Interesting Facts About Hummingbirds
Interesting Facts About Hummingbirds
Hummingbirds are captivating creatures that captivate the imagination with their diminutive size, astonishing agility, and vibrant plumage.
These tiny avian marvels belong to the family Trochilidae and are renowned for their unique abilities and behaviours.
Despite their petite stature, hummingbirds possess many fascinating traits that set them apart from other birds.
From their extraordinary flight capabilities to their remarkable feeding habits, the world of hummingbirds is filled with intriguing facts that never fail to astound and delight.
In this exploration, we delve into the enchanting realm of hummingbirds, uncovering the most interesting facts about hummingbirds.

1. Smallest Birds
Hummingbirds, particularly exemplified by the bee hummingbird of Cuba, claim to be the smallest birds globally.
These avian marvels measure a mere 2.0 to 2.4 inches (5 to 6 centimetres) in length, enchanting observers with their exquisite diminutiveness.
Despite their petite stature, they exude a remarkable presence, captivating with their delicate form and intricate beauty.
The bee hummingbird's miniature size is a testament to nature's capacity for intricate and efficient design, allowing these tiny creatures to thrive in diverse ecosystems and capture the imagination of all who encounter them.
2. Incredible Flight Skills
Hummingbirds are renowned for their unparalleled flight skills, and another interesting fact about them is that they defy the conventional limitations of avian mobility.
With astonishing precision, they effortlessly hover in mid-air, execute seamless backward flights, and even navigate upside down, showcasing their extraordinary aerial agility.
Their unique wing structure and rapid wing beats make these remarkable feats possible, which generate the necessary lift and thrust for such acrobatic maneuvers.
Their ability to control their flight with such finesse is a testament to the evolutionary adaptations that have honed their aerodynamic prowess over millennia. Witnessing a hummingbird in flight is to witness nature's mastery of dynamic movement.
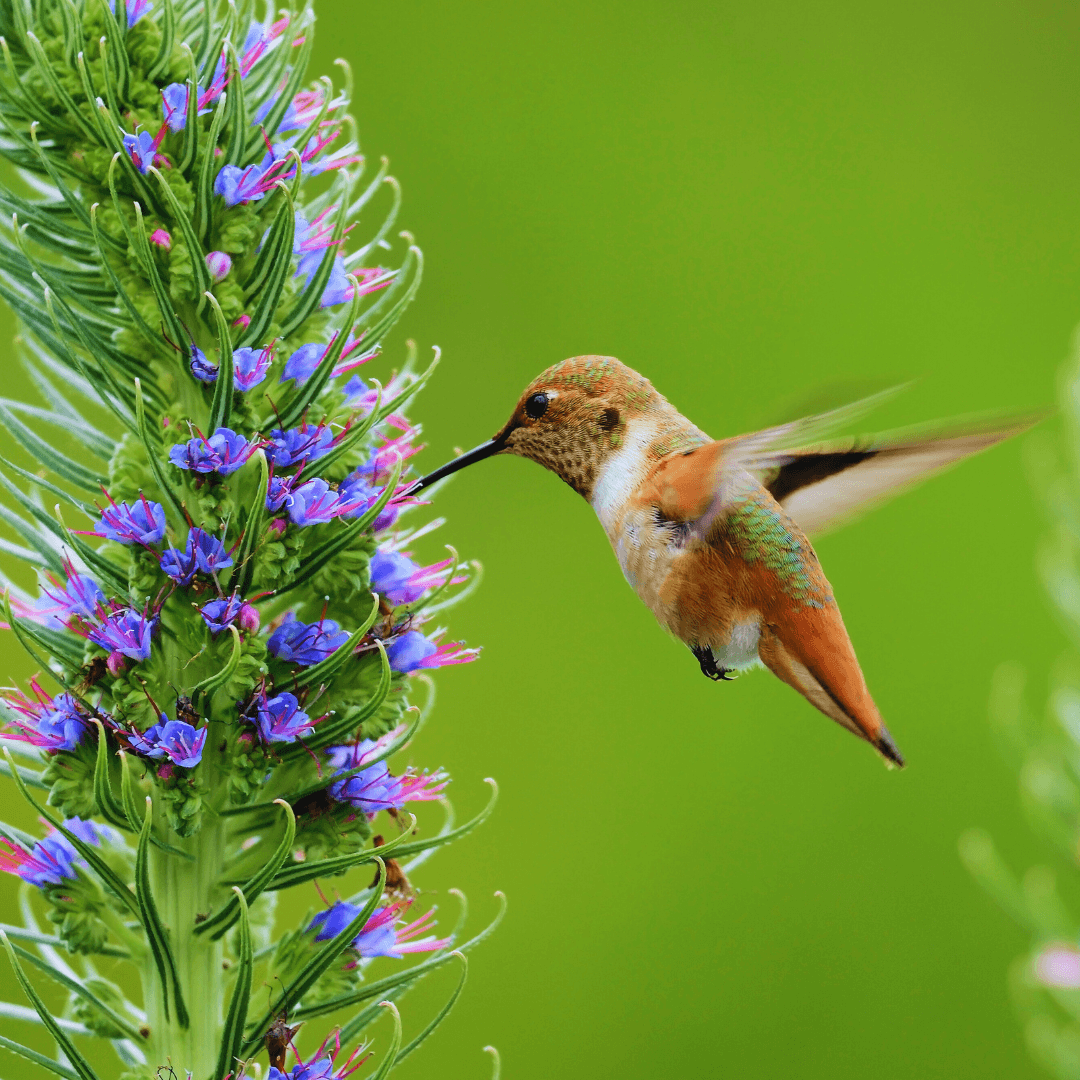
3. Rapid Wing Beats
Hummingbirds, with their wings beating at an astonishing rate of 50 to 80 times per second during standard flight, epitomize unparalleled aerial prowess.
This rapid wing movement enables them to achieve remarkable agility and speed, maneuvering their environment precisely and gracefully.
Such extraordinary aerial capabilities are essential for survival, allowing them to navigate dense vegetation, outmaneuver predators, and efficiently forage for nectar among flowers.
The frenetic pace of their wing beats is a testament to the incredible biomechanical adaptations that enable hummingbirds to thrive in diverse ecosystems.
Witnessing the blur of their wings in motion is a testament to their mastery of flight, captivating observers with their mesmerizing aerial displays.
4. High Metabolism
Hummingbirds maintain exceptionally high metabolic rates to sustain their energetic flight and rapid wing beats, a requirement born from their remarkable aerial abilities.
This elevated metabolism demands frequent nectar consumption to provide the necessary fuel for their ongoing activities.
Due to their small size and intense energy expenditure, hummingbirds must continually replenish their energy reserves, often visiting hundreds of flowers daily to meet their nutritional needs.
Their reliance on nectar as a primary source of sustenance underscores the intricate relationship between hummingbirds and flowering plants, highlighting their crucial role in pollination and ecosystem dynamics.
5. Unique Feeding Behaviour
Hummingbirds possess a unique and specialized feeding behaviour centred around extracting nectar from flowers.
Their long, slender bills and extendable, tube-like tongues allow them to access the deep floral structures where nectar is stored.
This intricate adaptation enables hummingbirds to extract the sugary liquid, their primary energy source, efficiently.
In addition to nectar, hummingbirds supplement their diet with insects and spiders, providing essential protein to support their metabolic needs, particularly during periods of high energy expenditure such as breeding and migration.
This diverse feeding strategy underscores hummingbirds' adaptability and ability to exploit various food sources to meet their nutritional requirements.
6. Colourful Plumage
Male hummingbirds are adorned with vibrant and iridescent plumage, captivating observers with dazzling colours.
These interesting facts about hummingbirds’ hues result from microscopic platelets within their feathers that refract light, creating mesmerizing displays that shimmer and change with movement.
The iridescence of their plumage serves a dual purpose: attracting potential mates and establishing territory.
During courtship displays, males flaunt their colourful feathers in elaborate aerial performances to impress females.
Additionally, the brilliance of their plumage serves as a visual signal to rival males, asserting dominance and delineating territorial boundaries.
The striking colours of male hummingbirds showcase their aesthetic beauty and highlight their evolutionary adaptations for communication and reproductive success in the competitive world of avian courtship.

7. Aggressive Behaviour
Despite their diminutive stature, hummingbirds exhibit surprisingly fierce territorial and aggressive behaviour, particularly during breeding.
These tiny birds fiercely defend their feeding territories, engaging in aerial skirmishes with intruders to maintain exclusive access to valuable nectar resources.
Male hummingbirds, in particular, aggressively defend their territories against rival males to secure mating opportunities with females.
Their territorial behaviour often involves dramatic aerial displays, with males darting and diving to assert dominance and intimidate competitors.
These aggressive interactions underscore the competitive nature of hummingbird society and highlight the importance of resource defence in ensuring reproductive success.
Despite their delicate appearance, hummingbirds are formidable competitors, adept at navigating the complexities of social hierarchy.
8. Extraordinary Memory
Hummingbirds exhibit exceptional spatial memory, enabling them to recall the precise locations of individual flowers for prolonged durations.
This extraordinary memory enables hummingbirds to efficiently forage for nectar by revisiting specific flower patches where they have previously found abundant resources.
By recalling the precise locations of high-quality flowers, hummingbirds can minimize energy expenditure and maximize nectar intake, which is essential for sustaining their high metabolic demands.
This exceptional memory also enhances their foraging efficiency during food scarcity or environmental changes, ensuring survival in challenging conditions.
Hummingbirds' ability to navigate their surroundings with such precision underscores their remarkable cognitive skills.
9. Long Migration
Certain hummingbird species undertake remarkable migratory journeys, traversing hundreds or thousands of miles to reach their breeding or wintering grounds.
These migratory feats showcase the endurance and adaptability of hummingbirds to diverse environments and climatic conditions.
For example, the ruby-throated hummingbird annually undertakes a daunting migration from its breeding grounds in North America to wintering grounds in Central America, spanning thousands of miles across continents.
Despite their small size, hummingbirds demonstrate remarkable navigational skills and physiological adaptations that enable them to complete these long-distance journeys.
Their ability to successfully navigate vast distances highlights their resilience and resourcefulness, underscoring their remarkable capacity to thrive in dynamic and ever-changing landscapes.
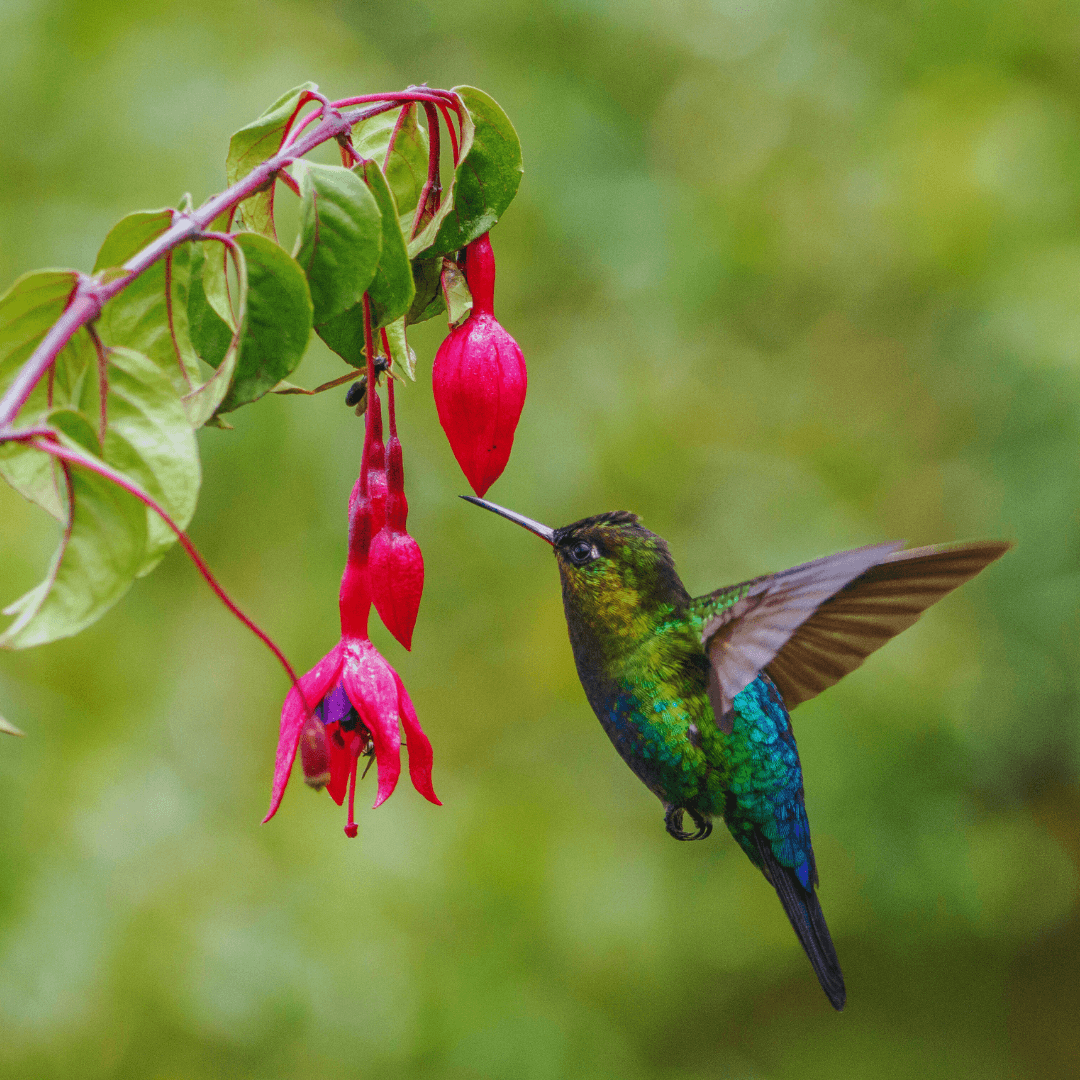
10. Torpor
Hummingbirds employ a remarkable survival strategy known as torpor—an interesting fact about the hummingbird. This is a temporary state of reduced metabolic activity.
During food scarcity or cold weather, hummingbirds lower their metabolic rate and enter a state akin to deep sleep.
Because of their physiological adaption, they can withstand low temperatures and lack nectar supplies, allowing them to preserve energy and survive hard environments.
By entering torpor, hummingbirds can significantly reduce their energy expenditure, minimizing the risk of starvation and conserving vital resources for essential bodily functions.
This remarkable ability to adjust their metabolism in response to environmental challenges highlights hummingbirds' resilience and adaptability, enabling them to endure unpredictable conditions and thrive in diverse habitats throughout their range.
11. Heart Rate
Hummingbirds possess astonishingly fast heart rates, ranging from 250 to 1,200 beats per minute, fluctuating based on their activity level.
Even during rest periods, their heart rates remain notably elevated, showcasing the extraordinary cardiovascular capacity necessary to sustain their rapid flight and high metabolic demands.
This heightened heart rate enables hummingbirds to efficiently oxygenate their muscles and vital organs, facilitating their unparalleled aerial agility and endurance.
Such rapid cardiac activity reflects the remarkable physiological adaptations that have evolved to support hummingbirds' unique lifestyle, emphasizing the intricate interplay between cardiovascular function, metabolic activity, and locomotor performance in these extraordinary avian athletes.
12. No Sense Of Smell
Hummingbirds possess limited olfactory capabilities compared to many other bird species, relying primarily on their acute eyesight to navigate their surroundings and locate food sources.
While some birds use their sense of smell to identify prey, find mates, or detect predators, hummingbirds have evolved to prioritize visual cues in their foraging and defensive behaviours.
Their keen eyesight enables them to distinguish between different flower species, assess the quality of nectar sources, and detect potential threats such as predators or rival hummingbirds.
This reliance on visual stimuli highlights the specialized sensory adaptations of hummingbirds. It underscores the importance of visual perception in their ecological interactions and survival strategies within their dynamic and competitive habitats.
13. Unique Courtship Displays
During the breeding season, male hummingbirds engage in elaborate aerial displays to court potential mates.
These displays are a spectacle of agility and finesse, involving intricate flight patterns, acrobatic maneuvers, and vocalizations.
Male hummingbirds showcase their physical prowess and genetic fitness through these displays, demonstrating their ability to navigate complex aerial movements with precision and grace.
The displays serve as a visual and auditory spectacle, captivating female hummingbirds and signalling the males' suitability as mates.
The competitive nature of these courtship displays underscores the importance of reproductive success in the evolutionary fitness of hummingbird species, driving males to demonstrate their superiority and attractiveness through dazzling aerial performances.
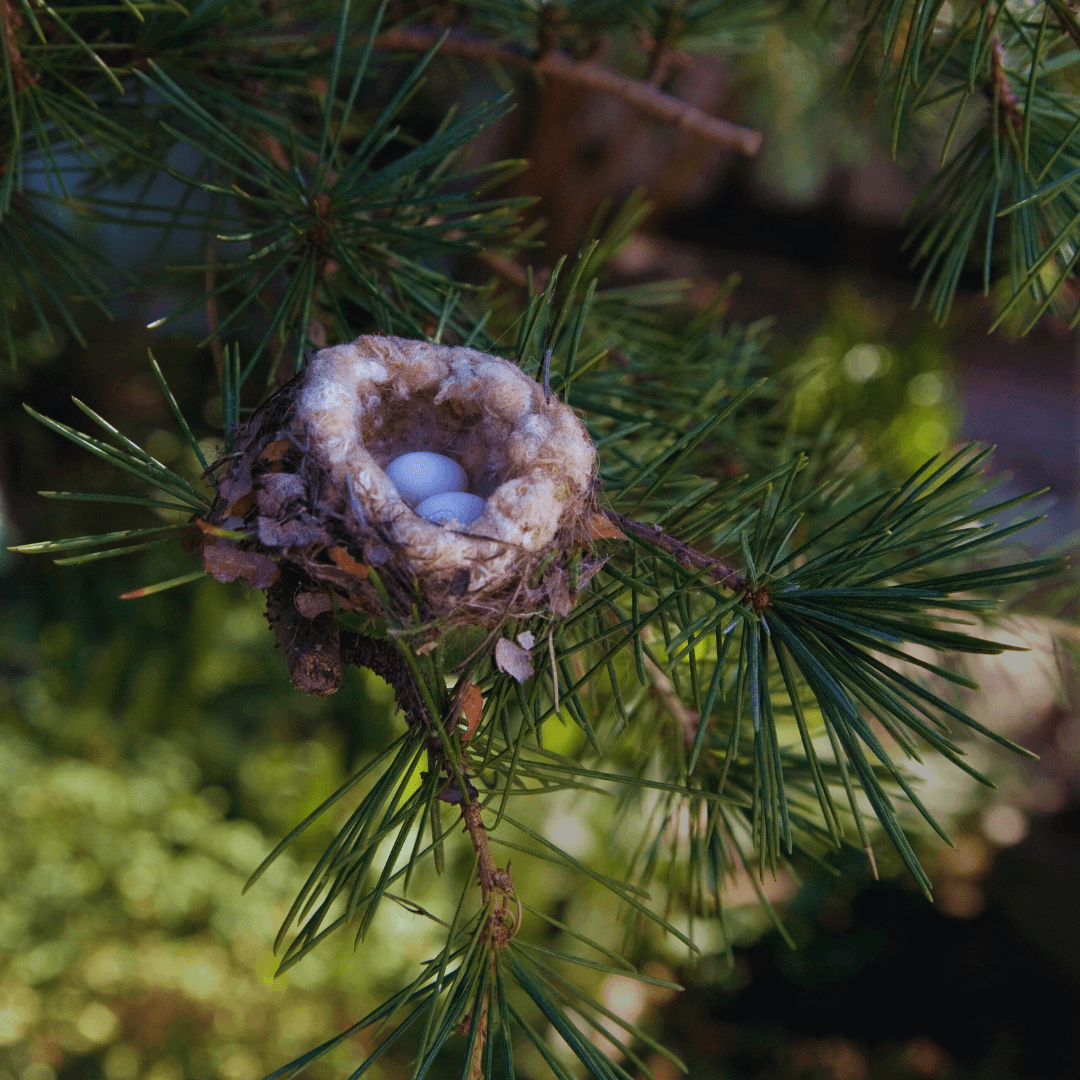

14. Surprising Size Of Eggs
Despite the small size of the adult bird, Hummingbird eggs exhibit a notable discrepancy in size, typically measuring around 0.5 inches (1.3 centimetres) in length.
These interesting facts about hummingbird's seemingly disproportionate size are crucial for accommodating the developing chick and providing ample space for growth during incubation.
Additionally, the larger size of hummingbird eggs allows for greater storage of nutrients, ensuring that the developing embryo receives adequate nourishment for optimal development.
The size of hummingbird eggs reflects the intricate balance between reproductive investment and resource allocation, highlighting the evolutionary adaptations that enable these tiny birds to reproduce and raise offspring in diverse environments.
15. Survival And Adaptability
The lifespan of wild hummingbirds varies depending on numerous factors, including predation, habitat quality, and environmental conditions.
Despite these challenges, some individuals have been observed to live for more than a decade in captivity, showcasing the remarkable resilience and adaptability of these tiny birds. In captivity, hummingbirds are provided with consistent food sources, protection from predators, and veterinary care, allowing them to thrive and reach advanced ages not typically attained in the wild.
This longevity underscores hummingbirds' ability to adapt to diverse environments. It also highlights the importance of conservation efforts to preserve their habitats and ensure their continued survival in the face of ongoing threats.
16. Diverse Habitats
Hummingbirds showcase remarkable adaptability by inhabiting diverse ecosystems, ranging from lush tropical rainforests to rugged high-altitude mountain ranges.
This versatility allows them to thrive in various environmental conditions and exploit multiple food sources.
In tropical rainforests, they flit among the vibrant blooms of exotic flowers, while in mountainous regions, they brave harsh climates to forage for nectar from hardy alpine plants.
Their ability to thrive in such disparate habitats underscores their resilience and evolutionary flexibility, enabling them to occupy niches across various landscapes.
This adaptability is a testament to the resourcefulness and ingenuity of hummingbirds in navigating the complexities of diverse ecosystems.
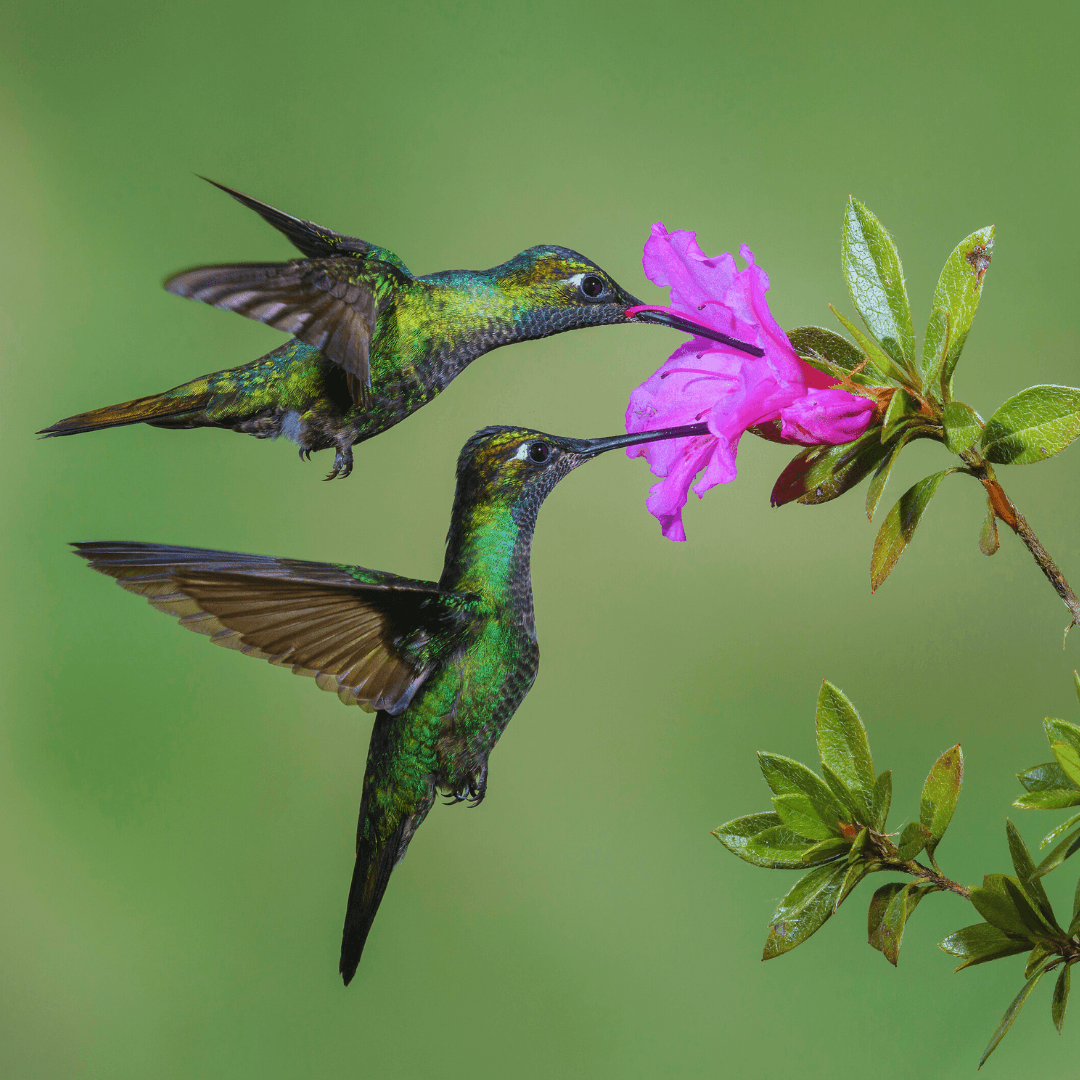
17. Essential Pollinators In Ecosystems
Hummingbirds are essential pollinators, playing a vital role in the reproductive success of flowering plants; another interesting fact about the hummingbird.
As they feed on nectar, their long bills and tongues enable them to reach deep into floral structures, inadvertently picking up and transferring pollen from one flower to another.
This pollen transfer facilitates fertilization, allowing the plants to produce seeds and propagate. By engaging in pollination, hummingbirds contribute to the maintenance of plant diversity and ecosystem stability.
Their foraging behaviours create symbiotic relationships with flowering plants, ensuring mutual survival and perpetuation.
As guardians of biodiversity, hummingbirds exemplify the interconnectedness of species within ecosystems and the delicate balance that sustains life on Earth.
18. Nest Construction
Female hummingbirds exhibit meticulous nest-building behaviour, crafting intricately designed cup-shaped nests using various natural materials.
These nests typically incorporate soft plant fibres, moss, and delicate strands of spider silk intricately woven together to create a sturdy and insulated structure.
Hummingbird nests are often concealed among foliage or camouflaged with lichen or bark, providing concealment from potential predators.
These nests, securely anchored to branches or twigs using spider silk and other adhesive substances, offer a haven for incubating eggs and raising offspring.
The female hummingbird's skill and attention to detail guarantee the nest's defensive properties and structural integrity, creating a nurturing atmosphere that helps the next generation of hummingbirds flourish.
19. Incubation Period
The time required for hummingbird eggs to hatch generally ranges between 14 to 23 days, with slight variations influenced by species and environmental conditions.
The female hummingbird delicately tends to the nest during this critical time, carefully controlling the humidity and temperature to provide the ideal conditions for embryo growth.
She carefully incubates the eggs with unwavering dedication, ensuring their protection and nurturing their growth until they hatch.
This period of attentive care reflects the profound maternal instincts of the female hummingbird and underscores her role as a devoted guardian of new life. Through her vigilant efforts, she maximizes the chances of successful hatching.
20. Agile Predators
Despite their diminutive size, hummingbirds are agile predators. They are proficient in catching flying insects mid-air using their specialized beaks and nimble flight maneuvers.
Their rapid aerial movements and precise targeting enable them to snatch insects with remarkable accuracy, showcasing their exceptional hunting skills.
Hummingbirds are excellent insectivores and natural pest controllers in their environments, contributing significantly to managing insect populations.
By consuming large quantities of insects, they help regulate insect numbers, contributing to the balance of their ecosystems and supporting overall biodiversity.
Thus, despite their small stature, hummingbirds wield significant ecological influence, demonstrating the interconnectedness of species and the importance of their roles in maintaining ecosystem health and stability.
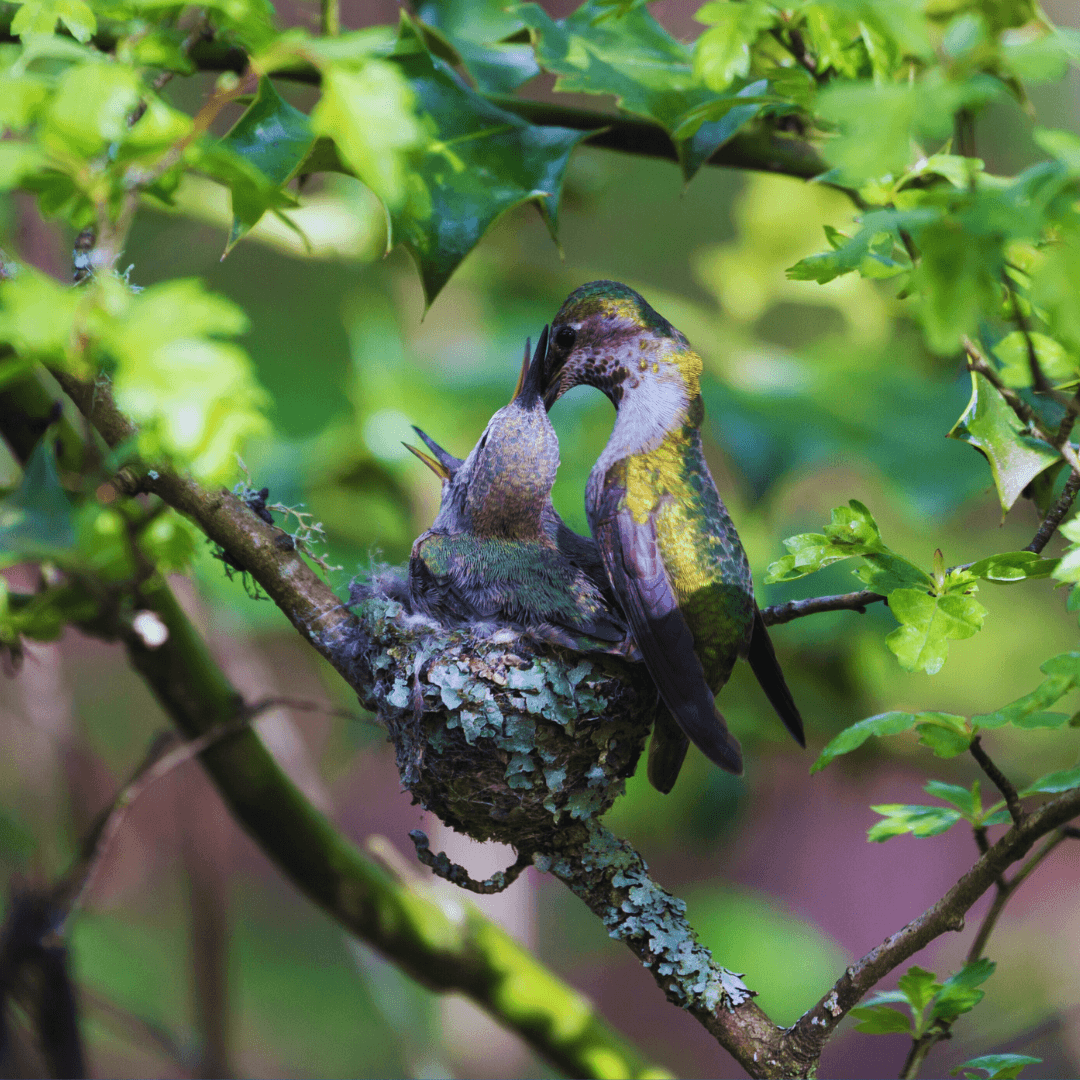
21. Chick Development
Hummingbird chicks enter the world as altricial beings, born naked and blind and reliant on parental care for survival.
Their vulnerable state necessitates round-the-clock attention from their devoted parents, who diligently provide nourishment and warmth.
Hummingbird chicks' diet consists primarily of regurgitated nectar and insects, which are rich in essential nutrients needed for their growth and development.
The parents tirelessly gather food and deliver it to the hungry chicks, ensuring they receive adequate nutrition to thrive.
As the chicks mature, their plumage develops, and their eyesight improves. Eventually, after intensive care, they reach a stage where they are ready to leave the nest and embark on their independent journey.
Conclusion
The hummingbird emerges as a remarkable marvel of the avian world, captivating with interesting facts about hummingbirds' characteristics and fascinating behaviours.
From its diminutive size to astonishing flight skills, the hummingbird captivates the imagination with its extraordinary adaptations and capabilities.
Its rapid wing beats, high metabolism, and intricate feeding behaviour underscore the remarkable physiological and ecological niche it occupies.
The hummingbird's role as a pollinator, diverse habitats, and contribution to ecosystem balance further highlight its significance in the natural world.
With its vibrant plumage, agile movements, and unwavering resilience, the hummingbird inspires awe and admiration, serving as a testament to the wonders of evolution and the intricate beauty of the natural world.
I trust you enjoyed this article in Interesting Facts About Hummingbirds. Please stay tuned for more blog posts soon. Take care!
JeannetteZ
Your Opinion Is Important To Me
Do you have thoughts, ideas, or questions? I would love to hear from you. Please leave me your questions, experiences, and remarks about this article, Interesting Facts About Hummingbirds, in the comments section below. You can also reach me by email at Jeannette@Close-To-Nature.org.
Disclosure
This post may contain affiliate links. As an Amazon Associate and other affiliate programs, I earn from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you. Please read my full affiliate disclosure.
You might also enjoy these blog posts:
Your Essential Companion Planting Guide
Natural Fertilizer For Indoor Herbs
Benefits Of Vitamin B12 For Women






