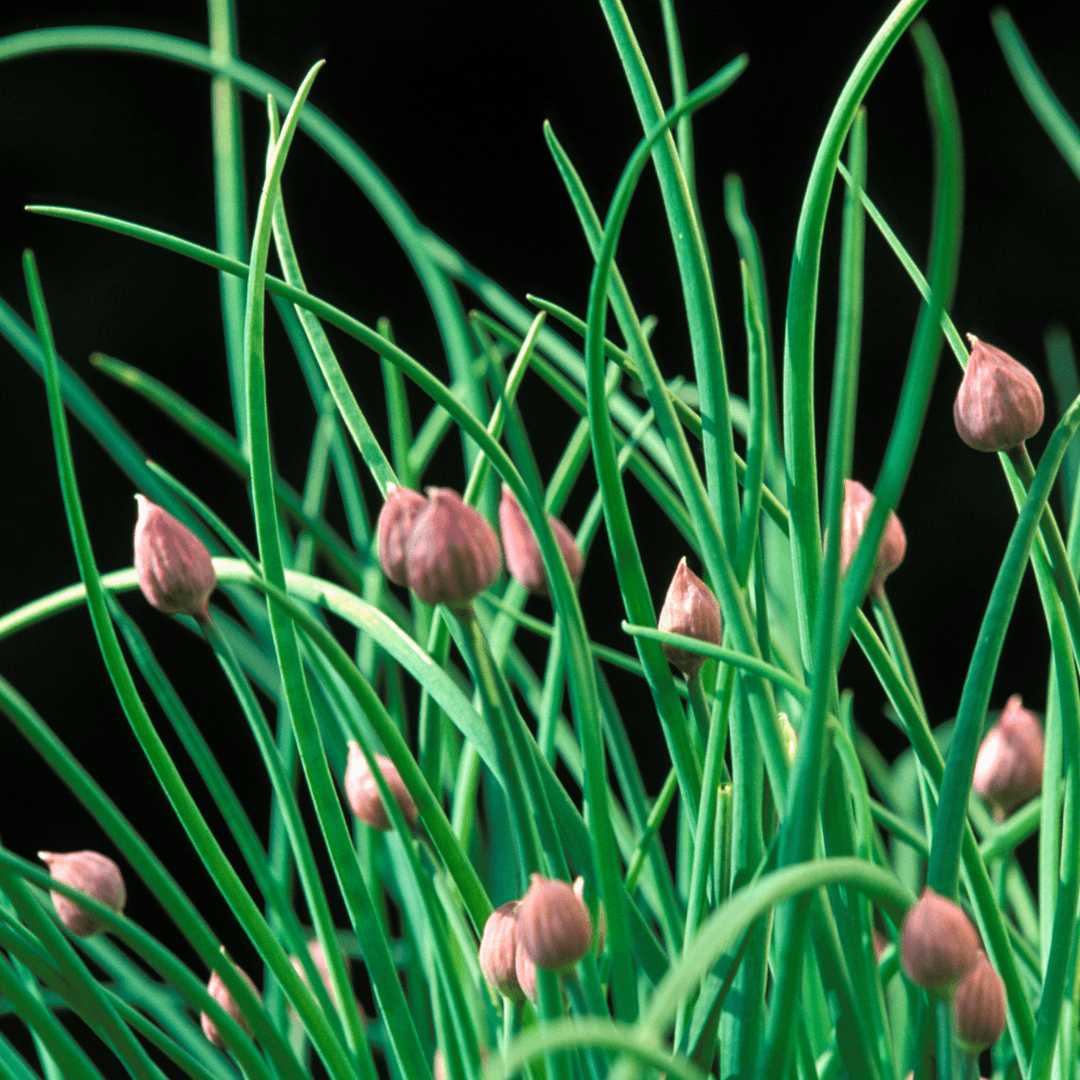

5. Chives
Chives emerge as beneficial companions for fruit trees, especially apple trees, due to their pest-repelling properties against common threats like apple scab.
Moreover, chives deter deer and rabbit browsing, safeguarding fruit trees from damage. Their vibrant purple flowers also attract essential pollinators, ensuring optimal fruit set and yield.
With these combined benefits, chives contribute significantly to the health and productivity of fruit trees in the garden or orchard.
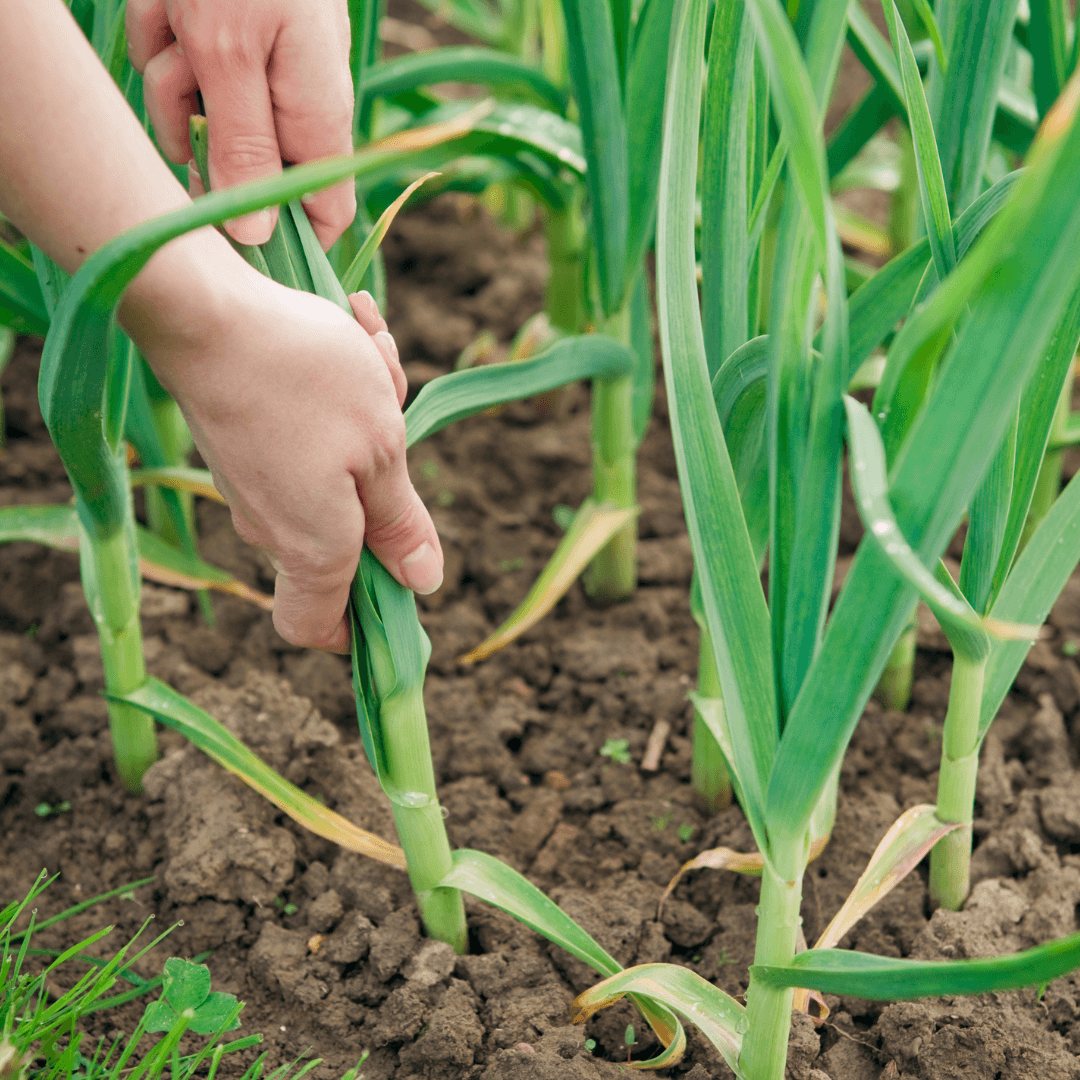

6. Garlic
Garlic is a natural pest deterrent for fruit trees, effectively repelling common nuisances like aphids, spider mites, and fruit tree borers.
Strategically planting garlic around fruit trees or within vegetable gardens can help mitigate pest infestations, reducing reliance on chemical pesticides.
By harnessing garlic's pest-repelling properties, gardeners can foster a healthier environment for fruit trees while minimizing the impact of harmful pests, ultimately supporting sustainable and eco-friendly cultivation practices.
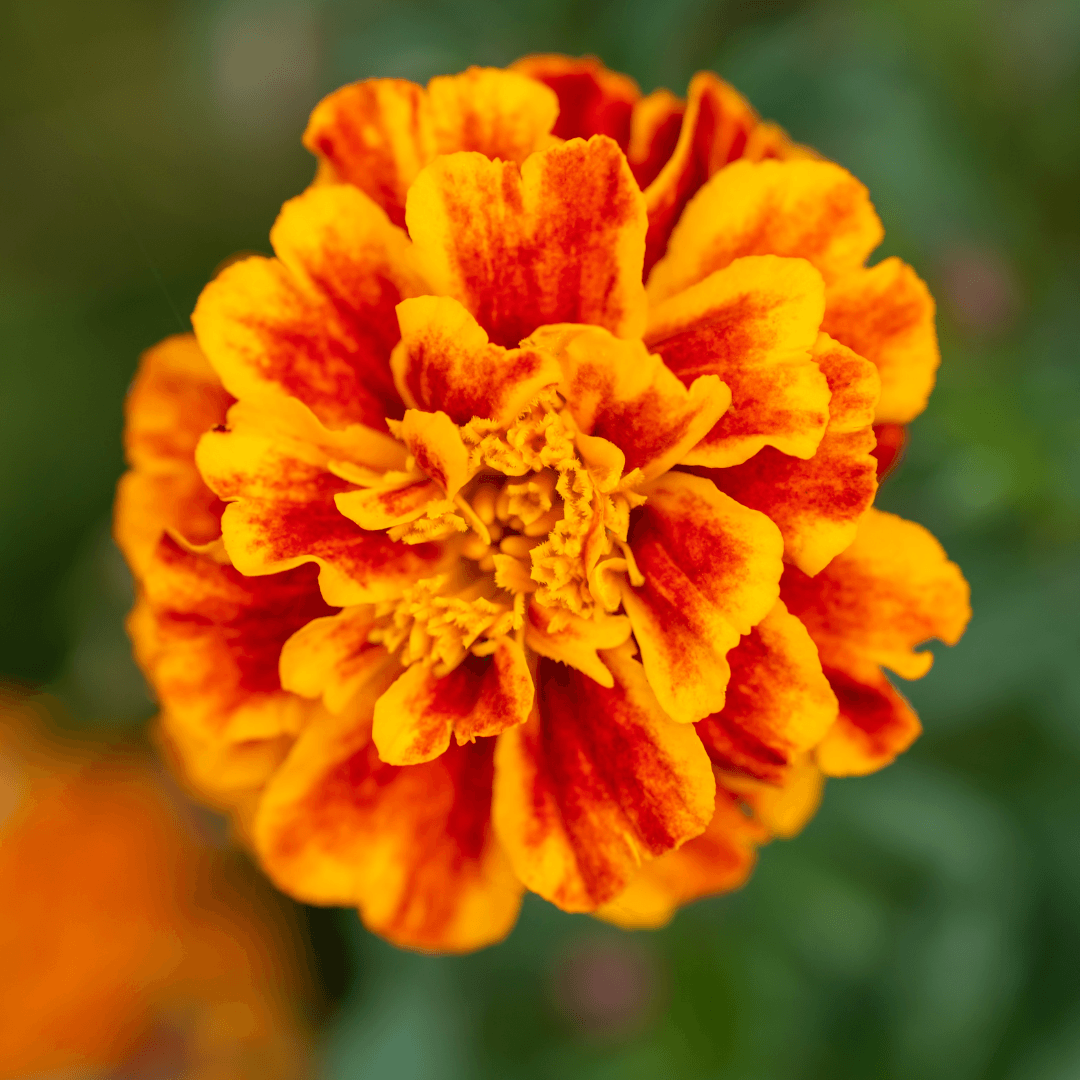

7. Marigolds
Marigolds offer valuable support as companion plants for fruit trees and bushes. Planted around them, marigolds act as natural nematode repellents, safeguarding the soil from these harmful pests.
Additionally, their vibrant flowers serve as beacons for beneficial insects like ladybugs and hoverflies, which play pivotal roles in controlling aphids and other garden pests.
By harnessing marigolds' dual benefits of nematode deterrence and insect attraction, fruit gardens can thrive in a healthier and more balanced ecosystem.
Vegetable Companion Plants
Companion planting with vegetables involves strategically selecting plants that offer benefits such as pest control, improved pollination, enhanced flavour, and space utilization.
Here are some common vegetable companion plants and their benefits:
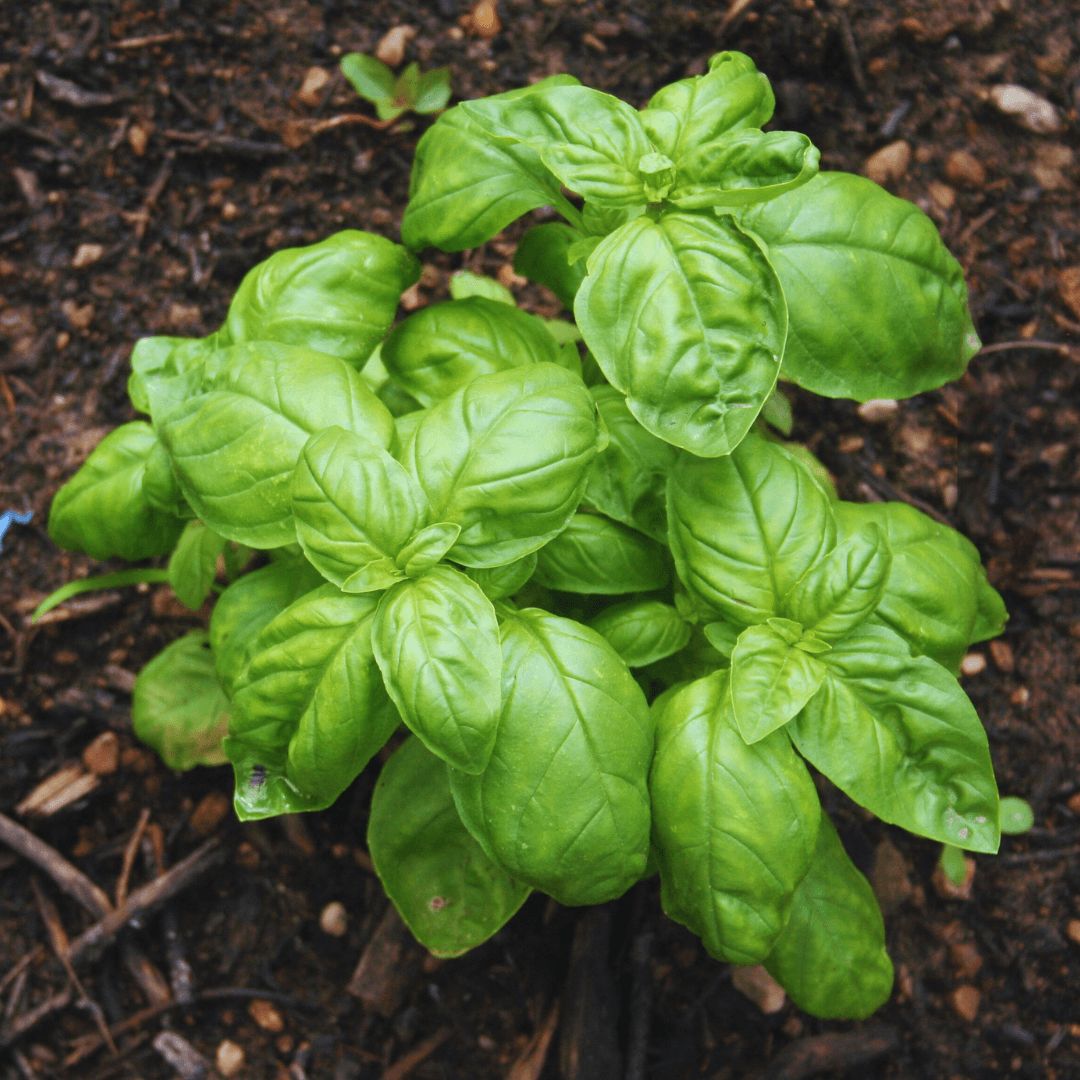

1. Basil
Basil is an exceptional companion for tomatoes, peppers, and various other vegetables in the garden.
Its potent aroma is a natural deterrent against pests such as aphids, mosquitoes, and flies, helping protect neighbouring plants.
Moreover, planting basil near tomatoes enhances their flavour, making it a doubly beneficial companion. With its pest-repelling properties and flavour-enhancing abilities, basil is a valuable addition to any vegetable garden.

2. Thyme
Thyme is a versatile companion plant for eggplants, potatoes, and cabbage. Its aromatic foliage is a natural deterrent against pests like cabbage worms and flea beetles, helping safeguard nearby plants.
By strategically planting thyme alongside vegetables, gardeners can promote a healthier garden environment while minimizing the risk of pest damage, making it an invaluable addition to any vegetable garden.
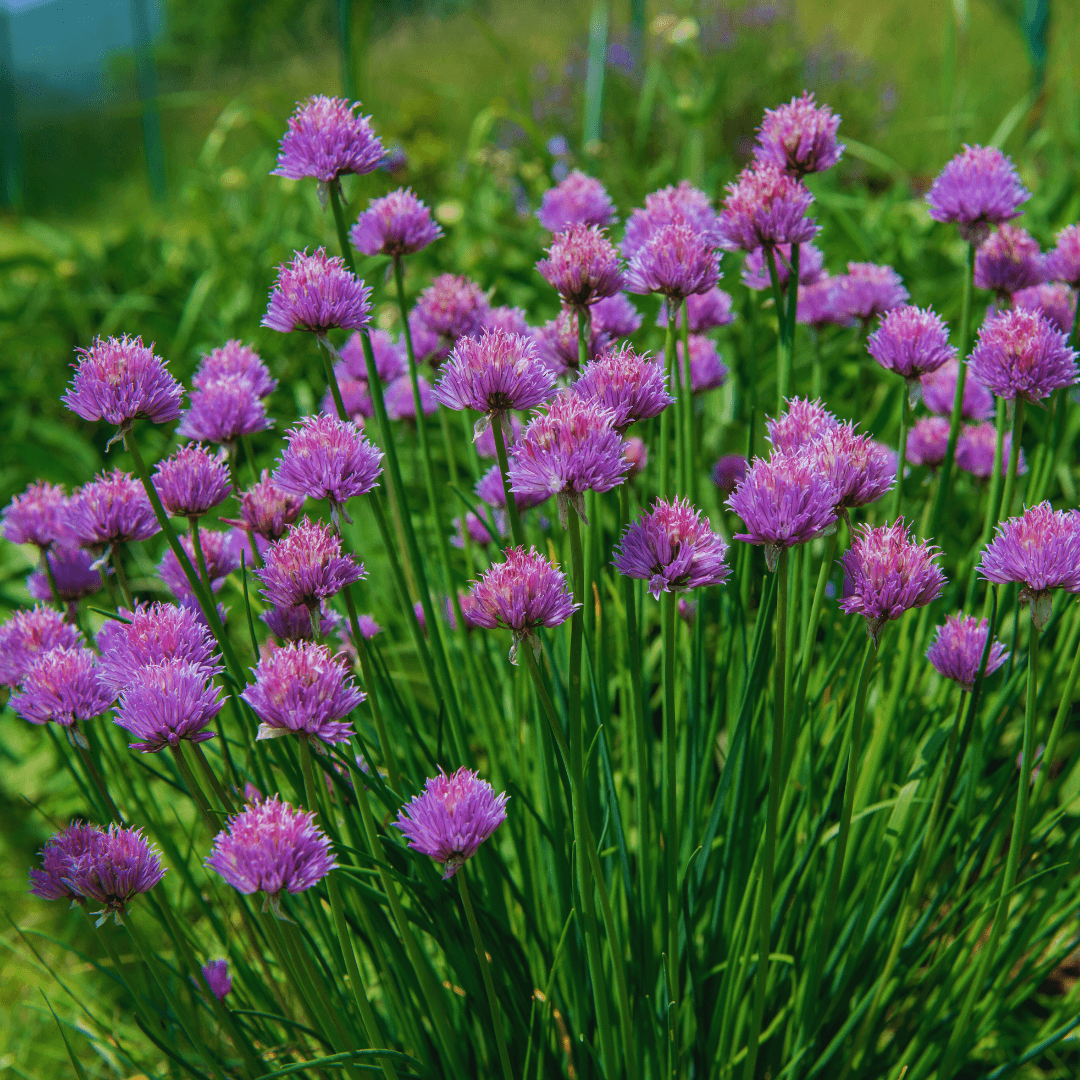

3. Chives
Chives are excellent companions for various vegetables in the garden, including carrots, tomatoes, and lettuce.
Their presence is a natural deterrent against pests like aphids. It also deters browsing by deer and rabbits, safeguarding neighbouring plants.
Furthermore, chives' attractive purple flowers attract essential pollinators, enhancing nearby crops' pollination and fruit set.
With their multi-faceted benefits, chives contribute significantly to the health and productivity of vegetable gardens.
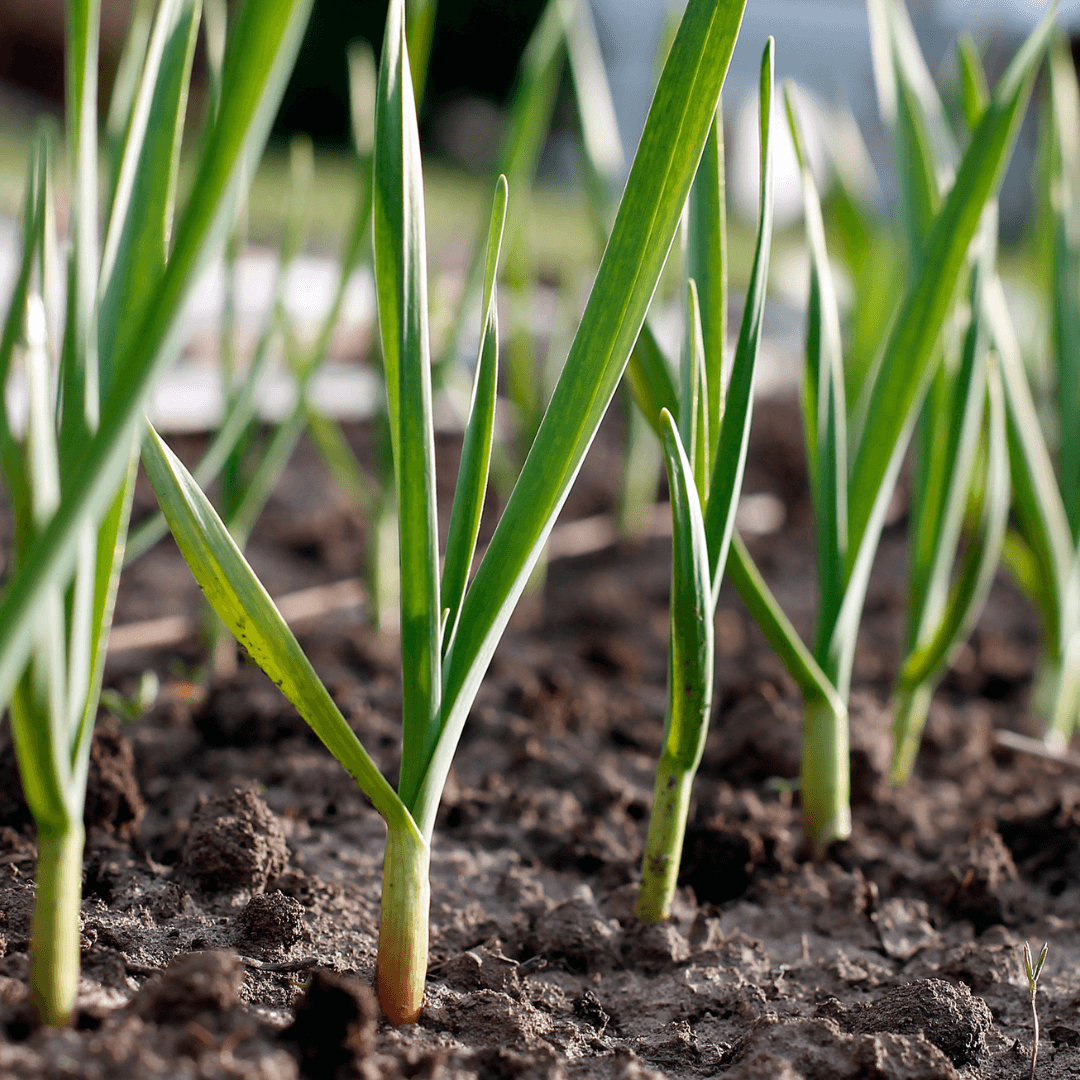

4. Garlic
Garlic is a great ally for garden vegetables such as tomatoes, lettuce, and cabbage.
Because of its potent scent, pests, including aphids, spider mites, and cabbage loopers, are naturally repelled from the area by it.
Garlic can be planted strategically around vegetables to provide a barrier against pests and lessen the need for chemical pesticides.
Garlic is a companion plant that helps vegetable gardens handle pests more sustainably and healthfully.
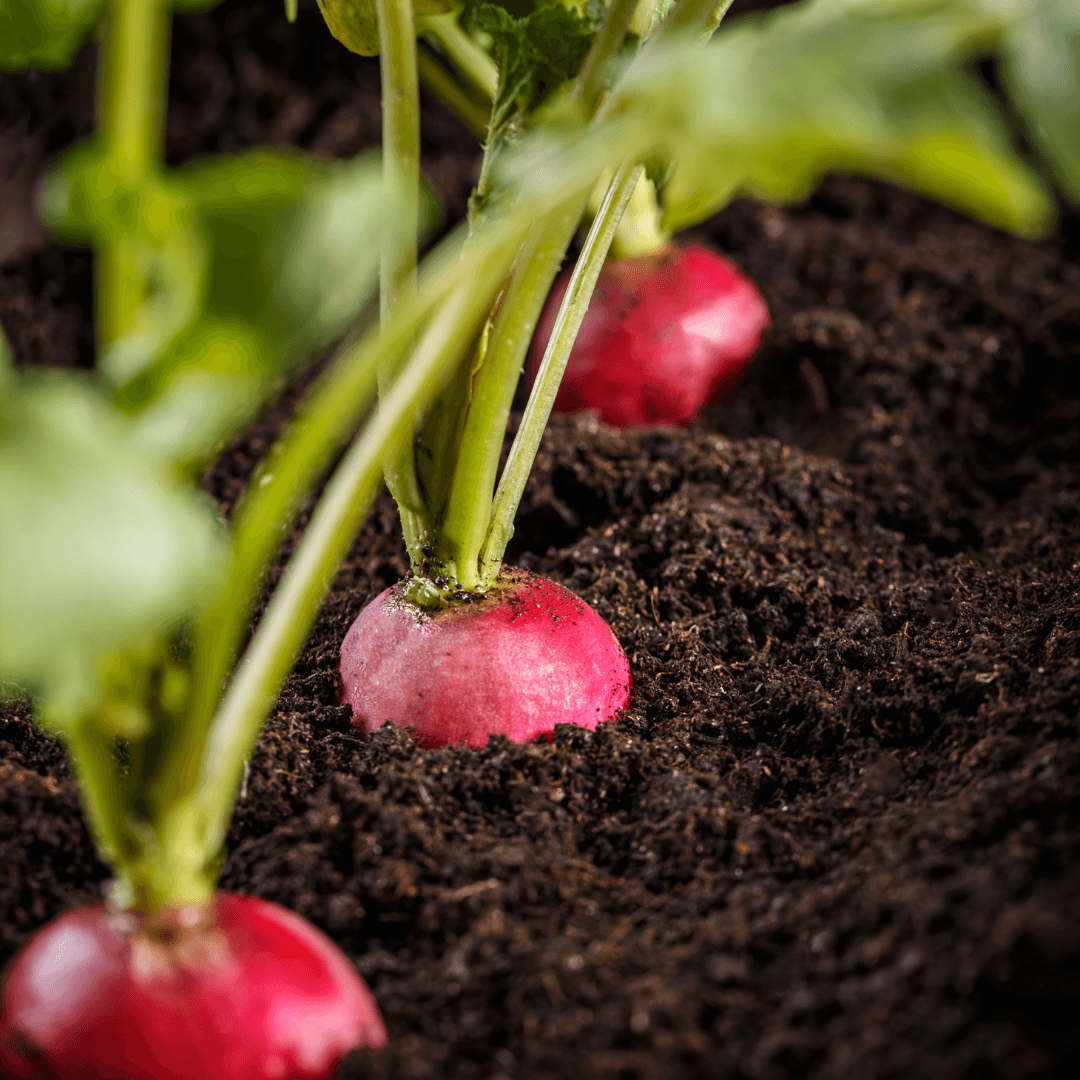

5. Radishes
Radishes are valuable companions for vine crops such as cucumbers and squash in the garden.
Radishes effectively repel pests like cucumber beetles and squash bugs, helping to protect neighbouring plants from damage.
Moreover, they can serve as a trap crop, diverting these pests away from more valuable plants and minimizing potential damage.
By integrating radishes into the garden, growers can implement an effective strategy for pest management while promoting the health and productivity of vine crops.
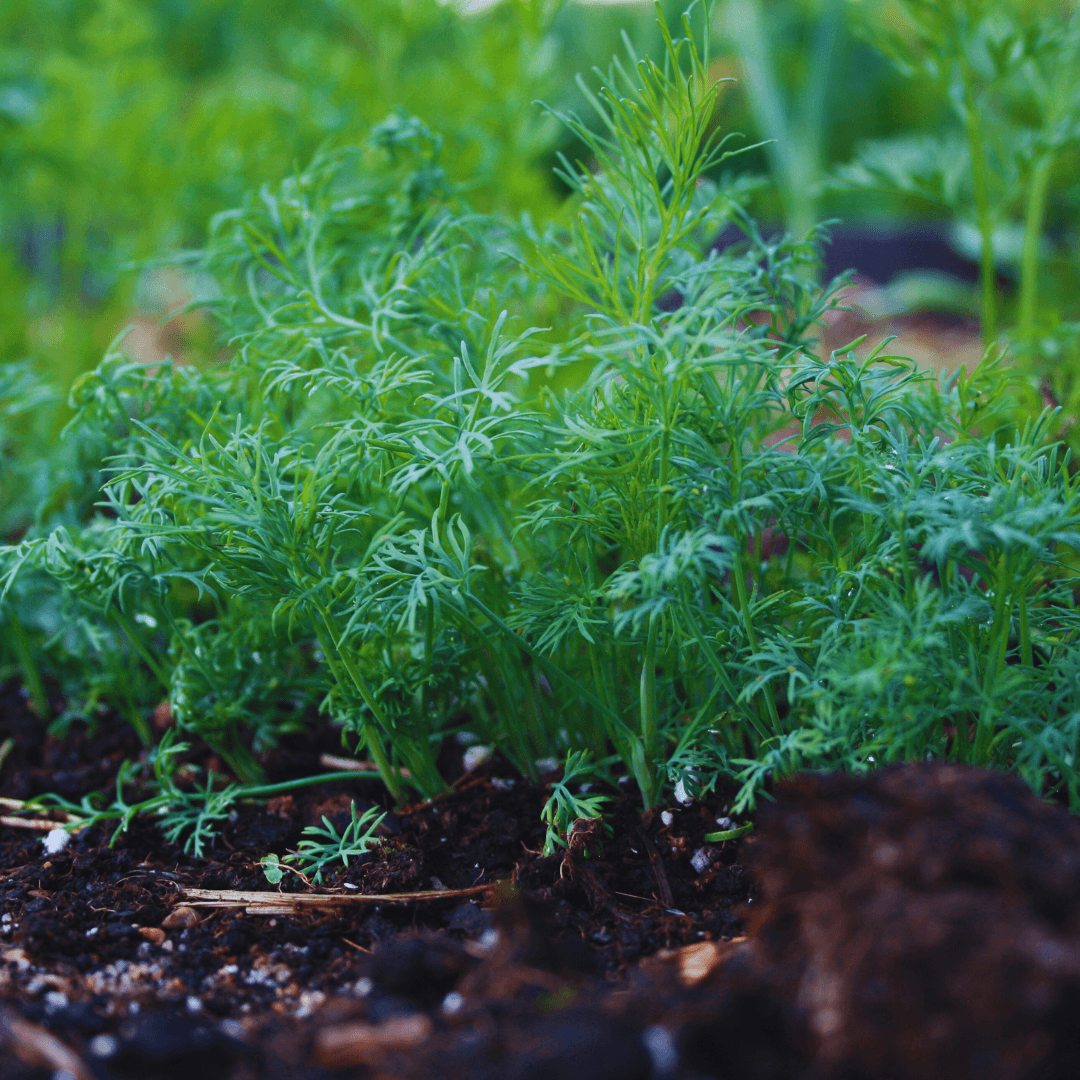

6. Dill
Dill is a beneficial companion for cabbage, broccoli, and other brassicas in the garden. Its presence attracts beneficial insects such as ladybugs and lacewings, which actively prey on aphids and other pests that commonly afflict brassicas.
By fostering populations of these helpful insects, dill aids in natural pest control, contributing to brassica crops' overall health and productivity. Integrating dill into the garden ecosystem is a proactive approach to pest management for these vegetables.

Herb Vegetable Companion Plants
Combining herbs with vegetables in companion planting not only enhances the flavours of your dishes but also provides various benefits such as pest control, improved pollination, and soil enrichment.
Here are some common herb and vegetable companion plants and their advantages:
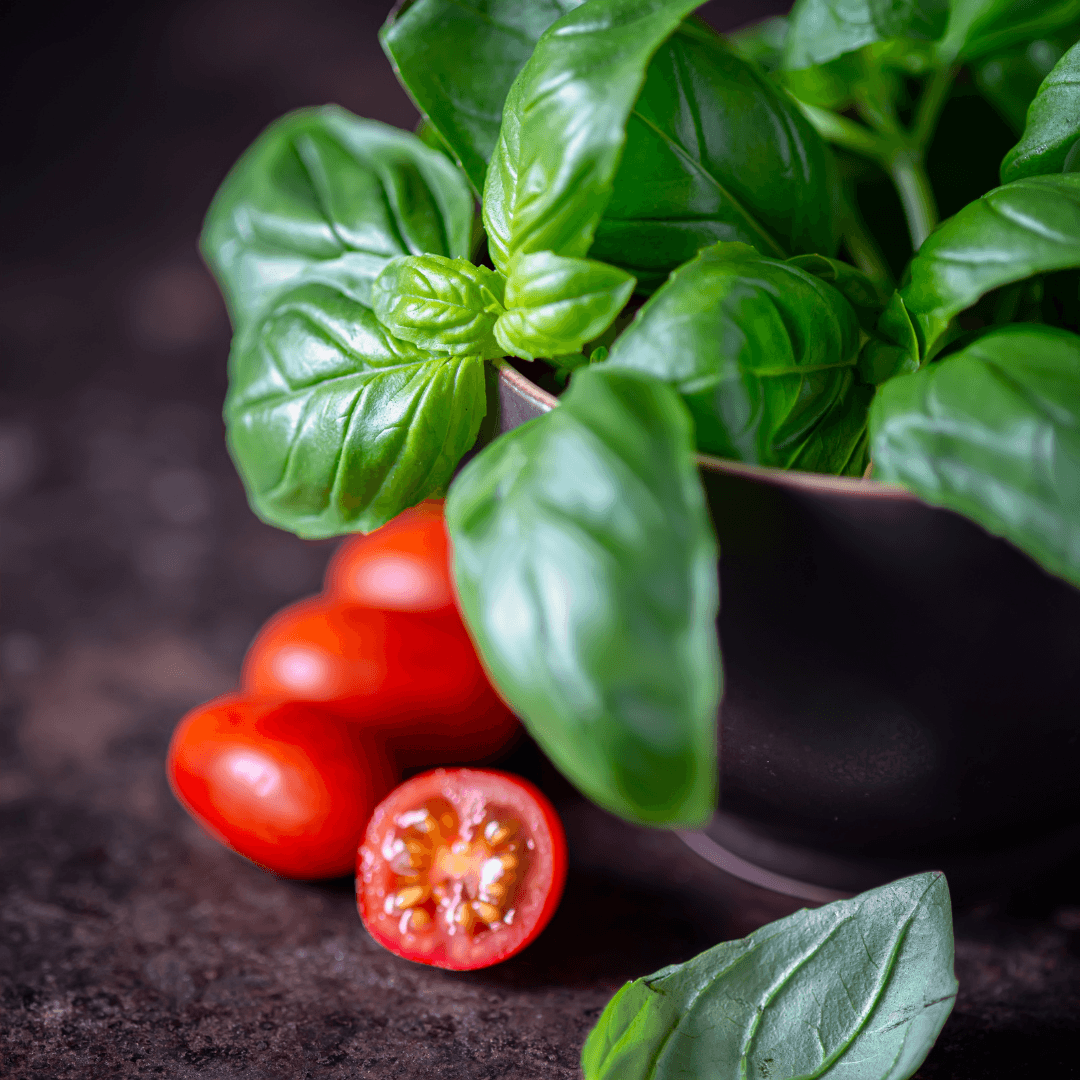

1. Basil And Tomatoes
Basil and tomatoes are classic garden pairings, serving as beneficial companions. Basil's aromatic foliage is a natural deterrent against pests such as aphids, mosquitoes, and flies, effectively protecting tomatoes from damage.
Moreover, planting basil near tomatoes is believed to enhance the flavour of the fruits, making it a doubly valuable companion.
By integrating basil into the garden alongside tomatoes, growers can promote healthier plants and a more abundant harvest.
2. Dill And Cabbage Family
Dill is beneficial when planted alongside cabbage family members such as cabbage, broccoli, and other brassicas.
Its presence attracts beneficial insects like ladybugs and lacewings, natural predators of aphids and cabbage worms, common pests that afflict brassicas.
By fostering populations of these helpful insects, dill aids in natural pest control and contributes to the overall health and productivity of cabbage family crops.
Integrating dill into the garden ecosystem is a proactive approach to pest management for these vegetables.
3. Chives And Carrots
Chives are excellent companions for carrots in the garden. Their presence is a natural deterrent against pests such as aphids and a deterrent against browsing by deer and rabbits, effectively safeguarding the carrots.
Additionally, the vibrant purple flowers of chives attract essential pollinators, enhancing the pollination and yield of the carrot crop.
Gardeners can promote healthier plants and a more abundant harvest by integrating chives alongside carrots while minimizing pest damage.
4. Thyme And Eggplants
Thyme is a versatile ally when planted alongside eggplants in the garden. Its aromatic foliage is a natural repellent against pests like flea beetles and cabbage loopers, which are common threats to eggplants.
By strategically planting thyme near eggplants, gardeners can create a protective barrier against these pests, promoting healthier plants and higher yields without chemical pesticides.
Incorporating thyme into the garden landscape offers a natural and effective solution for pest management in eggplant cultivation.
5. Sage And Beans
Sage is a valuable companion for beans and other garden legumes. Its aromatic foliage is a natural deterrent against pests like cabbage moths and bean beetles, effectively safeguarding beans from damage.
Additionally, sage enhances the flavour of beans when used together in cooking, providing a doubly beneficial relationship.
By integrating sage into the garden alongside beans, growers can promote healthier plants and more flavorful harvests while minimizing pest-related issues.
6. Rosemary And Broccoli
Rosemary is an ideal companion for broccoli in the garden. Its fragrant foliage not only complements the flavour of broccoli but also serves as a natural deterrent against pests like cabbage worms and aphids, which are common threats to broccoli plants.
By strategically planting rosemary near broccoli, gardeners can create a protective barrier against these pests, promoting healthier plants and higher yields without chemical pesticides.
Incorporating rosemary into the garden landscape offers a natural and effective solution for pest management in broccoli cultivation.
Companion Planting Guide
Companion planting involves strategically planting different crops to maximize growth, deter pests, and improve overall garden health.
This guide offers helpful advice and insights on using companion planting in your garden.
1. Understanding Plant Relationships
Understanding plant relationships is fundamental before embarking on companion planting endeavours.
It's vital to grasp how different plant species interact; while some flourish nearby, others may hinder growth or compete for resources.
By comprehending these dynamics, gardeners can make informed decisions when selecting plant pairings, ensuring harmonious coexistence and maximizing the benefits of companion planting in their gardens.
This knowledge enables gardeners to create synergistic plant communities where each species contributes to the overall health and productivity of the garden, fostering a thriving and balanced ecosystem.
2. Research Companion Planting Combinations
Suitable plant combinations that offer mutual benefits and compatibility must be researched to implement companion planting.
Utilize gardening resources, books, or online guides to identify plants that thrive together and complement each other's growth.
By conducting thorough research, gardeners can decide which plant pairings will maximize their garden's health and productivity.
This knowledge allows for the creation of harmonious plant communities where each species supports and enhances the growth of its companions.
With careful consideration and informed choices, gardeners can harness the power of companion planting to cultivate thriving and resilient gardens.
3. Consider Planting Zones And Seasons
When planning companion planting, it's vital to consider your planting zone and the seasonal needs of your plants.
Choose companion plants with similar needs for sunlight, water, and soil that are also acclimated to your local environment.
By aligning these factors, you can ensure that your plant combinations thrive together, optimizing growth and productivity in your garden.
Whether you're planting in a temperate zone or a tropical climate, thoughtful consideration of planting zones and seasonal requirements will help you create successful companion planting arrangements that support healthy and flourishing plant growth throughout the year.
4. Plan Your Garden Layout
When designing your garden layout, it's essential to incorporate companion planting principles to maximize plant health and productivity.
Start by sketching a garden plan considering plant spacing, sunlight exposure, and height. Arrange companion plants strategically in your garden beds, ensuring that taller plants provide shade for shorter ones and that each plant has enough space to grow and thrive.
By carefully planning your garden layout with companion planting in mind, you can create a harmonious and balanced ecosystem that supports healthy plant growth and enhances the overall beauty of your garden.
5. Utilize Vertical Space
Optimizing vertical space in your garden is key to maximizing its potential. Pair tall-growing plants with shorter ones to make the most of limited space.
For instance, train beans or cucumbers to climb trellises while planting low-growing crops like lettuce or radishes beneath them.
This strategic arrangement not only maximizes space but also promotes efficient resource utilization.
By effectively utilizing vertical space, gardeners can increase their yield without expanding their garden footprint, making companion planting an ideal solution for those with limited gardening space.
6. Rotate Crops
Crop rotation is an essential gardening technique for preserving the health of the soil and reducing pest and disease problems. Shifting crops to other garden sections can minimize soil erosion and the yearly accumulation of pests and illnesses.
It is advisable not to repeatedly grow crops belonging to the same family in the same area to minimize nutritional deficits and enhance vulnerability to pests and diseases.
Instead, follow a rotation plan alternating between different plant families to maintain soil fertility and balance. Crop rotation in your garden can promote healthier plants and improve overall productivity.
7. Interplant With Herbs And Flowers
Integrating herbs and flowers into your garden beds is a beneficial strategy to attract beneficial insects and deter pests.
Planting aromatic herbs such as basil, thyme, and mint alongside vegetables can create a natural pest management system and enhance overall garden health.
These fragrant plants emit scents that repel pests, reducing the need for chemical pesticides. Additionally, flowering plants like marigolds and calendula attract pollinators and beneficial insects, further contributing to a balanced ecosystem.
By interplanting herbs and flowers with vegetables, you promote biodiversity and create a visually appealing and thriving garden that supports the well-being of both plants and beneficial insects.
8. Experiment And Observe
Embrace experimentation in your garden by exploring various companion plant combinations. Allow yourself to try new pairings and observe the interactions between different plants.
Keep track of how each combination influences the growth and health of neighbouring plants over time.
By documenting your observations, you can gain valuable insights into which companion plant combinations are most effective in your garden.
Finding what works best for your particular growing situation requires experimentation. Be open to learning from successes and failures, as each experience contributes to your understanding of companion planting and helps create a thriving and harmonious garden ecosystem.
9. Companion Planting With Native Species
Integrating native plants into your companion planting strategy is a thoughtful way to enhance biodiversity and promote a healthy ecosystem in your garden.
Native plants are well-adapted to your local climate and soil conditions, making them resilient and low-maintenance additions to your garden.
By including native species, you provide essential habitat and food sources for local wildlife, pollinators, and beneficial insects.
This supports the overall health of your garden and contributes to the conservation of native plant species.
Additionally, native plants often have deep roots that improve soil structure and prevent erosion, further enhancing the sustainability of your garden.
By prioritizing native species in your companion planting scheme, you can create a thriving and ecologically diverse garden that benefits you and the environment.
10. Companion Planting In Containers
Extend the benefits of companion planting to container gardening by pairing compatible plants in containers.
Whether gardening on a balcony, patio, or windowsill, utilize companion planting principles to maximize space and promote healthy growth.
Choose plants with similar growing requirements and complement each other's growth habits. For example, pair trailing herbs like thyme or oregano with compact vegetables like lettuce or cherry tomatoes.
This strategic arrangement maximizes space, encourages efficient resource utilization, and creates a visually appealing container garden.
With companion planting in containers, even small gardening spaces can yield bountiful harvests and vibrant displays of plant diversity.
11. Monitor And Adapt
To maintain your garden's health and productivity, regularly monitor it for signs of pests, diseases, or nutrient deficiencies.
Keep a close eye on your plants and soil, checking for any abnormalities or changes in growth. Be prepared to adapt your companion planting strategies accordingly to address any issues.
This may involve adjusting plant pairings, introducing new companion plants, or implementing additional pest control measures.
You can identify and resolve problems early by staying vigilant and proactive, ensuring optimal garden productivity and plant health.
Regular monitoring and adaptation are key to successful companion planting and a thriving garden ecosystem.
12. Share Knowledge And Learn
Share your experiences and knowledge of companion planting with other gardeners in your community to foster a sense of community and collective learning.
Collaborate with fellow enthusiasts to exchange valuable insights, tips, and success stories. You can learn from each other's experiences through open dialogue and collaboration and discover new companion planting techniques and strategies.
Embrace the opportunity to continue learning and improving your companion planting practices, nurturing a culture of knowledge sharing and growth within your gardening community.
Through shared experiences and collective learning, you can all enhance your gardening skills and cultivate thriving and productive garden ecosystems.
Benefits Of Companion Planting
Companion planting offers many benefits for both plants and gardeners alike. Here are 15 key advantages:
1. Natural Pest Control
Companion plants emit scents or compounds that repel pests, reducing reliance on chemical pesticides.
This natural pest control method fosters a balanced garden ecosystem, promoting plant health while minimizing environmental harm.
By strategically incorporating companion plants, gardeners can effectively manage pests, ensuring healthier plants and a more sustainable gardening approach.
2. Enhanced Pollination
Companion plants are magnets for beneficial pollinators like bees and butterflies, drawing them into the garden to pollinate flowering crops.
As these pollinators move from flower to flower, they transfer pollen, facilitating fertilization and fruit formation.
Enhanced pollination rates result in larger and more abundant harvests and promote genetic diversity within plant populations.
3. Improved Soil Health
Certain companion plants possess nitrogen-fixing abilities, enriching the soil with vital nutrients and fostering robust plant growth.
By forming symbiotic relationships with nitrogen-fixing bacteria in their roots, these plants convert atmospheric nitrogen into a form that plants can utilize.
This process enhances soil fertility, promotes healthier root systems, increases nutrient uptake, and improves overall plant vigour.
4. Maximized Space Usage
Companion planting optimizes space utilization in the garden by strategically pairing plants with complementary growth habits.
This approach maximizes growing areas and enhances productivity, particularly in smaller garden spaces.
Additionally, gardeners can utilize vertical space efficiently by planting climbing or trailing companions alongside upright crops.
By carefully selecting plant combinations, gardeners can create harmonious arrangements that make the most available space.
5. Disease Prevention
Some companion plants exhibit inherent disease-resistant qualities as a natural defence mechanism against fungal and bacterial infections.
Gardeners can lower the danger of spreading disease by creating a protective barrier by interplanting these species with crops prone to disease.
To promote healthier plants and reduce the need for chemical interventions, these plants may release chemicals that limit the growth of diseases or produce antimicrobial compounds.
6. Increased Biodiversity
Companion planting promotes biodiversity by introducing various plant species into the garden.
This diversity creates a more resilient ecosystem, as different plants attract a wide array of beneficial insects and wildlife, contributing to overall ecosystem health.
Additionally, diverse plantings help to balance soil nutrients and reduce pest pressure, resulting in healthier plants and increased productivity.
7. Aesthetic Enhancement
Companion plants enhance the visual appeal of the garden landscape by introducing a diverse array of colours, textures, and fragrances.
These dynamic displays create visually striking scenes that captivate the senses and elevate the overall aesthetics of the garden.
Whether it's the vibrant blooms of flowering companions, the lush foliage of plants, or the delicate scents wafting through the air, companion planting adds beauty and interest to the garden environment.
8. Improved Flavour
Adding herbs and flowers alongside vegetables can enhance their flavour and aroma, enriching the culinary experience for gardeners and consumers.
For example, aromatic herbs like basil, thyme, and rosemary impart their distinct flavours to neighbouring vegetables, elevating their taste profiles.
Similarly, edible flowers such as nasturtiums and calendula add a delicate floral essence to dishes, enhancing visual appeal and taste.
By incorporating these flavorful companions into the garden, gardeners can enjoy a bountiful harvest of vegetables with enhanced flavours.
9. Balanced Ecosystem
Companion planting fosters a balanced ecosystem within the garden by attracting diverse beneficial insects and wildlife.
These include pollinators such as bees and butterflies and natural predators of garden pests like ladybugs and lacewings.
By creating a habitat that supports these beneficial organisms, companion planting reduces the need for chemical pesticides and promotes natural pest control.
10. Sustainable Gardening
Companion planting champions sustainable gardening practices by minimizing the dependence on synthetic fertilizers and pesticides.
Companion planting creates a self-sustaining ecosystem within the garden by harnessing natural processes such as pest repellency, nutrient cycling, and pollination enhancement.
This reduces the need for harmful chemical inputs, preserving soil health, safeguarding biodiversity, and minimizing environmental impact.
By embracing companion planting, gardeners can cultivate thriving gardens while championing eco-friendly practices that promote long-term sustainability and stewardship of the land.
11. Season Extension
Certain companion plants aid in extending the growing season by offering shade or shelter from adverse weather conditions.
For example, taller plants can shade delicate crops during hot summer, preventing wilting and sunburn.
Additionally, companion plants with dense foliage can offer protection from strong winds or heavy rainfall, shielding vulnerable plants from damage.
By strategically incorporating these companions into the garden, gardeners can prolong the growing season, allowing for continued harvests and plant growth even as weather conditions fluctuate.
12. Weed Suppression
Companion plants contribute to weed suppression by creating a dense canopy that shades the soil and competes with weeds for resources such as sunlight, water, and nutrients.
This natural weed control method reduces the need for manual weeding, saving gardeners time and effort.
Additionally, some companion plants release allelopathic compounds that inhibit weed seed germination or growth, further suppressing weed proliferation.
13. Improved Crop Yields
Companion planting optimizes plant growth and health, increasing crop yields for vegetables, fruits, and herbs.
By strategically selecting companion plants that complement each other's growth habits and nutrient needs, gardeners create an environment where plants thrive and produce abundantly.
Companion plants also enhance pollination rates and nutrient availability in the soil, further boosting yields.
14. Habitat Creation
Companion plants are vital in creating habitats for beneficial insects, birds, and other wildlife within the garden.
These plants offer shelter, food, and nesting sites, supporting a diverse array of beneficial organisms.
Beneficial insects, such as pollinators and natural predators of garden pests, are attracted to the diverse floral resources provided by companion plants, which contribute to natural pest control and pollination.
15. Educational Opportunities
Companion planting provides valuable educational opportunities for gardeners, offering a hands-on learning experience that deepens their understanding of plant interactions and ecosystem dynamics.
By observing how plant species interact and affect each other's growth, gardeners gain insights into companion planting principles and strategies.
Experimenting with various plant combinations allows gardeners to refine their gardening skills and discover which companion plant pairings work best in their specific growing conditions.
Conclusion
Companion planting offers a holistic approach to gardening that benefits both plants and gardeners alike.
By strategically selecting plant combinations based on their complementary traits and interactions, gardeners can enhance soil health, promote natural pest control, and increase biodiversity within the garden ecosystem.
Additionally, companion planting fosters sustainability by reducing the reliance on synthetic inputs and promoting eco-friendly gardening practices.
Moreover, it provides valuable educational opportunities for gardeners to deepen their understanding of plant relationships and ecosystem dynamics.
Adopting companion planting techniques can result in healthier plants, increased yields, and a more dynamic and long-lasting garden environment for future generations.
I trust you enjoyed this article in Your Essential Companion Planting Guide. Please stay tuned for more blog posts soon. Take care!
JeannetteZ
>>>Please click here to read my all-inclusive article about Container Gardening<<<
>>>Are you interested in homegrown herbs and medicine? Please click here to find out more about it!<<<
Your Opinion Is Important To Me
Do you have thoughts, ideas, or questions? I would love to hear from you. Please leave me your questions, experiences, and remarks about this article, Your Essential Companion Planting Guide, in the comments section below. You can also reach me by email at Jeannette@Close-To-Nature.org.
Disclosure
This post may contain affiliate links. As an Amazon Associate and other affiliate programs, I earn from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you. Please read my full affiliate disclosure.
You might also enjoy these blog posts:
Natural Fertilizer For Indoor Herbs
Benefits Of Vitamin B12 For Women
Understanding The Symptoms Of Stress