Interesting Yellow-Bellied Sapsucker Facts
Interesting Yellow-Bellied Sapsucker Facts
The Yellow-bellied Sapsucker is a fascinating bird species found primarily in North America. Known for its distinctive behaviour and appearance, this species captivates birdwatchers and nature enthusiasts.
With its vibrant plumage, specialized feeding habits, and unique role in forest ecosystems, the Yellow-bellied Sapsucker is an intriguing subject of study.
This article will explore the fascinating facts about Yellow-bellied Sapsuckers, shedding light on their physical characteristics, habitat preferences, feeding behaviour, breeding habits, and ecological significance.
Join us on a journey into the world of these remarkable woodpeckers and discover the secrets of the Yellow-bellied Sapsucker.

Physical Description Of The Yellow-Bellied Sapsucker
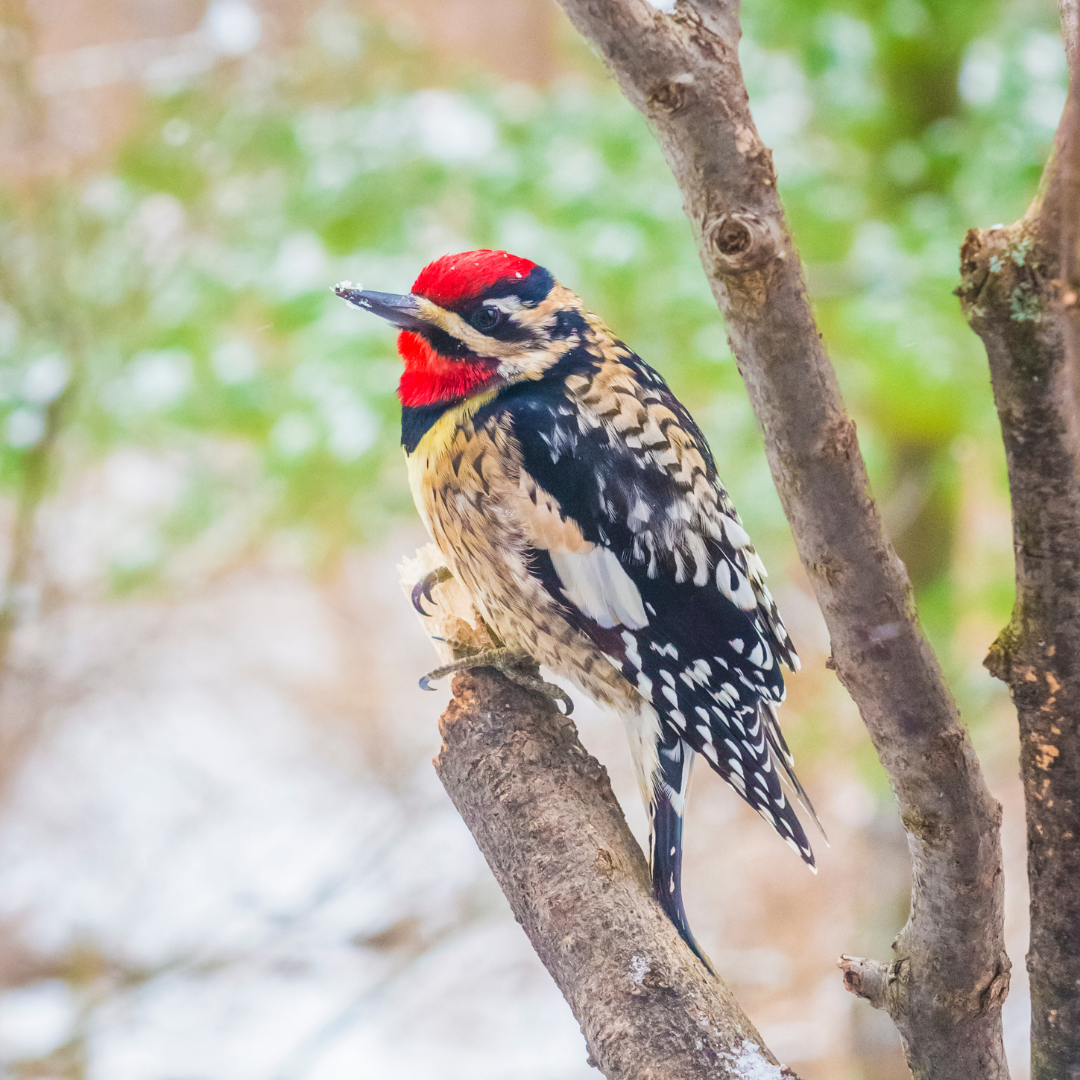
A medium-sized woodpecker with distinguishing features and plumage is the Yellow-bellied Sapsucker.
Adults measure approximately 7-8 inches (18-20 cm) in length and have a wingspan of around 13-16 inches (33-41 cm).
Their plumage is a striking combination of black, white, and yellow. The head of the Yellow-bellied sapsucker is adorned with a bold black-and-white striped pattern extending from the crown down to the nape.
The back and wings are predominantly black, with white barring and spots, while the underparts are mostly white, with a notable yellow belly.
Males and females share similar markings, but males may have additional red patches on their throats and foreheads.
These distinctive colours and patterns make the Yellow-bellied sapsucker easily recognizable among other woodpecker species.

Yellow-Bellied Sapsucker Facts
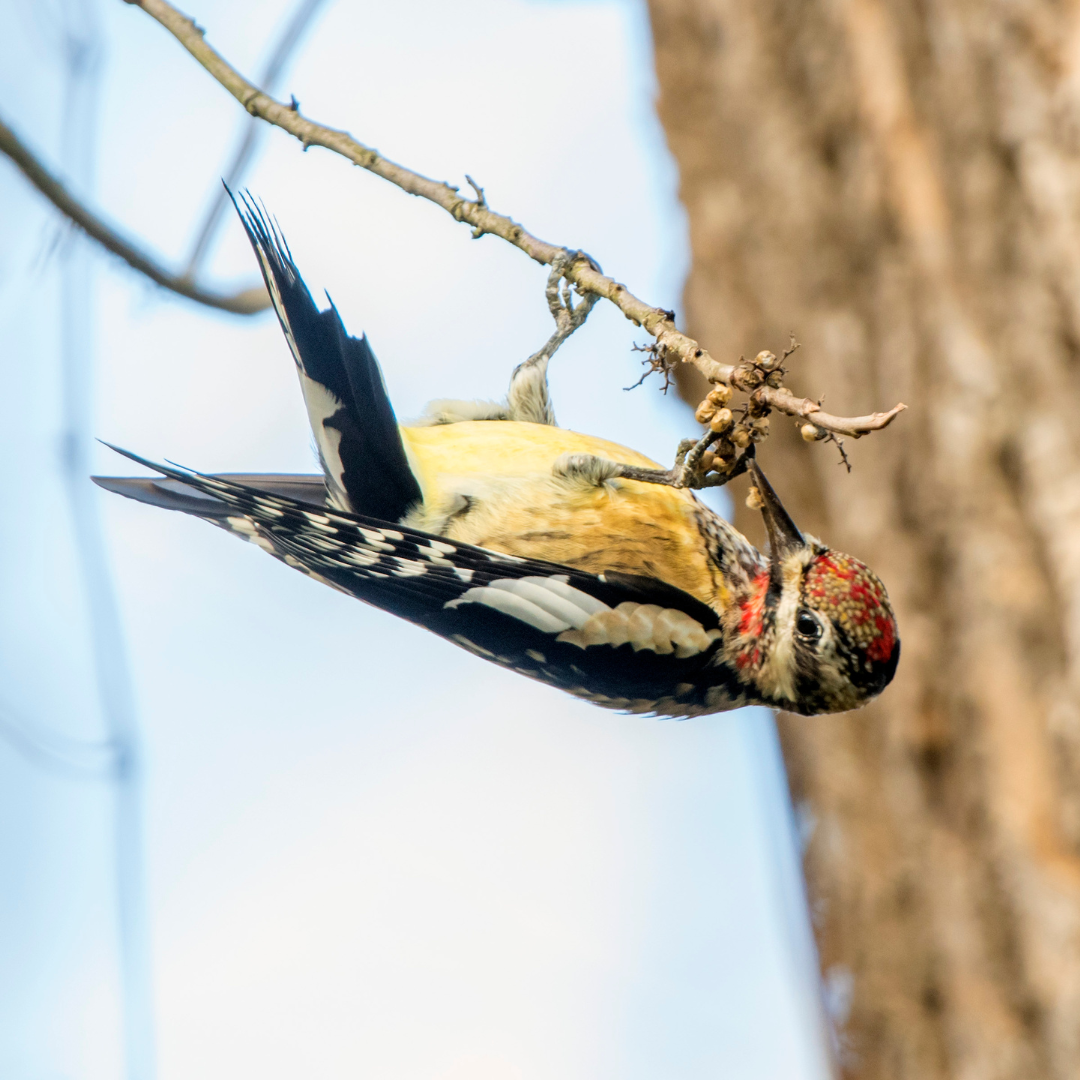
The Yellow-bellied sapsucker is a colourful figure in the intricate tapestry of North American woodlands. It commands attention with its distinctive look and unusual habits.
This woodpecker attracts attention and arouses interest with its black-and-white striped head, resembling a masked bandit.
The flash of yellow beneath its belly, a splash of colour in the woodpecker world, is revealed by its name, which also reveals a secret.
But this bird mystery is more complex than it first appears. The Yellow-bellied Sapsucker is an expert at creating sap wells in trees to enjoy the sweet nectar inside.
It morphs into an ecosystem architect searching for food, building sap-filled havens that attract other birds, insects, and even mammals. Here are some interesting facts about these unique birds:
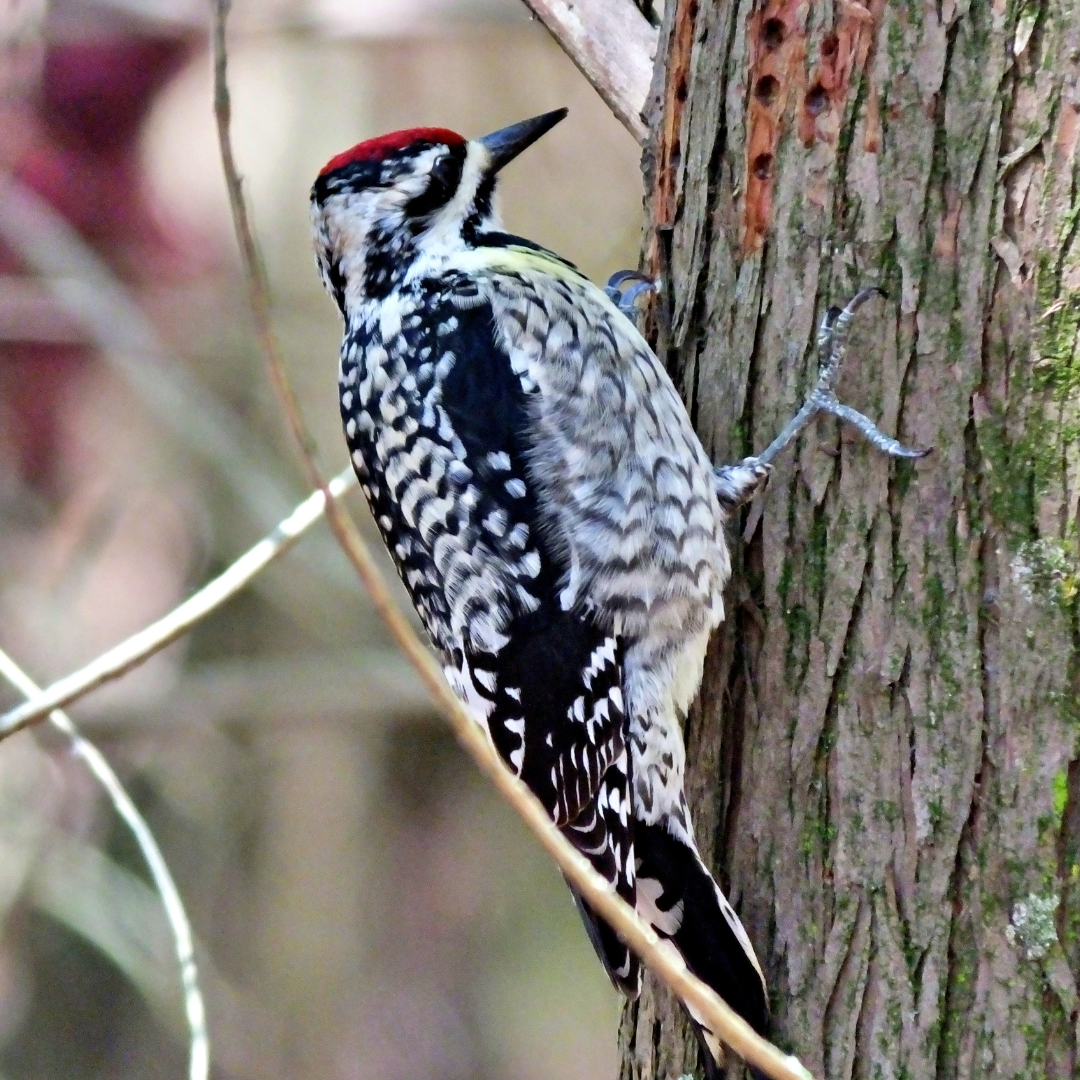

1. Plumage Of Yellow-Bellied Sapsuckers
Yellow-bellied sapsuckers (Sphyrapicus varius) display a striking and distinct plumage that sets them apart from other woodpecker species.
Adult males showcase a bold pattern of black and white on their heads, creating a distinctive striped appearance.
Their black crown and nape extend down to the back, while the face features a black patch that extends from the eye to the bill.
A vibrant touch of colour is found on the male's throat and forehead, adorned with a bright red patch. This red marking adds a captivating burst of colour to the overall plumage.
In contrast, females and juvenile Yellow-bellied Sapsuckers have a more subdued appearance.
They lack a prominent red throat and forehead patch, and their overall coloration is predominantly black and white, with a grayish or brownish hue on the back.
The most notable feature both sexes share is the yellow or cream-coloured belly, which contrasts beautifully against the rest of their plumage.
This combination of black, white, and yellow, along with the bold striped head pattern, makes the Yellow-bellied Sapsucker an easily recognizable and visually appealing woodpecker species.
2. Sap-Feeding Behaviour
Yellow-bellied Sapsuckers (Sphyrapicus varius) have a unique feeding behaviour that sets them apart from other woodpeckers.
They have a strong affinity for sap and actively seek out trees with a high sap content. Using their specialized bills, they create rows of small, evenly spaced holes in the bark of trees.
These holes, known as “sap wells,” are strategically placed in a pattern that maximizes sap flow. The sapsuckers then lap up the flowing sap with brush-like tongues, savouring its sugary goodness.
While sap is their primary food source, Yellow-bellied Sapsuckers also take advantage of the insects attracted to it. They feed on the trapped insects, supplementing their diet with this protein-rich food source.
The sapsuckers maintain their sap wells over time, repeatedly returning to feed on the sap and keeping the wells open by preventing them from healing.
This behaviour provides a reliable food source for the sapsuckers and creates a resource for other creatures, including hummingbirds, insects, and other bird species.
By engaging in their unique sap-feeding behaviour, Yellow-bellied Sapsuckers demonstrate their specialized adaptation for extracting sap and highlight their important ecological role within forest ecosystems.
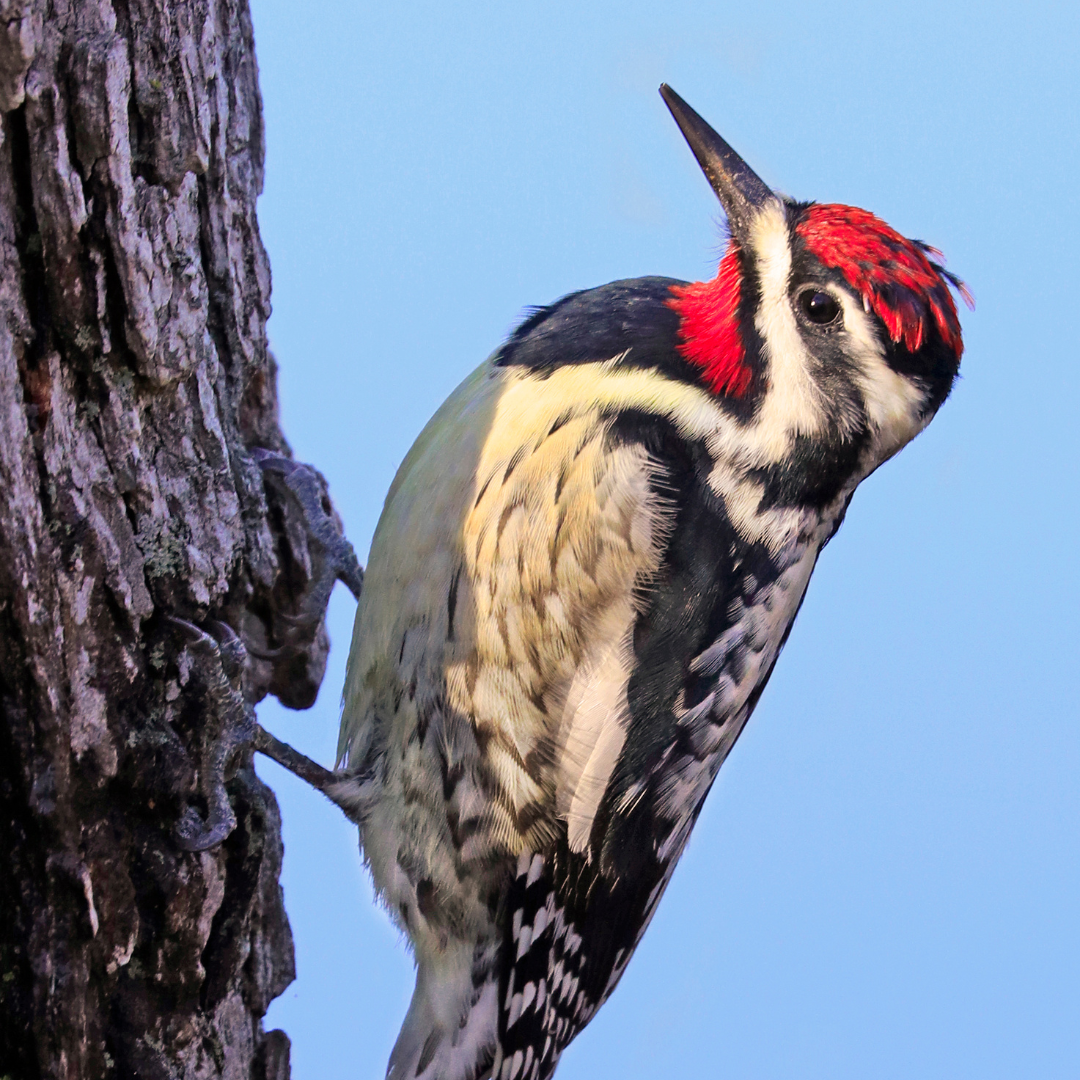

3. Migration
Yellow-bellied Sapsuckers (Sphyrapicus varius) are migratory birds undertaking seasonal journeys between breeding and wintering grounds.
During the breeding season, they can be found in the northern regions of North America, including parts of Canada and the northern United States.
Here, they establish their breeding territories in mature forests with abundant trees suitable for nesting and sap-feeding.
As the summer ends, these sapsuckers embark on their annual migration to their wintering grounds in the southern parts of their range.
Some individuals may also migrate further south to regions in Mexico and Central America. Their migration's exact timing and routes vary, but generally, they begin their journey in late summer or early fall and return to their breeding grounds in the following spring.
Migration allows the Yellow-bellied Sapsuckers to take advantage of seasonal changes in food availability and nesting conditions.
By moving to more favourable habitats during the winter, they can access abundant food resources and avoid the harsh conditions of their breeding range.
This remarkable migratory behaviour showcases the adaptability and resilience of these woodpeckers as they navigate long distances to ensure their survival and reproductive success.
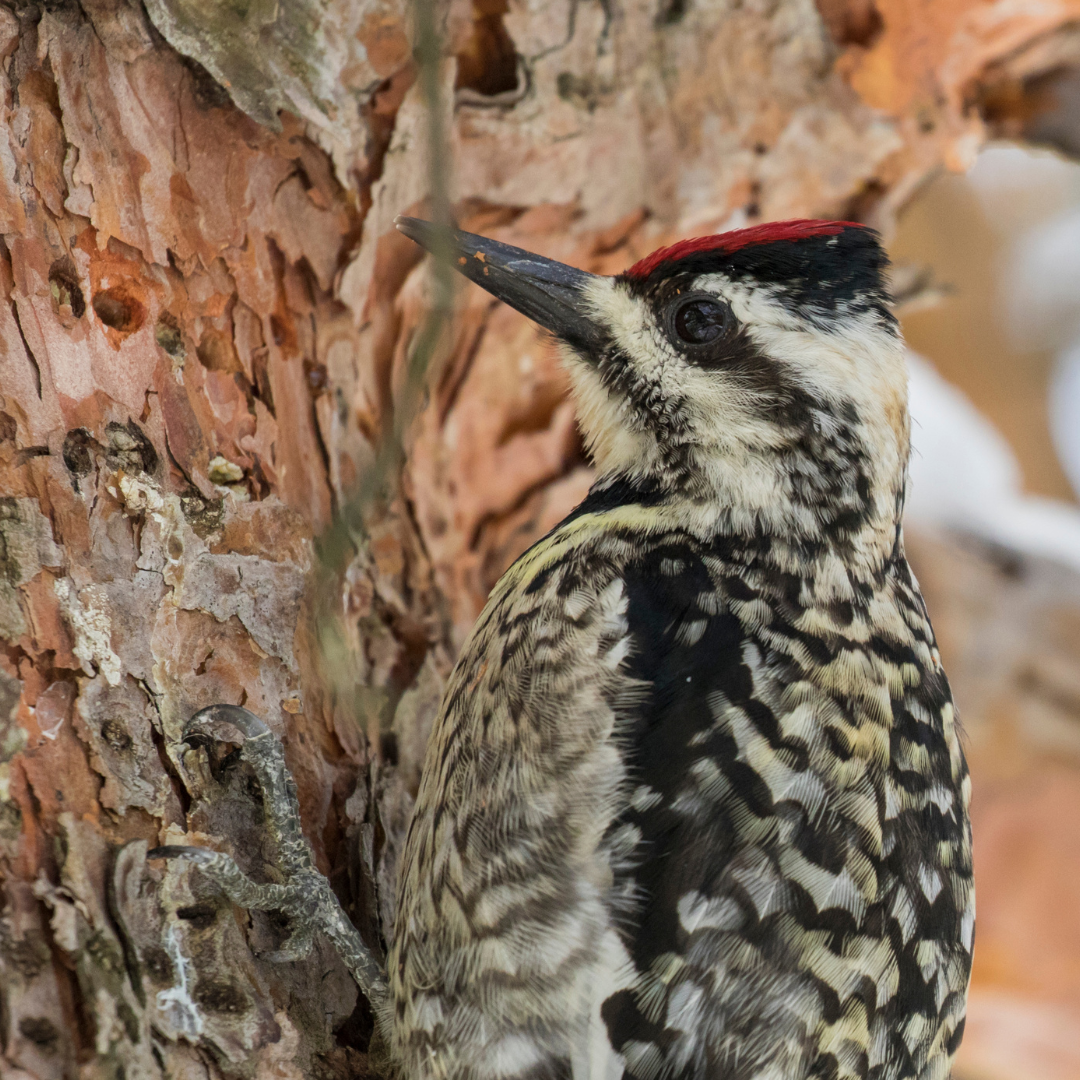

4. Drumming
Yellow-bellied Sapsuckers (Sphyrapicus varius) communicate through a distinctive drumming sound, which plays an important role in their territorial behaviour and attracting mates.
This drumming behaviour involves the rapid and rhythmic tapping of their bills against resonant surfaces, such as hollow branches, tree trunks, or even metal objects.
The resulting sound varies in intensity and frequency, depending on the purpose of the drumming. Male sapsuckers use drumming as a territorial display to establish their presence and defend their nesting territory.
The drumming serves as a signal to other males, indicating their ownership of a specific area and warning them to keep their distance.
The intensity and frequency of the drumming can convey information about the male's size, strength, and overall fitness.
During the breeding season, male sapsuckers may also use drumming to attract females. The rhythmic drumming, combined with other displays like wing fluttering and vocalizations, helps to advertise their availability and fitness as potential mates.
The distinct drumming of the Yellow-bellied Sapsucker is a means of communication and a fascinating behaviour that showcases their unique adaptations and social interactions within their woodland habitats.
5. Sap Well Gardens
Yellow-bellied Sapsuckers (Sphyrapicus varius) exhibit a fascinating “sap well gardening behaviour.” These woodpeckers create and maintain tree sap wells by repeatedly drilling small holes into the bark.
The sap wells are strategically arranged in neat horizontal or vertical rows, forming a “sap well garden.” The sapsuckers feed on the sap from these wells, but their interaction with the trees goes beyond simple sap consumption.
Frequently revisiting and keeping the sap wells active prevents the holes from healing and allows a continuous sap flow.
This behaviour provides a reliable food source for the sapsuckers themselves. The sugary sap also attracts a variety of other animals, including insects, hummingbirds, and even mammals.
The sapsuckers benefit from this diverse array of visitors by opportunistically capturing insects attracted to the sap. This unique behaviour of sap well gardening showcases the remarkable ecological impact of Yellow-bellied Sapsuckers.
They shape their environment and provide food resources for various organisms, creating a complex network of interactions within their woodland habitats.
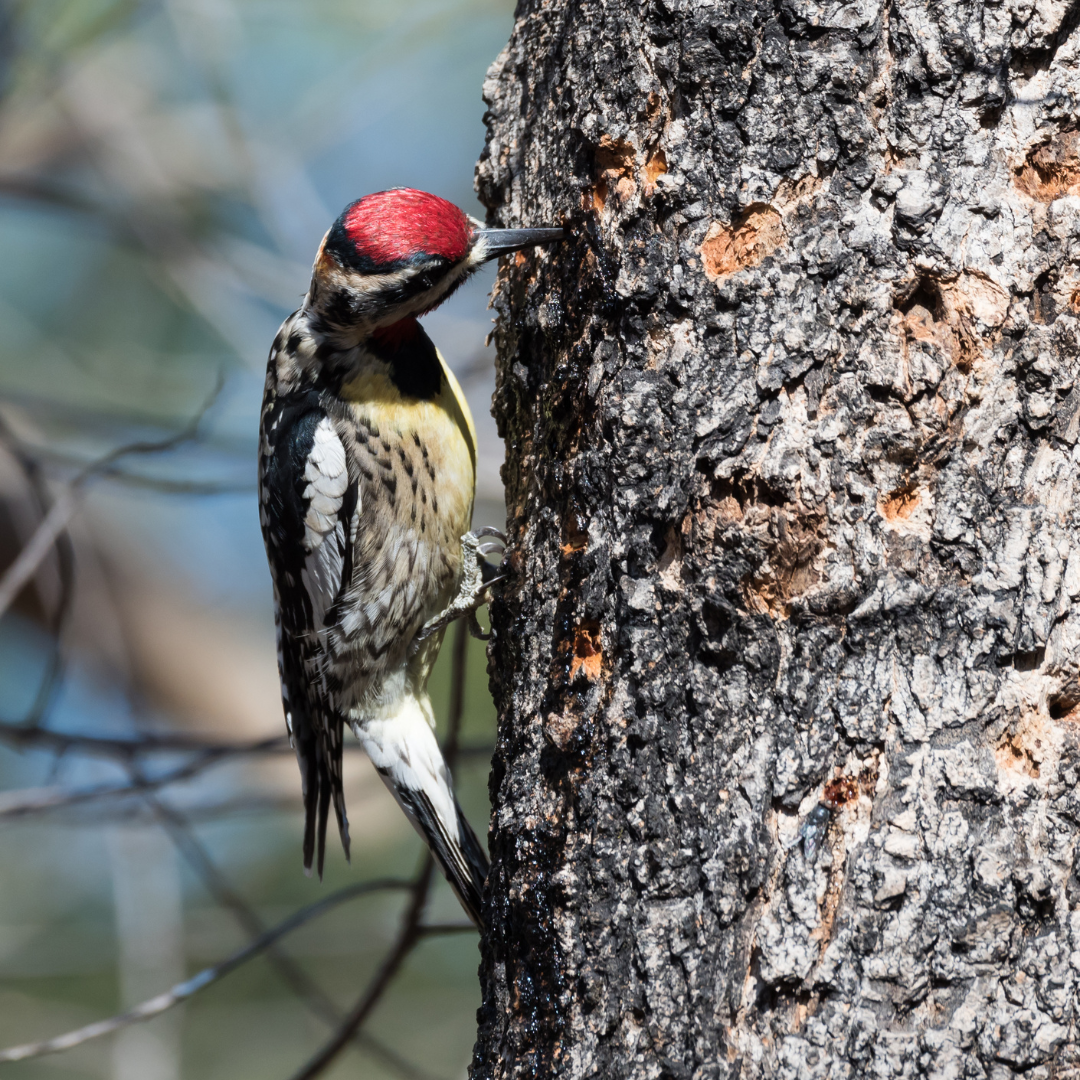

6. Insect Attraction
The sap wells created by Yellow-bellied Sapsuckers (Sphyrapicus varius) significantly impact the insect population within their habitat.
As the sapsuckers drill small holes into the bark of trees to access the sap, the sugary liquid attracts a wide range of insects.
These insects, including ants, beetles, flies, and bees, are lured by the abundant and easily accessible food source provided by the sap wells. The insects become trapped or immobilized in the sticky sap, becoming a ready and nutritious meal for the sapsuckers.
However, the presence of insects also attracts other insect-eating birds to the sap wells. Birds such as warblers, vireos, and hummingbirds take advantage of the abundant insect activity and join the sapsuckers in feeding on the trapped insects.
This creates a bustling feeding hub within the forest ecosystem, where multiple species converge to exploit the rich food resources.
The insect attraction generated by the sap wells benefits the sapsuckers and contributes to the forest habitat's overall biodiversity and ecological dynamics.
7. Territory Defense
Male Yellow-bellied Sapsuckers (Sphyrapicus varius) are highly territorial birds who employ various strategies to defend their chosen breeding territories.
One of their primary methods is drumming, which involves rapidly tapping their bills against resonant surfaces, such as hollow trees or branches.
The resulting rhythmic drumming sound serves as a territorial signal and a means of communication with potential rivals.
The drumming can be heard over considerable distances and is intended to establish the male's presence and assert his territory ownership.
In addition to drumming, male sapsuckers also vocalize, emitting distinctive calls and chattering sounds to demarcate their territory further and ward off intruders.
These vocalizations warn other males and communicate their readiness to defend their territory. In territorial disputes, males engage in aggressive displays, puffing up their feathers, raising their crests, and engaging in aerial chases or physical confrontations.
These intense territorial interactions can involve loud vocalizations and physical combat as males strive to maintain their exclusive breeding grounds.
The territorial defence behaviour of Yellow-bellied Sapsuckers is essential for ensuring access to resources, attracting mates, and securing successful breeding opportunities within their chosen habitat.
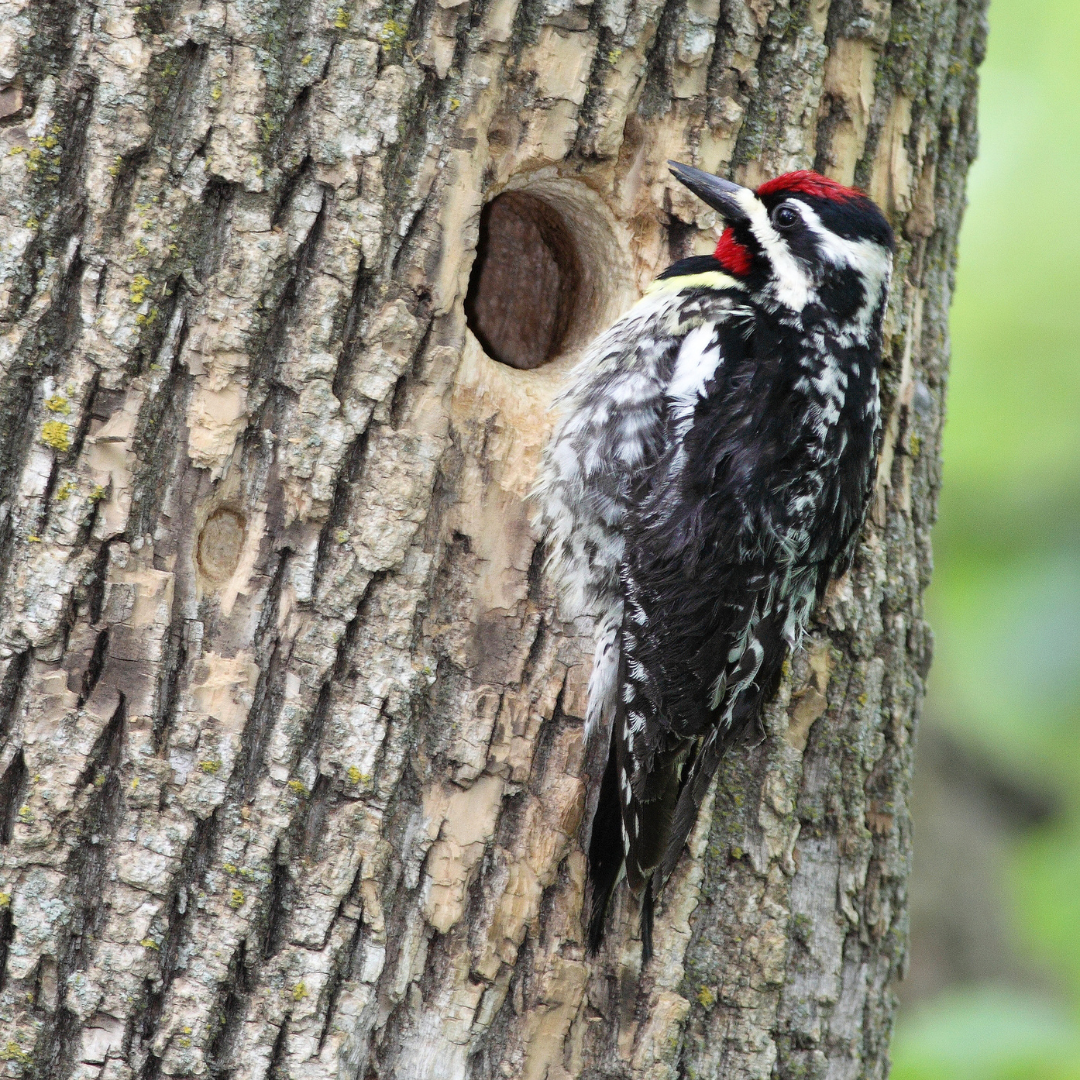

8. Incubation And Nestling Care
Yellow-bellied Sapsuckers (Sphyrapicus varius) exhibit cooperative breeding behaviour when incubating their eggs and caring for their nestlings.
Both male and female sapsuckers take turns incubating the eggs, sharing the responsibility of keeping them warm until they hatch.
This shared incubation allows for efficient nest defence as one parent can guard the nest while the other forages for food or rests.
Once the eggs hatch, both parents play an active role in caring for the nestlings. They provide nourishment by regurgitating partially digested insects and sap, ensuring a balanced diet for their young.
The parents also diligently remove waste from the nest to maintain cleanliness and prevent the accumulation of debris.
In addition to feeding, the parents protect the nestlings from potential predators and maintain the nest's structural integrity.
Both male and female sapsuckers exhibit a high level of parental investment, contributing to their offspring's survival and well-being.
This shared parental care is crucial in providing the necessary resources, protection, and guidance during the vulnerable stages of the nestlings' development.
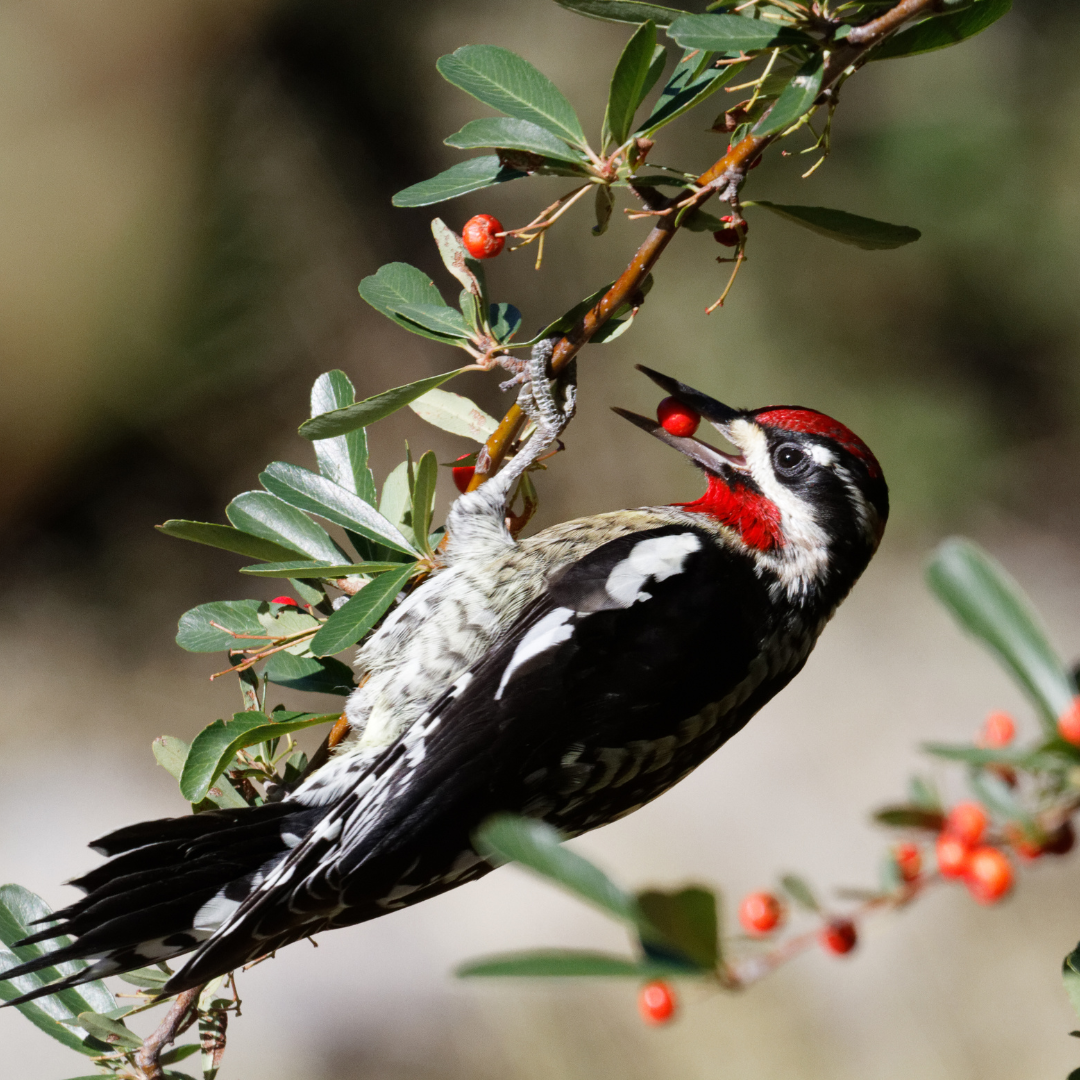

9. Hybridization With Red-Naped Sapsuckers
In areas where their ranges overlap, Yellow-bellied and Red-naped Sapsuckers occasionally hybridize, producing individuals that display characteristics of both species.
These hybridization events typically occur in regions where the breeding ranges of the two species overlap, such as parts of western North America.
The resulting hybrids exhibit intermediate traits, blending features from both parental species. These traits can include variations in plumage coloration, patterns, and markings.
Hybrids may have a mix of the black-and-white striped head characteristic of Yellow-bellied Sapsuckers and the red nape found in Red-naped Sapsuckers.
The occurrence of hybridization suggests some level of genetic compatibility and hybrid viability between the two species.
However, such hybrids are relatively rare and tend to be found in areas where the populations of both species are near.
The occurrence of hybridization provides valuable insights into the dynamics of species interaction and genetic diversity within woodpecker populations.
10. Ecological Significance
Yellow-bellied Sapsuckers are highly ecologically significant as “ecosystem engineers” due to their unique behaviour of creating sap wells.
By drilling rows of small holes in tree trunks, they access sap, a valuable resource for themselves and other species.
The sap wells provide a nutritious food source for many insects, including ants, bees, and beetles, which are attracted to the sugary sap.
These insects attract insectivorous birds and other small animals, creating a bustling feeding hub within the forest ecosystem.
The sapsucker's activities also have a beneficial effect on tree health. While excessive sap removal can harm a tree, moderate sap extraction by sapsuckers stimulates the tree's natural wound response, triggering the production of callus tissue and promoting healing.
Furthermore, the sap wells can influence the surrounding plant and animal communities.
The extra sap flow may benefit other tree-dwelling organisms, such as fungi and mosses, which can thrive in the nutrient-rich environment created by the sapsuckers.
Yellow-bellied Sapsuckers' ecological role as ecosystem engineers highlights their contribution to maintaining biodiversity and shaping the dynamics of forest ecosystems.
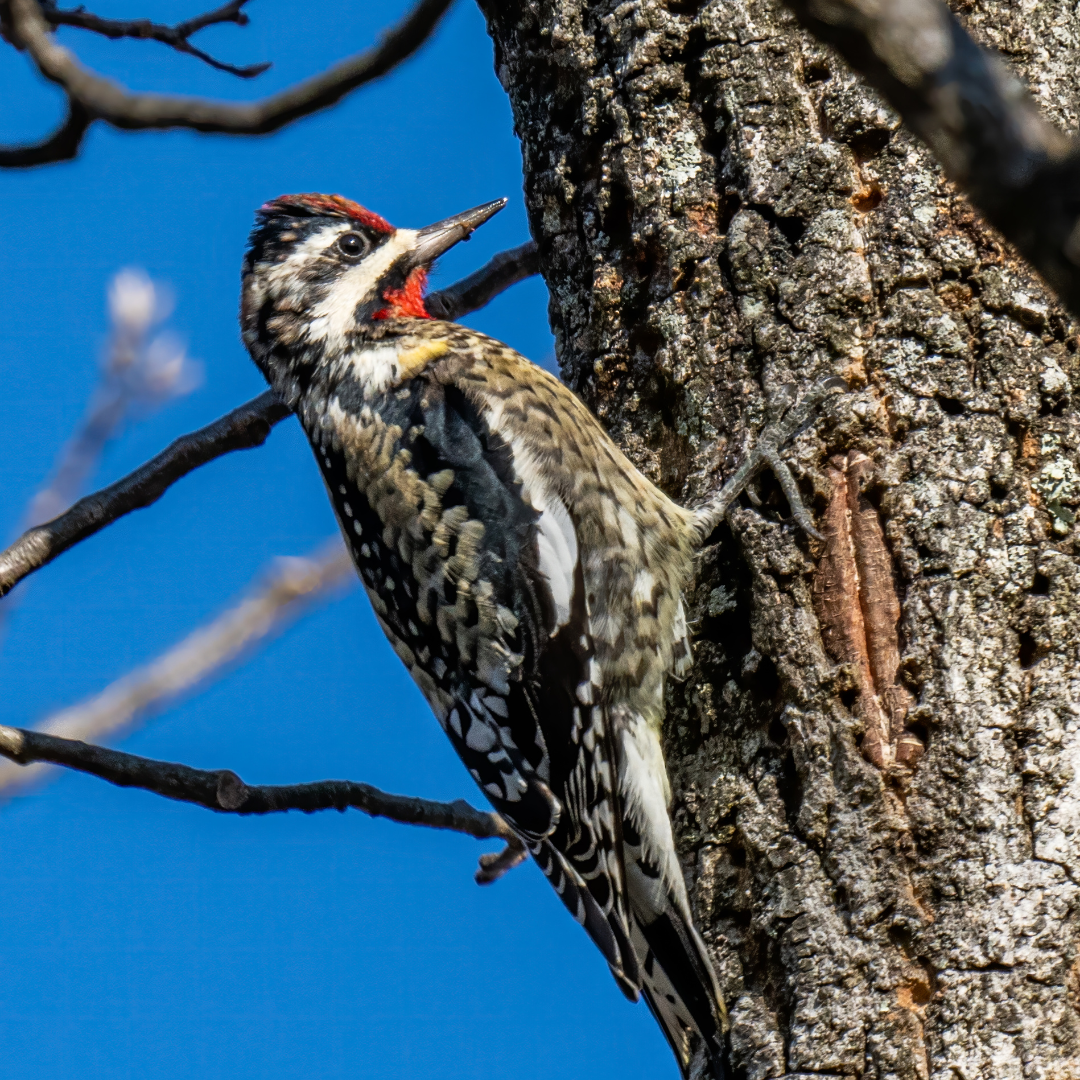

11. Migration Strategy
Yellow-bellied Sapsuckers employ a fascinating migration strategy known as ‘leapfrog migration.'
Unlike many other migratory birds, these sapsuckers have a breeding range that extends further north than their wintering range.
This means that individuals from the southern wintering grounds leapfrog over those from the northern breeding grounds during migration.
The availability of suitable habitats and food resources influences the leapfrog migration pattern.
By nesting in the northern regions where food is abundant during the breeding season, Yellow-bellied Sapsuckers can take advantage of the peak insect populations that coincide with the warmer months.
As winter approaches and insect activity declines north, the sapsuckers migrate south to their wintering grounds, where milder temperatures and more favourable conditions prevail.
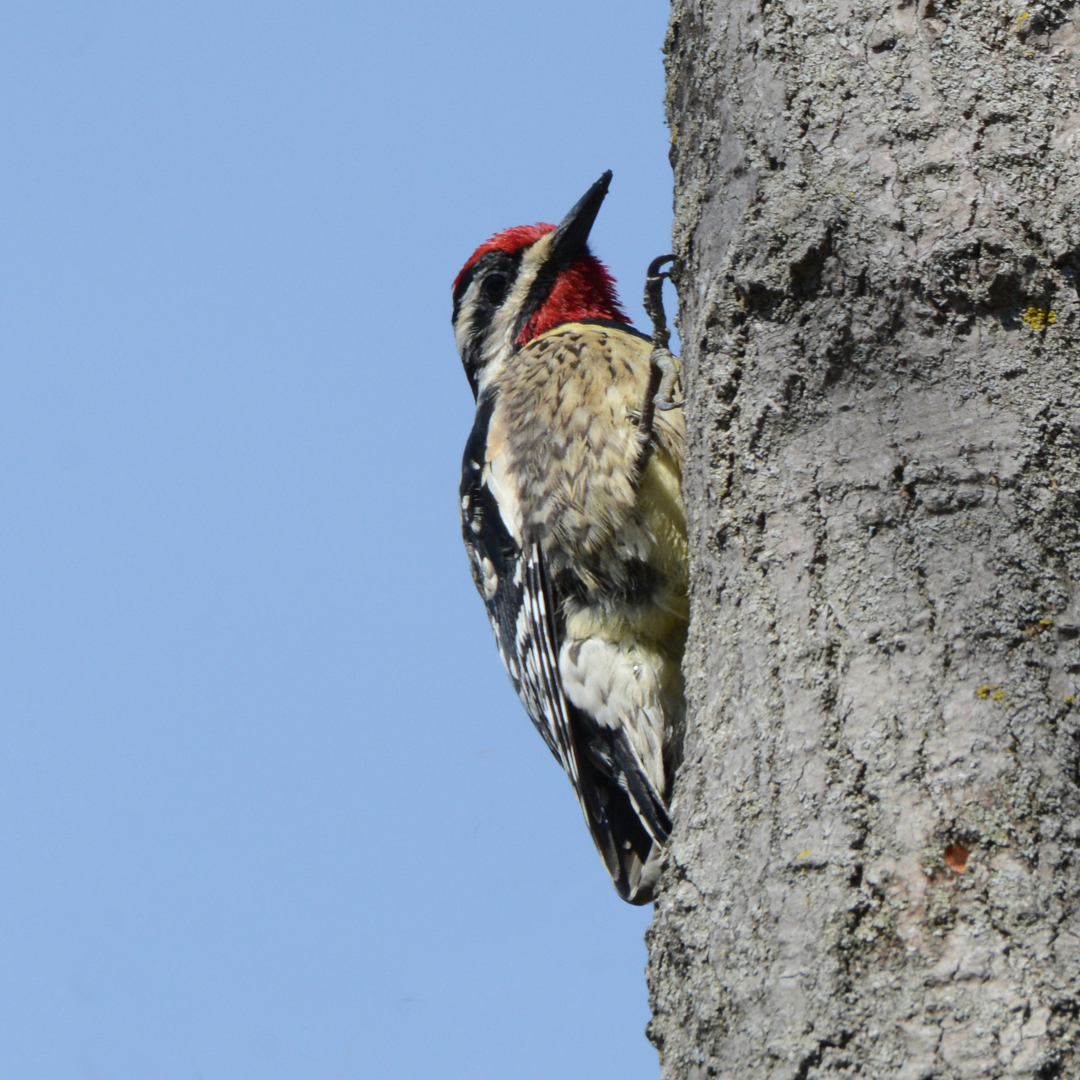

12. Diet
While Yellow-bellied Sapsuckers are renowned for their affinity for sap, their diet is not limited to this sticky liquid. In addition to the sap obtained from their distinctive sap wells, these woodpeckers consume various other food items.
Insects play a significant role in their diet, particularly during the breeding season when they are actively foraging to feed their nestlings.
Yellow-bellied Sapsuckers have a keen eye for spotting insects on tree trunks and branches, and they use their sturdy bill to probe and extract their prey. They feed on insects, including beetles, ants, caterpillars, and spiders.
Beyond insects, these sapsuckers incorporate plant matter into their diet. When available, they consume berries and fruits, such as elderberries and cherries. In some instances, they may also feed on tree buds.
This dietary versatility allows Yellow-bellied Sapsuckers to adapt to seasonal changes in food availability and meet their nutritional needs throughout the year.
While sap remains their primary food source, insects, berries, fruits, and buds provide a diverse and well-rounded diet.
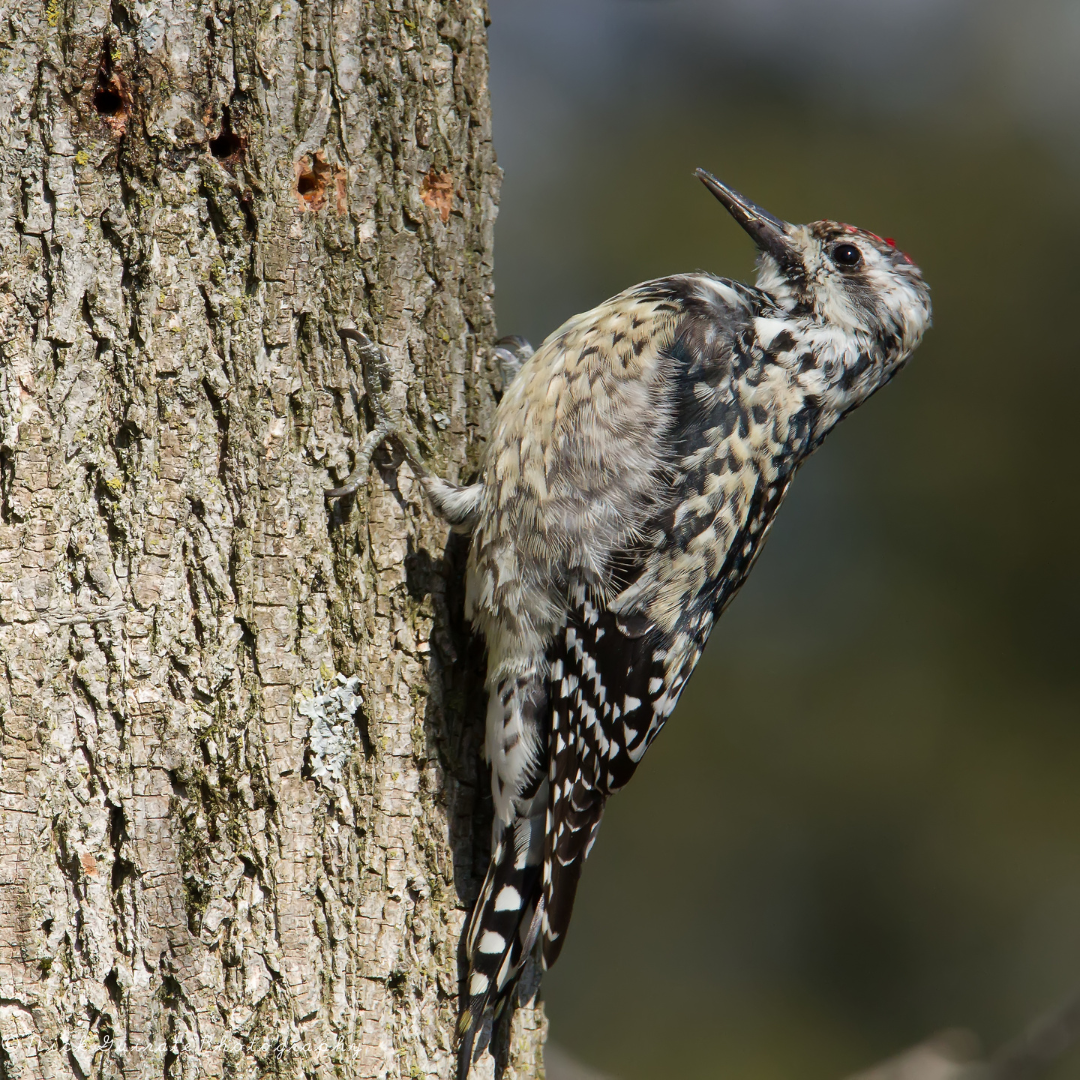
13. Conservation Status
According to the International Union for Conservation of Nature's (IUCN) current classification of Yellow-bellied Sapsuckers as a species of “Least Concern,” they are not considered globally threatened.
However, like many bird species, they face various environmental challenges that could impact their populations. One significant threat to Yellow-bellied Sapsuckers is habitat loss and degradation.
As mature woods with a mix of deciduous and coniferous trees make up their preferred habitat, deforestation and land development can reduce areas ideal for nesting and feeding.
Fragmentation of forests can also disrupt their natural movements and breeding patterns. Extreme weather events like storms and droughts can also impact their nesting success and overall population health.
Conservation efforts that focus on preserving and restoring suitable forest habitats, managing forests sustainably, and raising awareness about the ecological importance of Yellow-bellied Sapsuckers can contribute to their long-term survival.

Conclusion
In conclusion, Yellow-bellied Sapsuckers are fascinating woodpeckers known for their unique behaviours and ecological significance.
Their distinctive plumage, sap-feeding habits, and territorial behaviours leave a mark on the forests they inhabit.
Their creation of sap wells provides a food source for themselves and attracts a diverse array of insects and other birds, creating a hub of activity within the forest ecosystem.
While not globally threatened, yellow-bellied sapsuckers still face habitat loss and climate change challenges, emphasizing the importance of conservation efforts.
Understanding and preserving their habitats and promoting sustainable forest management practices can contribute to their continued presence in our natural landscapes.
We learn more about how intricately different species interact with one another and how crucial they are in preserving the health and balance of our ecosystems as we come to respect and defend these endearing woodpeckers.
I trust you enjoyed this article on Interesting Yellow-Bellied Sapsucker Facts. Please stay tuned for more blog posts soon. Take care!
JeannetteZ
>>>Please click here to read my all-inclusive article about Why Is Wildlife Important And How Can We Protect It<<<
>>>Are you interested in Natural Healing And Stress Relief through Herbs? Please click here for my #1 Recommendation<<<
Your Opinion Is Important To Me
Thoughts? Ideas? Questions? I would love to hear from you. Please leave your questions, experiences, and remarks about the Interesting Yellow-Bellied Sapsucker Facts article in the comments below. You can also reach me by email at Jeannette@Close-To-Nature.org.
Disclosure
This post may contain affiliate links. As an Amazon Associate and other affiliate programs, I earn from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you. Please read my full affiliate disclosure.
You might also enjoy these blog posts:
Interesting American Redstart Facts
How Natural Calm Gummies Reduce Stress
Best Holistic Self-Care Practices
Best Holistic Wellness Tips For Everyday Life
Best Holistic Wellness Retreats