Explore African Elephant Habitats And Their Natural Glory
Explore African Elephant Habitats And Their Natural Glory
Welcome to an exploration of the African Elephant Habitat. The African elephant, one of the largest land mammals on Earth, is an iconic species known for its intelligence, social behaviour, and remarkable physical characteristics.
This magnificent creature is native to Africa's diverse and expansive habitats, where it roams across various landscapes, from dense forests to vast savannas.
The African elephant's habitat is crucial to its survival, providing the necessary resources and conditions for its well-being.
This article will delve into the fascinating world of the African elephant's habitat, exploring its range, environmental factors, and the significance of preserving these habitats for the long-term conservation of this incredible species.

What Is The African Elephant?
The African elephant (Loxodonta africana) is the largest land animal on Earth, belonging to the family Elephantidae. It is characterized by its enormous size, distinctive trunk, long tusks, and large, flapping ears.
African elephants are herbivorous mammals that inhabit various sub-Saharan African habitats, including savannahs, grasslands, forests, and wetlands.
These magnificent creatures play a crucial role in shaping their ecosystems. They are considered keystone species, as their feeding and browsing activities contribute to maintaining biodiversity and shaping vegetation patterns.
African elephants are known to create clearings and pathways as they move through their habitats, providing opportunities for other species to thrive.
Bulls are male African elephants which can grow up to 10-13 feet (3-4 meters) in height and weigh between 5,000 and 14,000 kg.
Females, known as cows, are slightly smaller, reaching heights of 8-9 feet (2.4-2.7 meters) and weighing around 2,700 to 6,000 kilograms.
Both males and females have elongated, curved tusks, although the size and shape can vary between individuals.
African elephants are incredibly social creatures living in elaborate family units under the leadership of a matriarch, often the oldest and most seasoned female.
These groups, known as herds, can consist of several related females and their offspring. Male elephants tend to live solitary lives or form smaller bachelor groups.
Unfortunately, African elephants face numerous threats, including habitat loss, poaching for ivory, human-wildlife conflict, and illegal wildlife trade.
Conservation efforts, including protected areas, anti-poaching initiatives, and community-based conservation programs, are crucial for African elephants' long-term survival, well-being, and habitats.
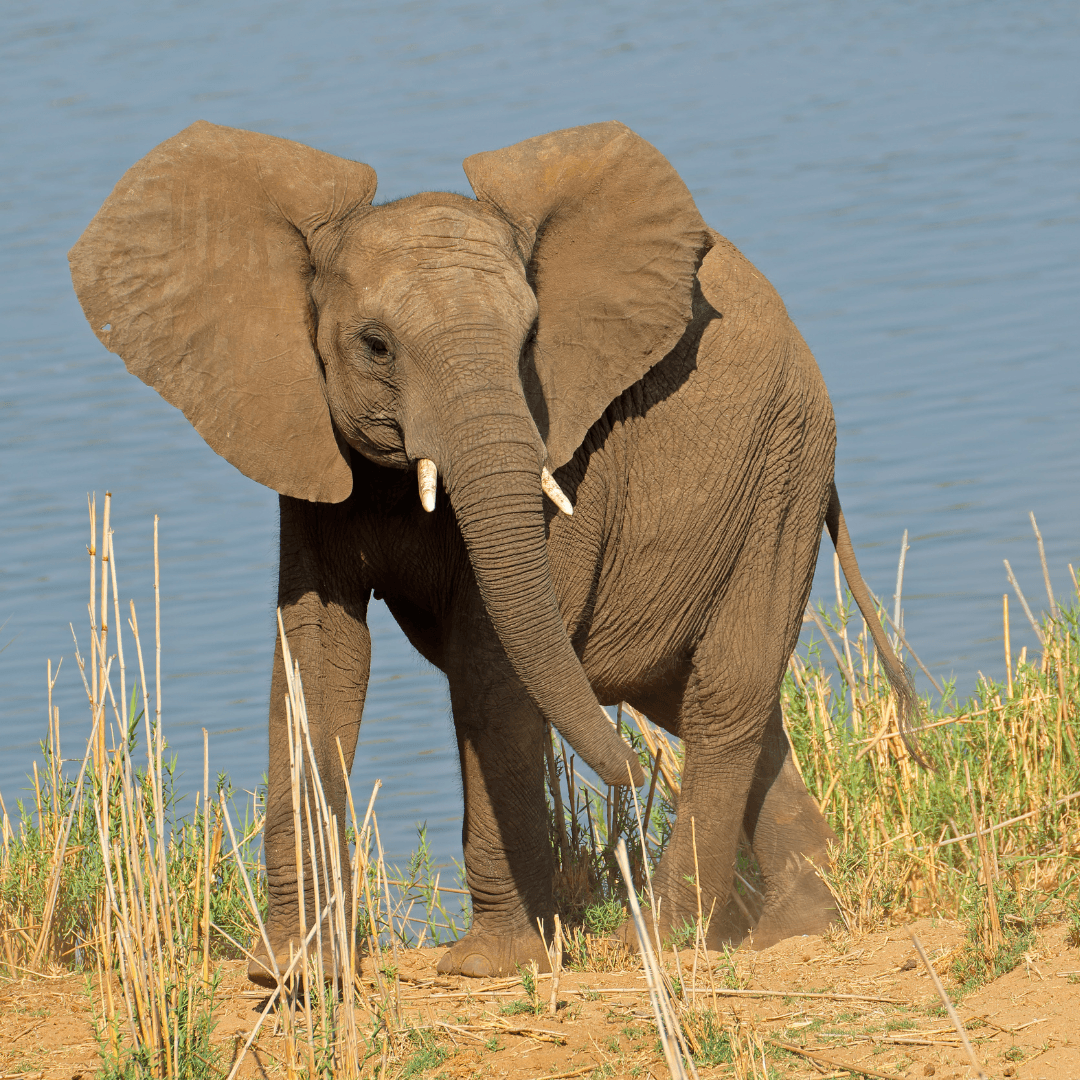

The World Of African Elephant Habitats
African elephants shape the ecosystems and support biodiversity through their behaviours. From seed dispersal to digging water holes, their role in nature is vital, yet climate change threatens their survival.
1. Savannas And Grasslands
Savannas and grasslands are prominent habitats for African elephants, especially in regions like East and Southern Africa.
These expansive landscapes are characterized by grasses, scattered trees, and shrubs, providing a diverse array of vegetation for the elephants to feed on.
The availability of water sources, such as rivers, lakes, and watering holes, is crucial for sustaining these large herbivores.
One of the remarkable features of savannas and grasslands is their seasonal changes. During the wet season, these areas become lush and green, offering an abundance of nutritious plants for the elephants to graze on.
As the dry season sets in, the vegetation becomes more scarce, and water sources may dwindle, leading to migratory patterns as the elephants seek food and water.
The vastness of the savannas allows for the formation of large elephant herds consisting of several individuals, including matriarchs, adult females, and their offspring.
These herds offer social benefits, as elephants are highly social animals, and a cohesive group protects and supports the younger members.
However, human activities, such as agriculture, settlements, and infrastructure development, pose significant threats to these vital habitats.
As human populations expand, there is increased pressure to convert savannas into agricultural land or urban areas, leading to habitat fragmentation and loss.
This fragmentation can disrupt elephant migration routes and isolate populations, limiting genetic diversity and increasing the risk of inbreeding.
Conservation efforts focused on protecting savannas and grasslands are essential for the survival of African elephants. Establishing protected areas, national parks, and wildlife corridors can help preserve these crucial habitats, allowing elephants to roam freely and maintain their natural behaviours.
Additionally, sustainable land-use practices, community-based conservation initiatives, and responsible tourism can contribute to the coexistence of elephants and local communities, ensuring the preservation of these magnificent creatures and their unique savanna habitats for generations to come.
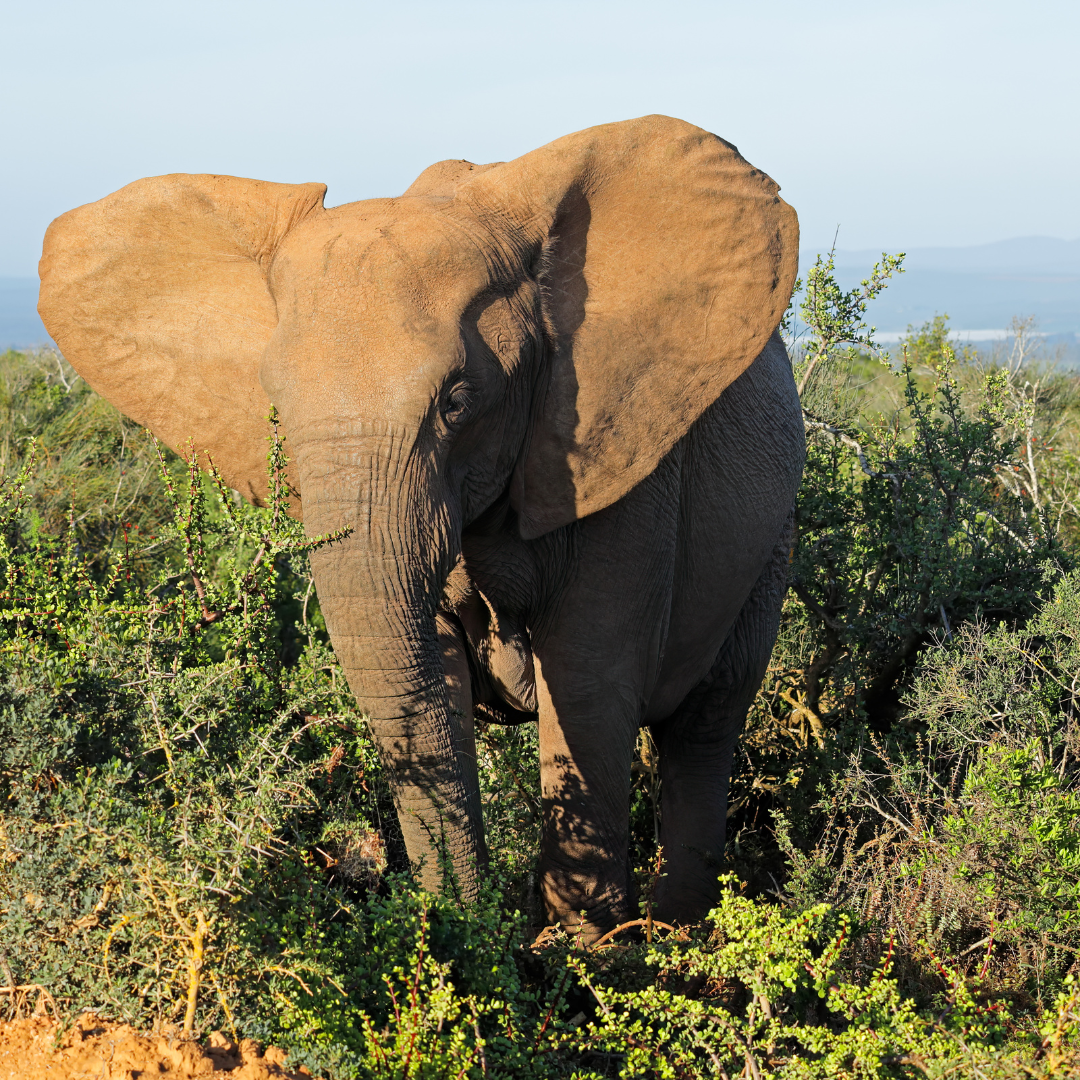

2. Forests And Woodlands
Forests and woodlands are essential habitats for African elephants, particularly the forest elephants (Loxodonta cyclotis).
These elephants are specially adapted to thrive in the dense rainforests and woodlands of Central and West Africa. Forest elephants are generally smaller and have straighter tusks than their savanna counterparts.
The forest elephants' diet in these habitats consists of various plant species, including fruits, leaves, and bark. The lush vegetation provides them with abundant food resources throughout the year.
They are selective feeders, utilizing their elongated trunks to pluck fruits and leaves from the trees and their tusks to scrape bark for consumption.
The dense forest canopies offer several advantages to the elephants. The thick foliage provides shelter from harsh weather conditions and protection from potential predators.
Forest elephants also rely on their excellent memory and navigation skills to traverse the dense vegetation, creating well-worn pathways known as “elephant highways.”
These pathways allow them to move efficiently through the forests to access various food and water sources. However, forest elephants face unique challenges due to the remoteness and inaccessibility of their habitat.
Human activities, such as logging, agriculture, and infrastructure development, pose significant threats to these sensitive ecosystems.
Encroachment into their habitat can lead to habitat fragmentation and disrupt migration patterns, limiting the elephants' access to resources and potential mates. Conservation efforts focused on protecting the rainforests and woodlands are critical to safeguarding forest elephants.
Establishing protected areas and implementing sustainable land-use practices are essential to preserving these critical habitats and supporting biodiversity.
Additionally, combating illegal poaching for ivory, which remains a significant threat to all elephant populations, is crucial for the survival of these magnificent creatures.
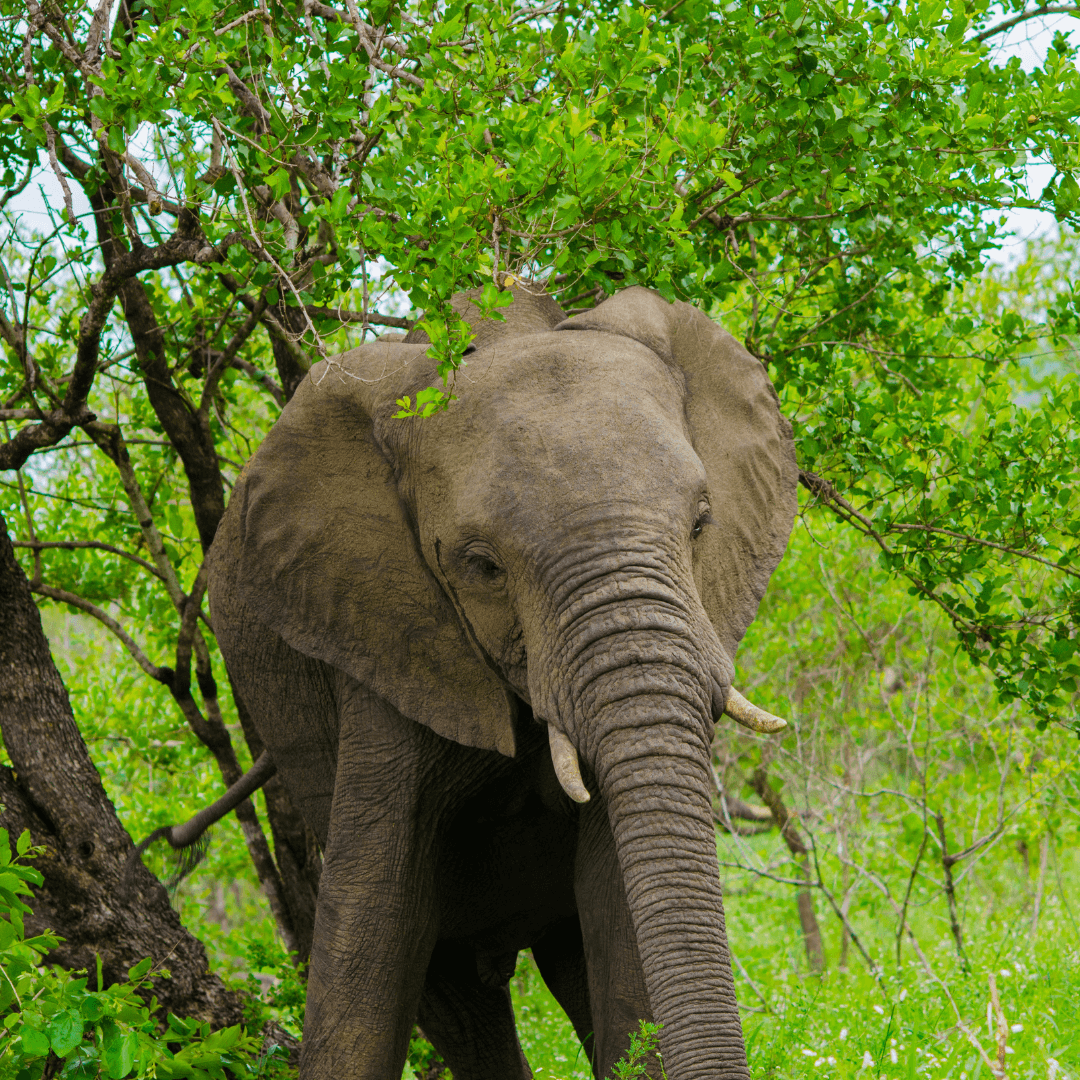

3. Wetlands And Swamps
Wetlands and swamps are essential habitats for African elephants, offering unique ecological benefits that contribute to their existence.
These regions are characterized by their waterlogged conditions, which are highly attractive to elephants, particularly during dry seasons when water sources may become scarce in other habitats.
One of the primary advantages of wetlands and swamps for elephants is the abundance of water.
Elephants are highly dependent on water for survival, and these areas serve as crucial watering holes, ensuring a steady water supply throughout the year.
Additionally, water in wetlands and swamps supports the growth of lush vegetation, providing elephants with a diverse range of food resources.
Beyond drinking, elephants also engage in various water-related activities in these habitats. Bathing and mud wallowing are common behaviours observed in elephants.
Mud wallowing serves multiple purposes, including protecting their skin from harsh sun exposure and insect bites and maintaining body temperature through evaporative cooling.
The wet mud acts as a natural sunscreen and helps prevent skin dryness and cracking. The ecological significance of elephants in wetland and swamp ecosystems is noteworthy.
As they move through these habitats, they create pathways and clearings, inadvertently creating valuable habitats for other species.
Their foraging activities help disperse seeds, contributing to the dispersal and regeneration of plant species, and their dung provides nutrients to the soil, enhancing fertility and promoting plant growth.
However, like other habitats, wetlands and swamps are vulnerable to human activities such as drainage for agriculture, urbanization, and resource extraction.
These activities can lead to habitat degradation and loss, directly impacting the elephants' ability to access water and food sources.
Conservation efforts focused on protecting wetlands and swamps are crucial for the long-term survival of African elephants.
Implementing sustainable management practices and designating protected areas are essential to preserving these vital habitats and the ecological services they provide.
By safeguarding these areas, we can ensure the continued existence of African elephants and the rich biodiversity that relies on these unique ecosystems.
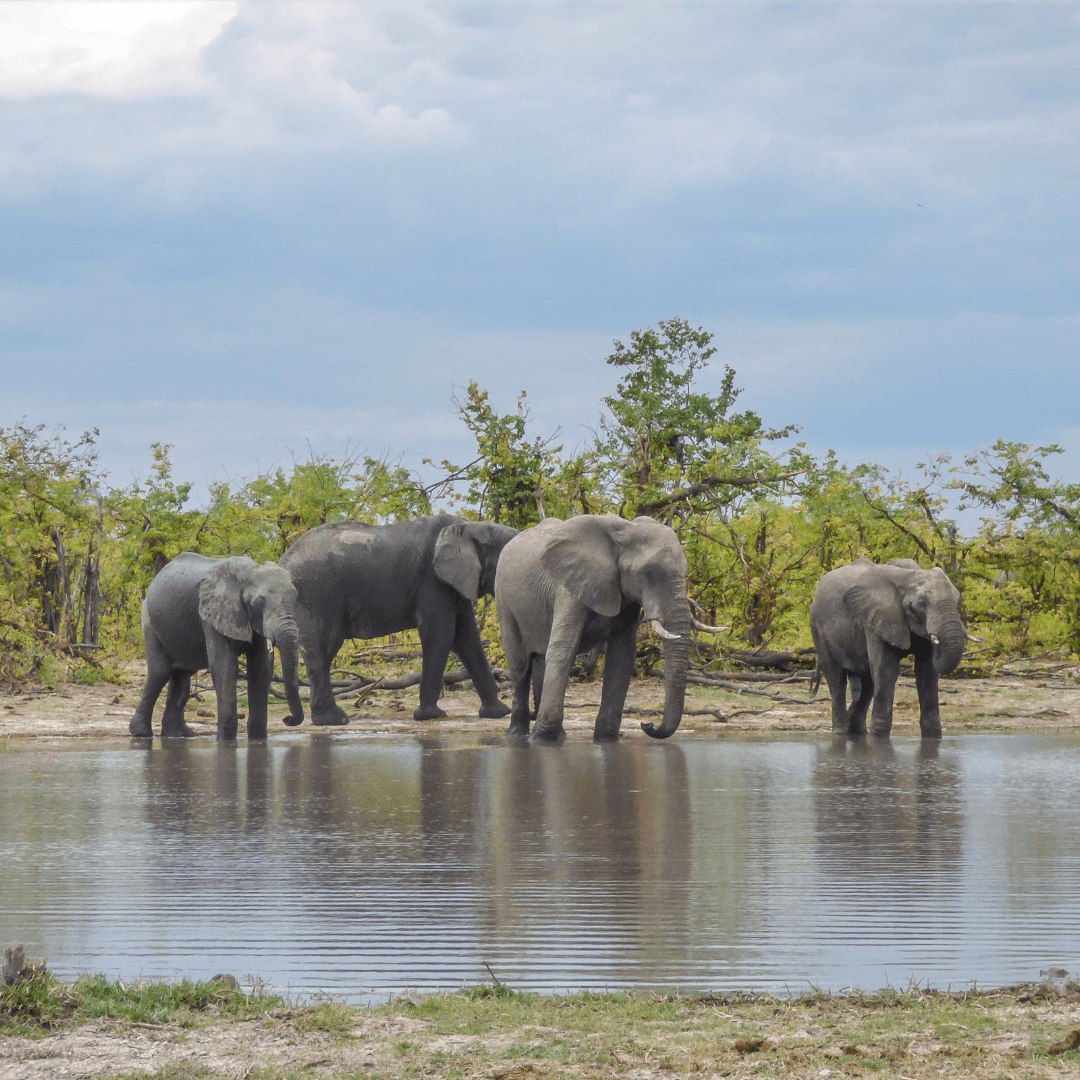

4. Deserts And Arid Regions
African elephants' ability to thrive in deserts and arid regions is a testament to their remarkable adaptability and survival instincts.
In some parts of Africa, elephants are found in arid areas like the Sahara Desert and the Kalahari Desert, where water and food resources are scarce, and temperatures can be extreme.
Surviving in these challenging landscapes requires elephants to exhibit unique behaviours and adaptations. Their large ears play a crucial role in thermoregulation, as they help dissipate heat and keep the elephants cool in the scorching sun.
Elephants are also known to dig for water, utilizing their strong trunks to reach underground water sources or creating makeshift waterholes by digging in dry riverbeds. Another remarkable aspect of their survival in deserts is their ability to travel vast distances for food and water.
Elephants have excellent memory and use their knowledge of the landscape to find reliable water sources, even if it means travelling long distances to reach them.
This migratory behaviour is crucial for their survival during the dry seasons when water becomes scarce in their immediate surroundings.
African elephants' diet in arid regions mainly consists of drought-resistant plants, such as succulents and hardy grasses. While these plants may not be as nutritionally rich as those found in other habitats, elephants have adapted to extract the necessary nutrients and moisture from these vegetation types.
However, like in other habitats, elephants in deserts and arid regions face significant challenges due to human activities.
Encroachment of human settlements and agriculture can disrupt their migratory routes and limit their access to essential resources.
Additionally, illegal poaching for ivory and human-elephant conflicts pose significant threats to their populations. Conservation efforts focused on preserving the delicate balance of these arid ecosystems are vital for the long-term survival of African elephants.
Creating protected areas and promoting sustainable land management practices can ensure elephants exhibit extraordinary adaptability and resilience in these challenging environments.
We can secure a sustainable future for African elephants in deserts and arid regions by safeguarding their habitats and addressing human-induced threats.

5. Seed Dispersal – The Silent Gardeners Of The Wild
African elephants play a critical ecological role as nature’s most effective seed dispersers. Their immense appetite for vegetation includes a wide range of fruits, leaves, bark, and roots from countless plant species.
As they move across landscapes, elephants consume thousands of seeds daily. However, their most important contribution comes after digestion.
Unlike many other animals, elephants have a relatively inefficient digestive system. This inefficiency allows seeds to pass through their system largely intact.
When elephants excrete seeds miles away from where they consumed the fruit, they effectively transport plant life across vast areas.
The nutrient-rich dung not only protects and nourishes the seeds but also creates ideal conditions for germination and early growth. This process enhances biodiversity, supports forest regeneration, and maintains healthy grasslands.
Seed dispersal by elephants has long-term impacts on the structure and resilience of ecosystems. Many tree and plant species have evolved to rely specifically on elephants for regeneration.
Without these gentle giants, certain forests could struggle to renew themselves. In tropical rainforests of Central Africa and the savannas of East Africa, studies show that tree diversity and density decrease in areas where elephant populations have been reduced or eliminated.
The movement of seeds also helps prevent the overgrowth of dominant plant species, promoting ecological balance. By creating mosaic landscapes of shrubs, trees, and grasses, elephants help sustain diverse habitats that support everything from insects and birds to predators and prey.
In short, elephants are not just wanderers—they are active gardeners of their environment. Their digestive process supports plant reproduction on a massive scale, ensuring that Africa’s forests and grasslands continue to thrive long after each herd has passed through. Protecting elephants, therefore, means preserving the future of plant life and biodiversity in their regions.
6. Water Access – Creating Life In Dry Lands
In the harsh and unpredictable climates of Africa, water can be the difference between life and death for countless species. During dry seasons or drought conditions, rivers dry up, and traditional water holes disappear.
But elephants, with their incredible memory and unique physical capabilities, often come to the rescue of the ecosystem by locating and accessing hidden underground water sources.
Using their tusks, trunks, and feet, elephants dig deep into dry riverbeds to expose underground water. These makeshift wells often become life-saving watering holes for numerous other species.
Zebras, antelopes, birds, and even predators like lions rely on these sources during dry periods. What may look like an act of survival for elephants turns into a communal gift for the ecosystem.
This behaviour demonstrates the elephants’ ability to shape their environment in profound ways. Their strength, intelligence, and understanding of natural water cycles allow them to survive and assist other species in areas that would otherwise become uninhabitable.
In some parts of Namibia and Kenya, elephants have been observed returning year after year to the same riverbeds to dig wells, teaching younger generations through learned behaviour.
These elephant-dug water sources help stabilize populations of many species, especially in remote or arid areas where access to water is limited. Their actions often support biodiversity hotspots that would not exist without their intervention.
In addition to digging, elephants can widen and deepen existing waterholes by wallowing and bathing, creating long-lasting reservoirs.
This further emphasizes their role as keystone species—animals whose presence significantly shapes and maintains the structure of the ecosystem.
When we protect elephant populations, we are also protecting access to water for countless other species. Their contribution to survival during dry spells is a powerful reminder of how interconnected life is in Africa’s wild landscapes.
7. Climate Change – A Growing Threat To Elephant Habitats
One of the most significant long-term dangers to African elephants and their natural habitats is climate change. These changes are already visible in many parts of the continent, where rising temperatures, unpredictable rainfall, and prolonged droughts are becoming more frequent.
For elephants, whose survival depends on the availability of food and water across large distances, such environmental shifts can be devastating.
Elephants rely on seasonal migrations to track food and water sources. Traditionally, they followed well-established migratory routes based on historical rainfall and vegetation patterns.
However, as climate change disrupts these cycles, elephants are increasingly forced into unfamiliar or human-populated areas in search of resources.
This not only puts them at greater risk of conflict with people but also reduces their ability to maintain their health and herd structure.
Climate changes also affect plant growth. Droughts reduce the abundance of grasses and trees, while excessive rains may damage delicate plant ecosystems.
Both extremes limit the availability of the elephants’ primary food sources, putting additional stress on populations. Malnutrition at crucial developmental phases in young elephants can result in permanent health problems or even death.
In forest regions, increased temperatures and shifting humidity levels alter the composition of tree species. As certain plants disappear or migrate due to temperature change, elephants may struggle to adapt or face reduced nutritional diversity.
This diminishes their natural role as ecosystem engineers, affecting the entire chain of biodiversity. Climate change also compounds other threats like habitat loss and poaching.
As landscapes shrink or become less viable, competition intensifies among both humans and wildlife. Addressing climate change means not only reducing emissions but also investing in ecosystem resilience.
Protecting elephant migration corridors, restoring degraded landscapes, and preserving water access points are all essential.
Without such efforts, the magnificent African elephant may find itself without a place to roam, and the ecosystems it supports could collapse alongside it.

Conclusion
Protecting African elephant habitats means safeguarding some of the richest ecosystems on our planet. These majestic creatures are not just icons of the wild—they are vital to maintaining environmental balance.
As climate change, deforestation, and human encroachment threaten their homes, the time to act is now. By supporting conservation efforts and raising awareness, we can protect African elephants.
Together, we can help them thrive in their natural glory for generations to come.
I trust you enjoyed this article on Explore African Elephant Habitats And Their Natural Glory. Please stay tuned for more blog posts shortly. Take care!
JeannetteZ
>>> Please click here to read my all-inclusive article about Why Is Wildlife Important And How Can We Protect It <<<
Your Opinion Is Important To Me
Do you have thoughts, ideas, or questions? I would love to hear from you. Please leave your questions, experiences, and remarks about Explore African Elephant Habitats And Their Natural Glory in the comments below. You can also email me at Jeannette@Close-To-Nature.org.
Disclosure
This post may contain affiliate links. As an Amazon Associate and other affiliate programs, I earn from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you. Please read my full affiliate disclosure.
You might also enjoy these blog posts:
Best Natural Healing Therapies For Migraines
Best Tips For Keeping Horses Cool In Summer
Most Expensive Horses In The World