Understanding The Symptoms Of Stress
Stress affects us all at various points in life, manifesting in physical and mental symptoms. From headaches and muscle tension to anxiety and irritability, the signs of stress can be diverse and impactful.
Understanding these symptoms is crucial for managing stress effectively. By recognizing when stress affects our well-being, we can take steps to mitigate its impact and prioritize our mental health.
In this blog, we'll delve into the common symptoms of stress, explore how they manifest, and offer strategies for coping.
What Is Stress?
Stress is a normal reaction to demands or obstacles, whether psychological, emotional, or physical. The body reacts to a perceived threat or pressure, triggering physiological changes.
Symptoms of stress vary widely, encompassing both physical and emotional manifestations. Physical manifestations of stress often include headaches, muscle tension, fatigue, and sleep disruptions.
Emotionally, stress can manifest as irritability, anxiety, or feelings of being overwhelmed. Cognitive symptoms may involve difficulty concentrating, memory problems, or racing thoughts.
Behavioural changes, such as changes in appetite, withdrawal from social activities, or increased use of substances like alcohol or tobacco, can also indicate stress.
Symptoms Of Stress
Stress manifests in various ways, encompassing a spectrum of physical, emotional, cognitive, and behavioural symptoms.
Understanding the Symptoms of stress is essential for effectively identifying and managing stress. Let's explore them in more detail.
1. Headaches
Stress-induced headaches vary in intensity and presentation, with tension headaches and migraines being the most common Symptoms of Stress.
Due to elevated muscular tension, tension headaches frequently present as a dull aching or pressure in the neck, forehead, or temples.
At the same time, migraines cause intense, throbbing pain, typically on one side of the head, accompanied by nausea and sensitivity to light.
Stress triggers headaches by exacerbating muscle tension, altering blood flow in the brain, and heightening pain sensitivity.
Managing stress through relaxation techniques and seeking healthcare support is crucial for alleviating stress-related headaches and maintaining overall well-being.
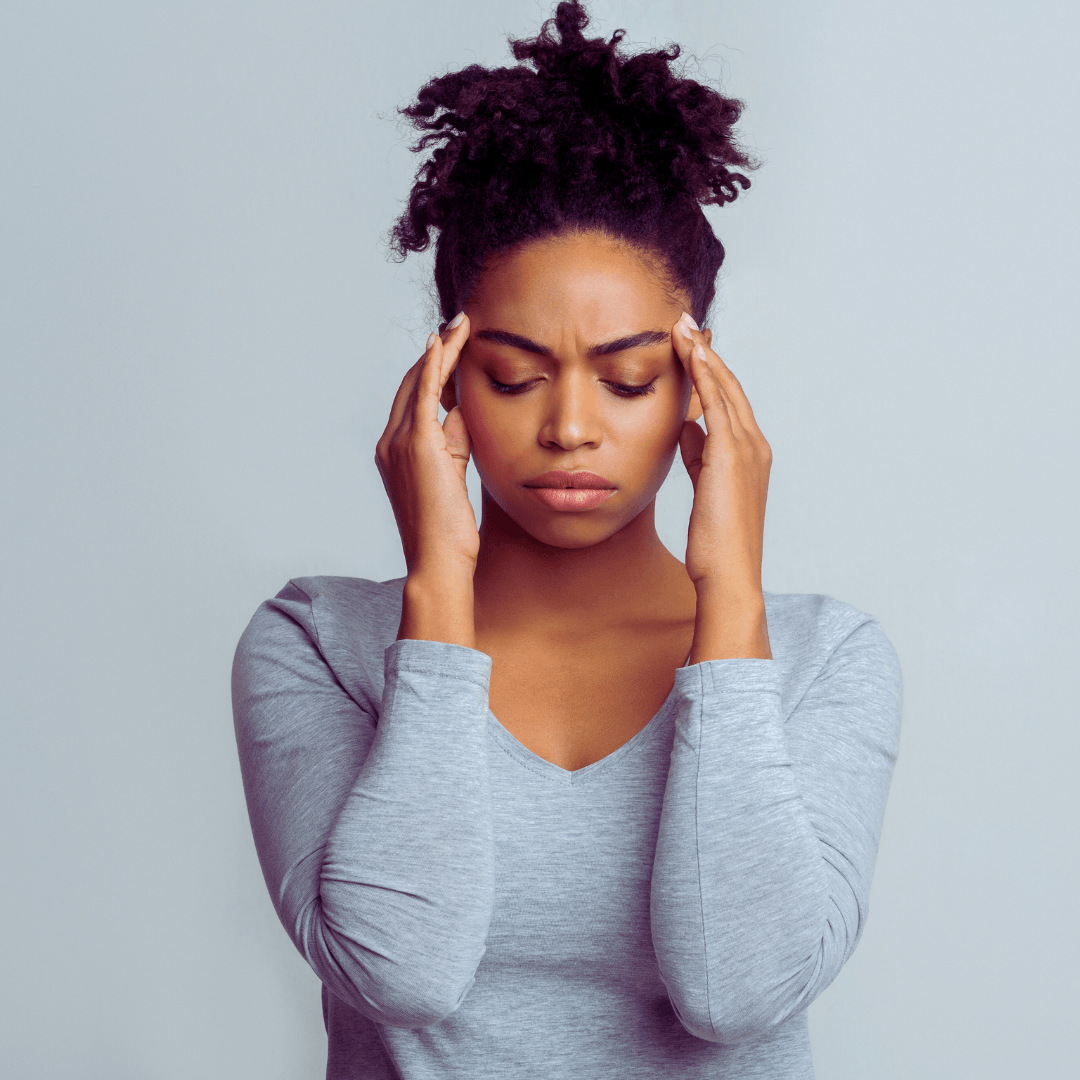

2. Muscle Tension
The fight-or-flight response is one of the physiological reactions triggered by stress. This reaction causes the neck, shoulders, and jaw muscles to tense up in preparation for action in response to perceived threats.
However, when stress becomes chronic, these muscles may remain tense for extended periods, leading to discomfort, stiffness, and even pain, which can worsen stress symptoms in a cyclical pattern.
Prolonged muscle tension can contribute to a range of other health issues, including headaches, jaw pain (temporomandibular joint disorder or TMJ), and back pain.
Therefore, managing stress through relaxation, massage, or exercise is essential for immediate relief and long-term health and well-being.
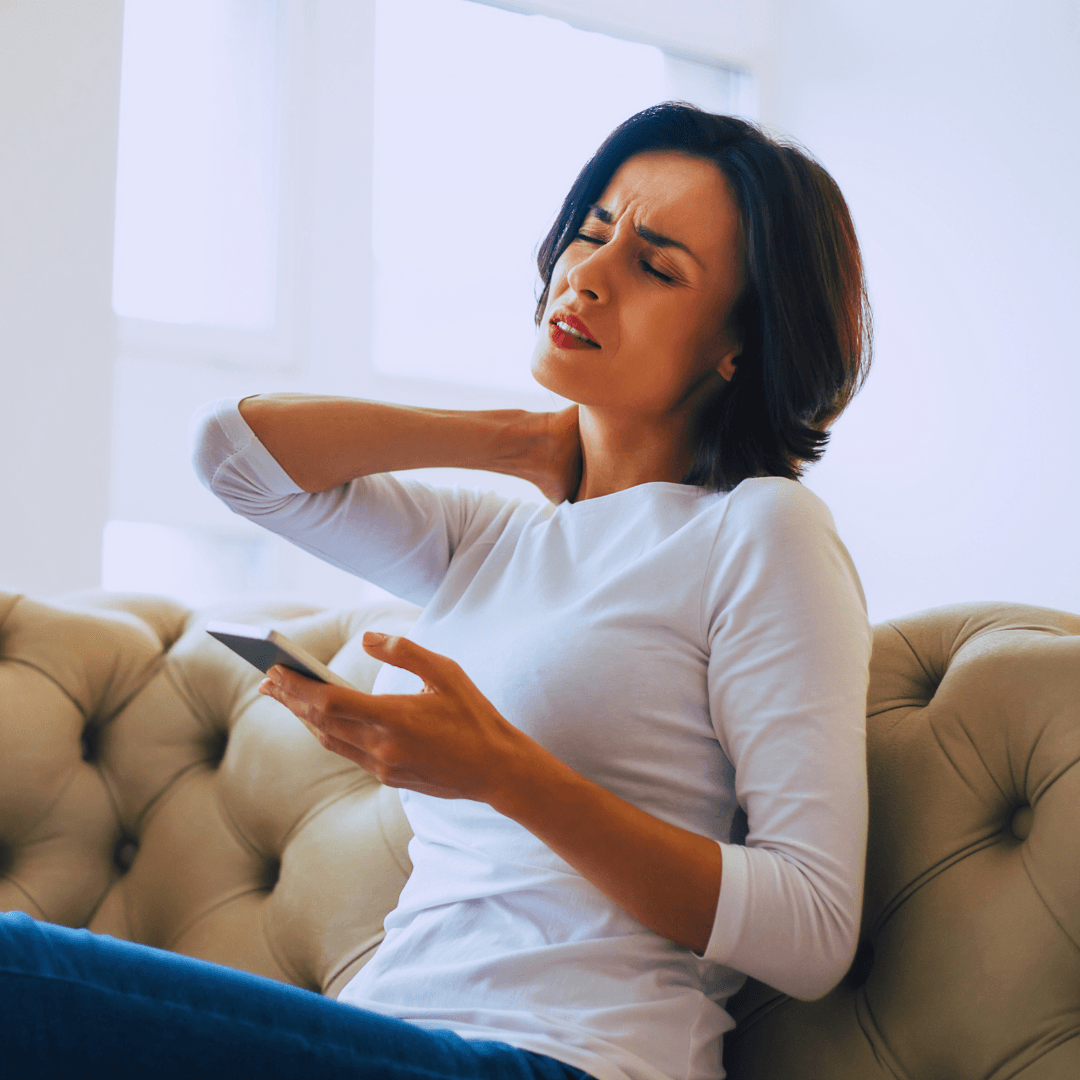

3. Fatigue
Chronic stress takes a toll on energy levels, often resulting in persistent fatigue, another symptom of Stress. The body's stress response, marked by the release of hormones like cortisol and adrenaline, wreaks havoc on sleep patterns and hinders restorative sleep.
This disruption makes it difficult to fall or stay asleep and reduces the quality of sleep. Moreover, the constant state of heightened alertness associated with stress can drain both physical and mental reserves, leaving individuals feeling weary and lethargic despite attempts to rest.
This persistent fatigue becomes a significant burden, impacting daily functioning and overall well-being. It highlights the importance of managing stress to preserve energy and vitality.
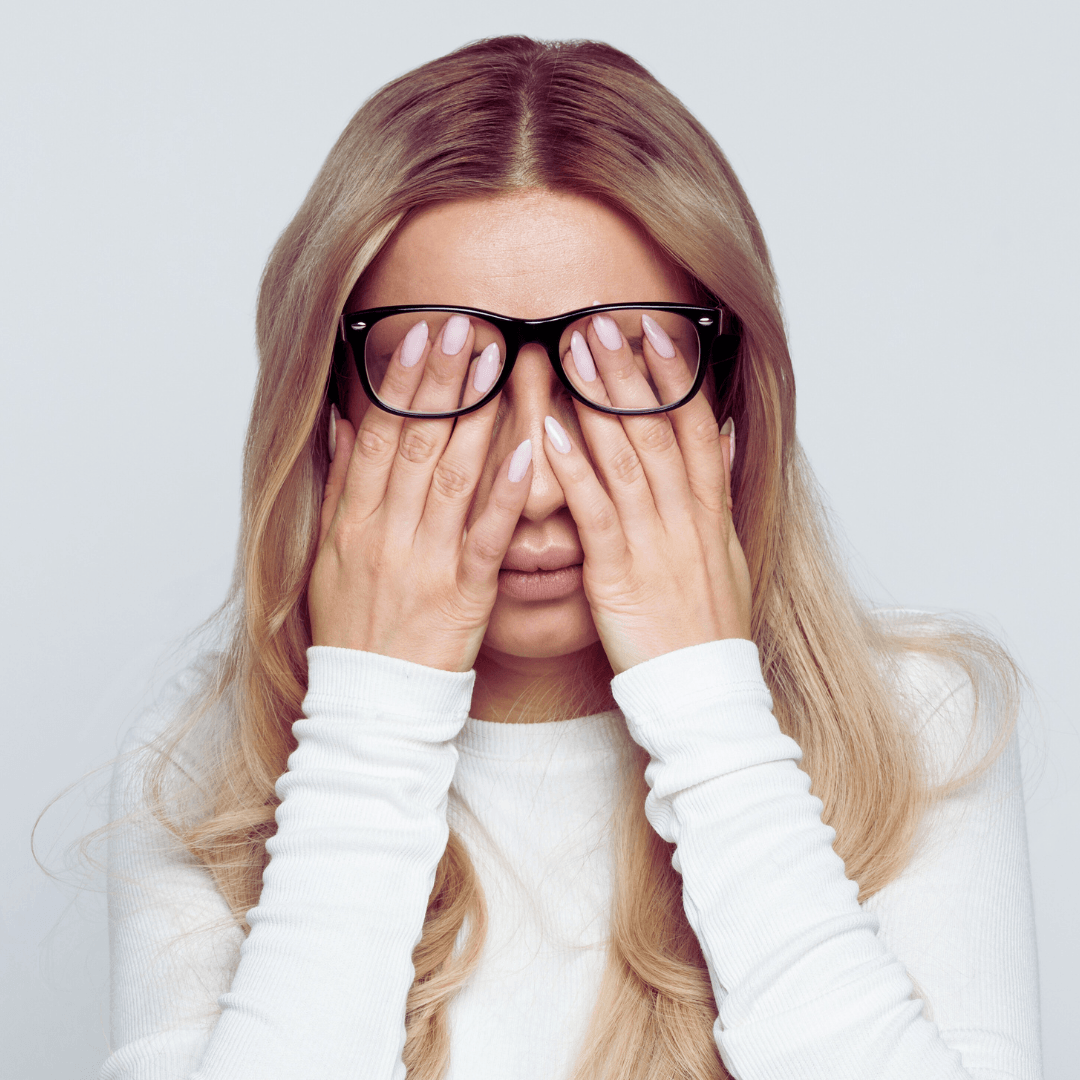

4. Sleep Disturbances
Stress frequently disrupts sleep patterns, causing difficulty falling asleep, staying asleep, and achieving restful sleep. Those under stress often struggle with racing thoughts and worries, which can keep them awake at night, tossing and turning.
Even if they manage to fall asleep, they may awaken repeatedly throughout the night, unable to maintain deep, uninterrupted rest. These sleep disturbances exacerbate daytime fatigue, leading to irritability and difficulty concentrating.
The cumulative effect of poor sleep due to stress can significantly impair daily functioning and overall well-being, highlighting the importance of addressing stress to restore healthy sleep habits.

5. Digestive Issues
Stress significantly impacts the digestive system, often manifesting as various gastrointestinal symptoms that are strong indicators.
These symptoms include stomach cramps, bloating, nausea, and changes in bowel habits, such as diarrhea or constipation.
The complex interactions between the brain and the gut are essential in this relationship. Stress disrupts the delicate balance of gut bacteria, triggers inflammation in the digestive tract, and affects the movement of food through the intestines.
Consequently, these disruptions can lead to digestive discomfort and other issues, underscoring the profound influence of stress on gastrointestinal health.
6. Changes In Appetite
Stress has a multifaceted impact on appetite, often leading to changes in eating habits and food preferences. For some individuals, stress triggers an uptick in appetite, accompanied by cravings for comforting, indulgent foods rich in sugar, fat, or carbohydrates.
However, this pattern can contribute to excessive food intake and subsequent weight gain, particularly if these eating behaviours persist.
Conversely, stress can suppress others' appetites, leading to a loss of interest in food or difficulty eating due to nausea or stomach discomfort.
These Symptoms of Stress stem from the body's heightened state of arousal during periods of stress, which can disrupt normal digestive function and suppress hunger cues.

7. Irritability And Mood Swings
Stress often manifests in emotional symptoms like irritability, mood swings, and heightened emotional reactivity. The continuous activation of the body's stress response keeps individuals on edge, making them easily agitated or prone to anger.
Even minor, manageable stressors can suddenly feel overwhelming, leading to emotional outbursts or conflicts in personal and professional relationships.
These heightened emotional Symptoms of Stress underscore the profound impact of stress on mental well-being and interpersonal dynamics.
Thus, it is crucial to implement effective stress-management strategies to cultivate emotional resilience and maintain healthy relationships, ultimately fostering a sense of balance and well-being amid life's challenges.

8. Anxiety
Stress and anxiety frequently intertwine, with stress acting as a catalyst for heightened anxious feelings or worsening existing anxiety disorders.
Anxiety symptoms, such as nervousness and restlessness, and physical manifestations, like trembling and palpitations, are often exacerbated by stress.
Prolonged stress can sustain a state of heightened anxiety, potentially leading to conditions like generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) if left unchecked.
This complex relationship underscores the importance of proactive stress management to prevent its escalation into more severe anxiety-related conditions.
By effectively addressing stress, individuals can cultivate emotional resilience and promote overall mental well-being, enhancing their ability to cope with life's challenges.

9. Depression
Prolonged or intense stress can significantly contribute to the development or exacerbation of depression.
Chronic stress disrupts the delicate balance of neurotransmitters in the brain, particularly serotonin and dopamine, which play pivotal roles in regulating mood—a fundamental aspect stress affects.
This disruption often precipitates enduring feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and despair, hallmark symptoms of depression. The intricate interplay between anxiety and depression underscores the profound impact of stressors on mental health.
Emotional well-being in the face of adversity is, therefore, crucial, and stress management becomes essential to reducing the likelihood of developing or exacerbating depressive symptoms.
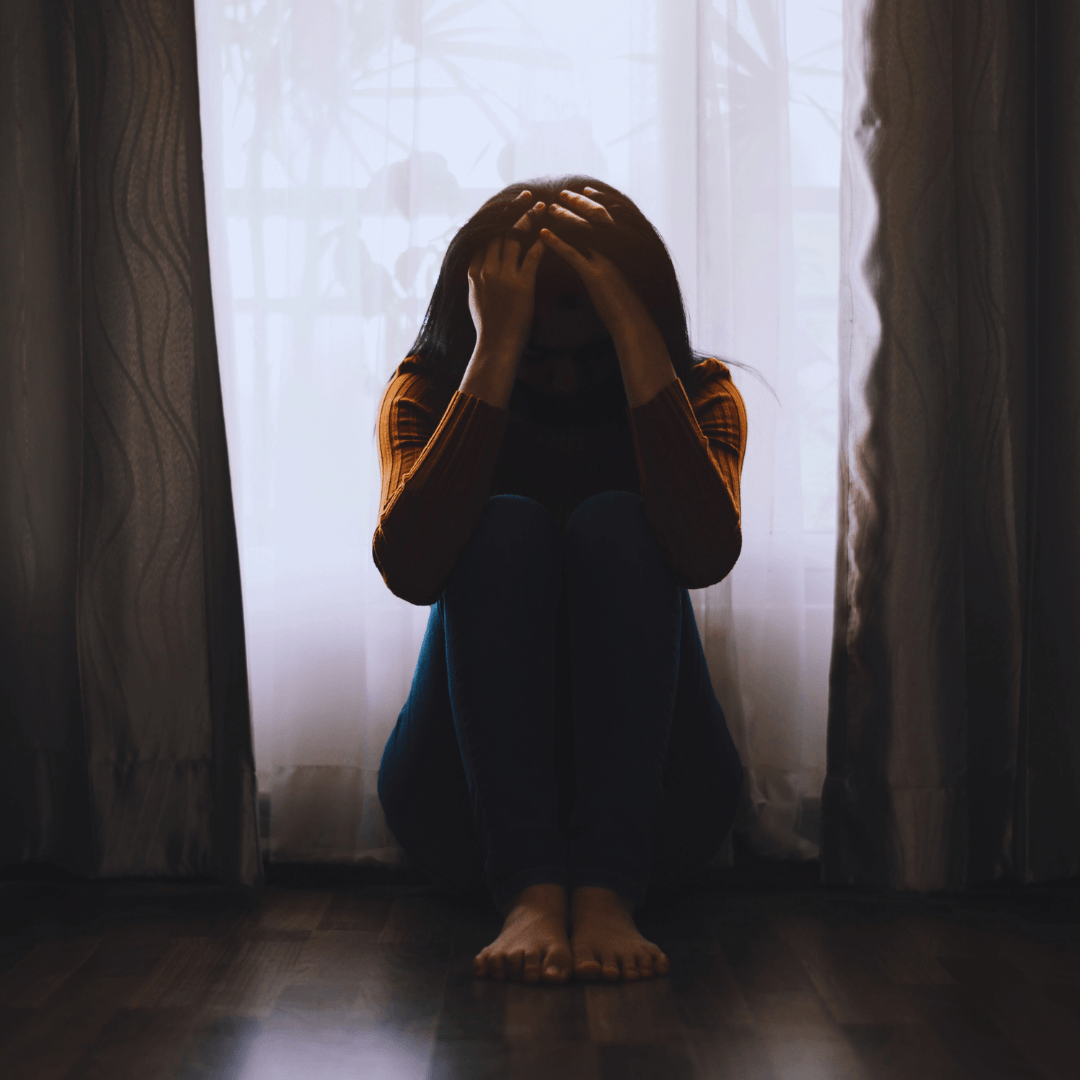

10. Cognitive Impairment
Stress significantly burdens cognitive function, disrupting memory, concentration, and decision-making processes, a critical Symptom of Stress.
Individuals grappling with stress often struggle to focus on tasks, retain crucial information, or make rational choices.
These cognitive challenges extend beyond mere inconvenience; they can profoundly impact work, academic pursuits, and daily responsibilities, resulting in diminished productivity and performance.
Moreover, untreated stress exacerbates these cognitive impairments, perpetuating a cycle of decreased cognitive function.
Therefore, prioritizing effective stress management strategies is imperative to mitigate immediate cognitive strain, safeguard long-term cognitive health and optimize performance across various facets of life. Investing in stress management is an investment in cognitive resilience and overall well-being.
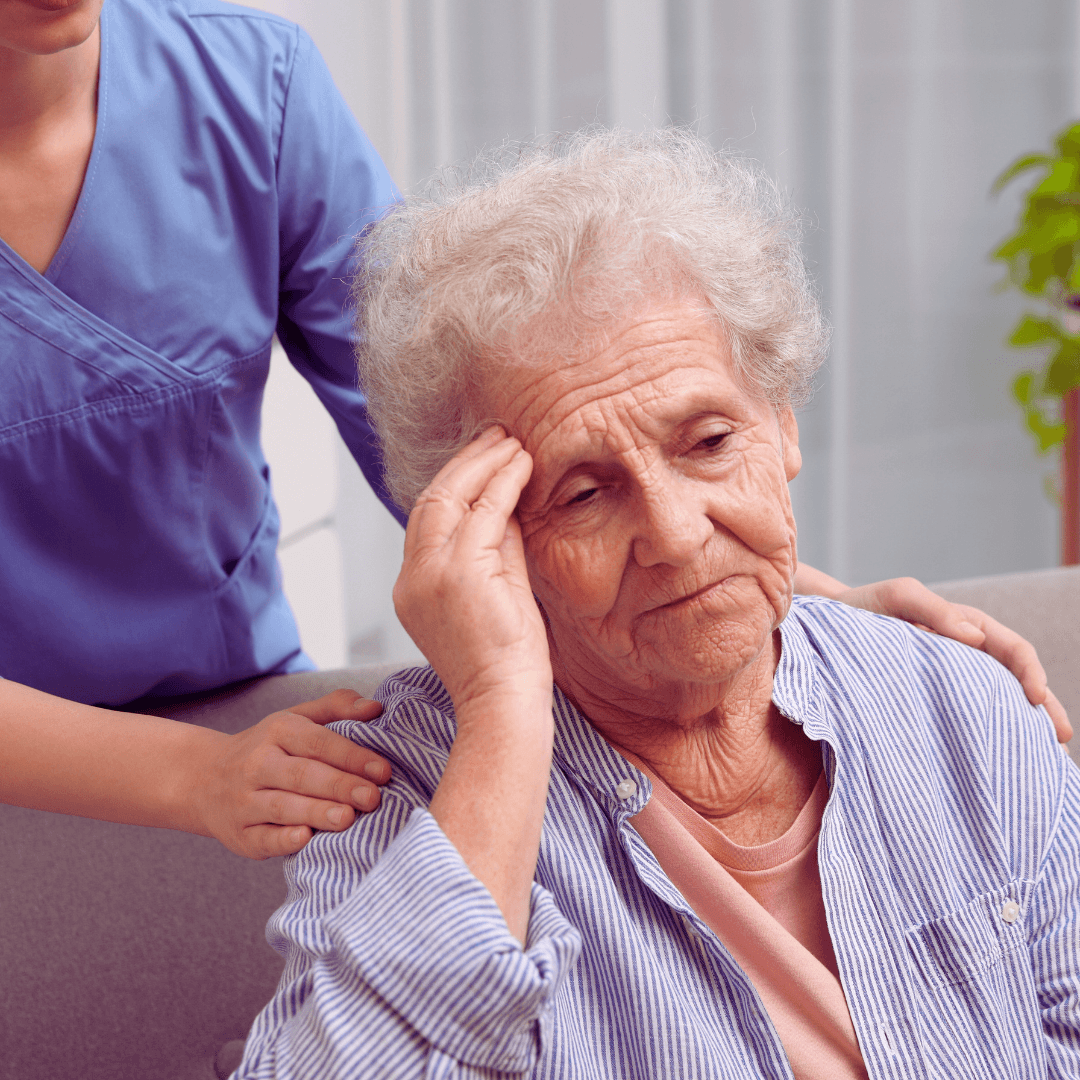

11. Social Withdrawal
When stress reaches overwhelming levels, individuals often retreat from social engagements, distancing themselves from friends, family, and support systems.
This withdrawal from social interactions can intensify feelings of loneliness, compounding stress and perpetuating a cycle of isolation and distress.
The absence of social support exacerbates the burden of stress, making it even more challenging to cope with life's demands.
Moreover, prolonged isolation can have detrimental effects on mental and emotional well-being, further amplifying the negative impact of stress.
Breaking the cycle of isolation requires realizing the value of social connections in managing stress symptoms, cultivating meaningful relationships, and asking for help from loved ones.

Management Of Stress In Psychology
Life will inevitably include stress. Stress can motivate, but too much or long-term stress can harm one's physical and emotional well-being.
In psychology, understanding stress management is crucial for promoting well-being and resilience.
This blog post explores various psychological strategies for managing stress effectively and addresses key symptoms of stress along the way.
Create a Profitable Holistic Business That Transforms Lives
🌿 Discover inspiring holistic business ideas that blend nature, wellness, and purpose.
Learn how passionate nature lovers are building income streams while helping others live more balanced, mindful lives.
Read Profitable Holistic Business Ideas That Transform Lives
1. Identifying Stress Triggers
Recognizing stress triggers serves as a cornerstone of effective stress management. Individuals can tailor their coping mechanisms by identifying situations that elicit stress responses. Typical stressors include work deadlines, financial worries, relationship conflicts, and major life transitions.
Understanding these triggers empowers individuals to take proactive measures to mitigate their effects and cultivate resilience in the face of future stressors. This self-awareness forms the foundation for a proactive approach to stress management.
2. Stress Symptom Awareness
Awareness of the diverse physical, emotional, and cognitive symptoms of stress is crucial for effective management. Stress levels are mostly indicated by physical symptoms such as headaches, tense muscles, exhaustion, and irregular sleep patterns.
Emotional symptoms like irritability, anxiety, and mood swings also signal heightened stress. Additionally, cognitive symptoms such as difficulty concentrating and memory issues underscore the profound impact of stress on mental function.
Recognizing these symptoms enables individuals to implement targeted interventions to alleviate stress and promote overall well-being.
3. Cognitive-Behavioural Techniques
In psychology, cognitive-behavioural techniques can be effective for managing stress by addressing maladaptive thought patterns and behaviours.
Cognitive restructuring, a core component, involves recognizing and disputing negative thought patterns that contribute to stress.
By substituting them with more realistic and adaptive perspectives, individuals can reframe their outlook and responses to stressors.
This approach empowers individuals to cultivate resilience and cope more effectively with life's challenges, fostering psychological well-being.
4. Mindfulness And Meditation
Mindfulness-based interventions have surged in popularity for stress management because they foster present-moment awareness and acceptance.
These practices involve observing thoughts, emotions, and bodily sensations without judgment, promoting a sense of inner calm.
Techniques like mindfulness meditation and loving-kindness meditation cultivate resilience against stress by reducing reactivity and enhancing overall well-being.
By incorporating mindfulness into daily life, people can develop powerful coping mechanisms that help them handle pressures more skillfully and resiliently, promoting a long-lasting sense of harmony and tranquillity.
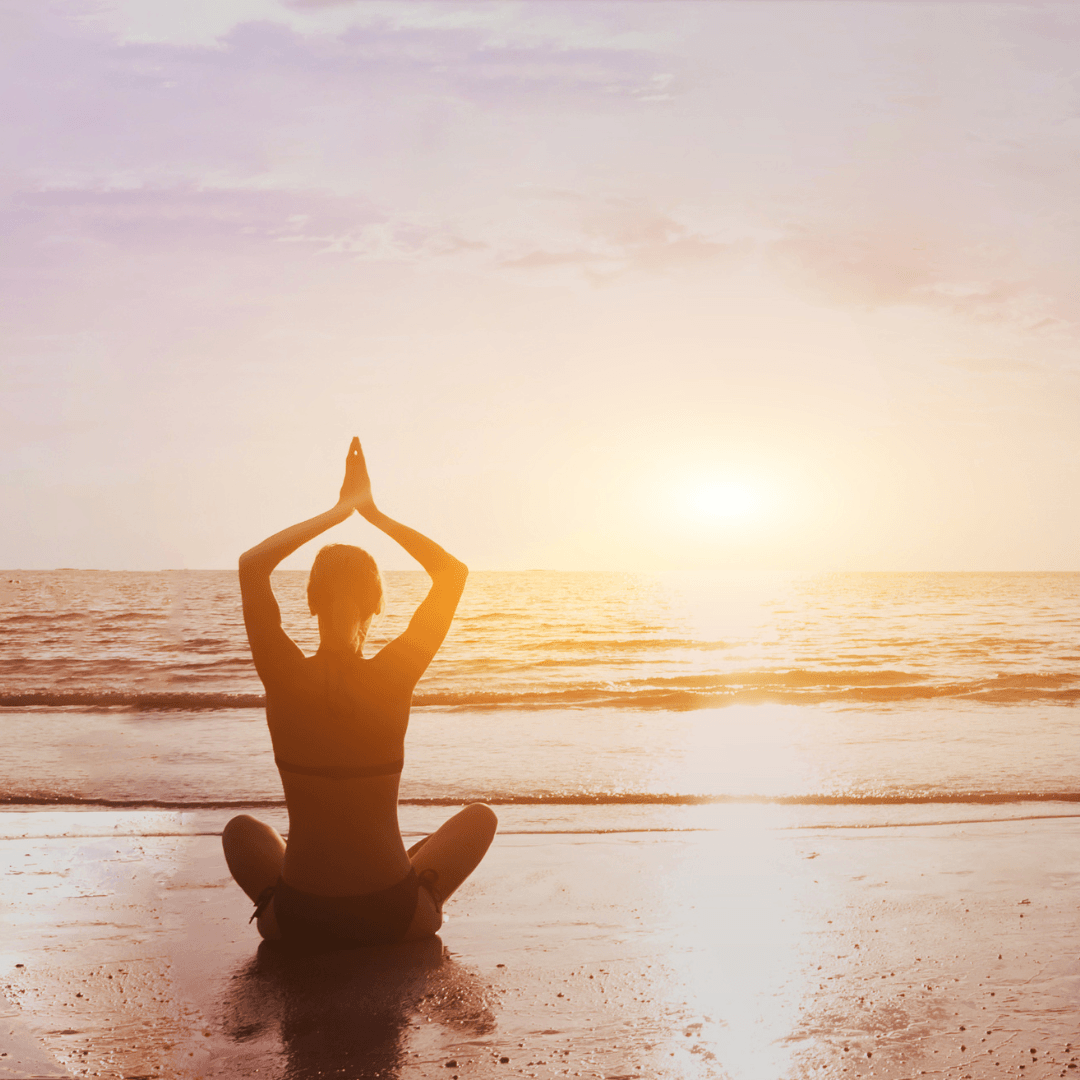

5. Stress Reduction Through Physical Activity
Engaging in physical activity can effectively mitigate stress and enhance mental well-being.
Exercise causes the body to release endorphins, organic substances that improve mood and reduce pain while promoting calmness and well-being.
Frequent exercise also lowers muscle tension, enhances self-esteem, and improves sleep quality, all of which assist in lowering stress. Exercises like yoga, tai chi, walking, and running are very helpful for stress relief.
6. Social Support And Connection
Social support plays a crucial role in buffering the effects of stress and promoting resilience, especially when individuals experience symptoms of anxiety.
Spending time with supportive friends, family members, or peers can provide emotional validation, practical assistance, and a sense of belonging, alleviating feelings of loneliness and isolation often associated with stress.
Engaging with others provides chances to share stress-related experiences, gain perspective, and receive helpful feedback, all of which aid in effective stress management.
7. Healthy Lifestyle Choices
Embracing a healthy lifestyle is paramount for stress management and holistic well-being. This encompasses ensuring sufficient sleep, adhering to a nutritious diet, moderating caffeine and alcohol intake, and refraining from tobacco use.
Additionally, participating in activities that evoke joy and fulfillment, like hobbies, creative endeavours, and outdoor pursuits, can effectively alleviate stress and fortify resilience.
By prioritizing these lifestyle factors, individuals can cultivate a robust foundation for managing stress and nurturing a balanced, fulfilling life.
8. Time Management And Prioritization
Mastering time management is pivotal for reducing stress and enhancing productivity. By breaking tasks into manageable steps, setting achievable goals, and prioritizing activities based on significance and urgency, individuals regain control and diminish overwhelm.
Techniques like the Pomodoro Technique, time blocking, and task prioritization further streamline efficiency, alleviating stress induced by procrastination and time constraints.
Cultivating effective time management skills empowers individuals to navigate their responsibilities with greater ease and composure, fostering a more balanced and productive lifestyle.
9. Seeking Professional Help
Managing stress may require professional intervention, especially when symptoms become overwhelming or persistent.
Cognitive-behavioural therapy (CBT) is a prevalent method for tackling stress-related disorders, equipping individuals with practical tools and strategies for coping.
Under the supervision of a psychologist or mental health specialist, people can investigate underlying stressors, confront unfavourable thought patterns, and create more constructive coping strategies.
Getting help from a specialist helps people manage stress more effectively, building resilience and improving overall well-being.
FAQs
Q1: How Is A Stress Test Done For Pregnancy?
During a pregnancy stress test, fetal heart rate and maternal contractions are monitored in response to mild stressors like physical activity or uterine stimulation.
This non-invasive procedure, often conducted via electronic fetal monitoring, offers insights into the baby's well-being and the uterus's ability to manage stress.
By evaluating these physiological responses, healthcare providers can better manage high-risk pregnancies and ensure the safety of both mother and child. The stress test is a valuable tool in prenatal care, facilitating early detection and intervention when necessary.
Q2: How Is Stress Related To Depression?
Stress and depression share a complex relationship. While stress is a common trigger for depressive episodes, chronic or overwhelming stress can also exacerbate existing depression.
Persistent activation of the body's stress response system can disrupt the balance of neurotransmitters, altering how the body regulates mood.
Prolonged stress can also exacerbate depressive symptoms such as weariness, worthlessness, and hopelessness.
Conversely, individuals with depression may experience heightened sensitivity to stressors, making them more susceptible to stress-related symptoms.
Overall, managing stress effectively is crucial in both preventing and managing depression.
Q3: How Is Stress Calculated?
Stress isn't typically expressed as a numerical value. Instead, it's assessed qualitatively through various methods such as self-report questionnaires, interviews, or physiological measures.
In research or clinical settings, stress levels are often assessed using factors such as perceived stressors, coping mechanisms, and physiological responses, including heart rate variability and cortisol levels.
These assessments provide insight into an individual's subjective experience of stress and its potential impact on their health and well-being.
Q4: How Long Does Stress Last?
The duration of stress varies greatly depending on individual circumstances and the nature of the stressor. Acute stress, triggered by a specific event, typically lasts for a short duration, ranging from minutes to hours.
However, chronic stress, stemming from ongoing or persistent stressors such as work pressures, financial difficulties, or relationship issues, can endure for weeks, months, or even years if left unaddressed.
Effective stress management strategies, support systems, and coping mechanisms can mitigate the impact of stress and promote resilience, potentially reducing its duration.
Q5: When Should I Talk To A Doctor About Stress?
If you're dealing with chronic or severe stress that affects your everyday functioning, relationships, or general well-being, it's best to consult a healthcare provider.
Additionally, if you notice physical symptoms such as frequent headaches, digestive issues, or sleep disturbances, or if you're struggling to cope with stress despite attempting self-help strategies, seeking medical guidance is important.
A doctor can provide support, offer coping strategies, and, if necessary, refer you to a mental health specialist for further evaluation and treatment. Don't hesitate to seek help when stress becomes difficult to manage on your own.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the symptoms of stress is crucial for recognizing its impact on physical, emotional, and cognitive well-being.
By identifying symptoms such as headaches, muscle tension, fatigue, sleep disturbances, irritability, and changes in appetite, individuals can recognize stress and take proactive steps to address it.
Understanding these signs enables prompt action and effective stress-reduction techniques to prevent stress-related problems from worsening and to enhance resilience and overall health.
They addressed stress symptoms through lifestyle modifications, relaxation techniques, social support, or professional intervention, which empowers individuals to navigate life's challenges more effectively and enhances their quality of life.
I trust you enjoyed this article on Understanding The Symptoms Of Stress. Please stay tuned for more inspiring guides, helpful tips, and ideas to help you live closer to nature every day.
Take care!
— JeannetteZ🌿
💬 Your Opinion Is Important To Me
Do you have thoughts, ideas, or questions? I’d love to hear from you. Please leave your comments below or email me directly at Jeannette@Close-To-Nature.org.
📚 More Nature-Inspired Reads
Explore more ways to connect with nature, nurture your pets, and live in harmony with the world around you 🌿