Types Of Hydroponic Systems
There are various types of hydroponic systems, each offering unique benefits for the efficient, soil-free cultivation of crops. These systems provide efficient methods for cultivating crops with less water, space, and time.
From deep-water culture to aeroponics, each hydroponic system has its own approach, providing sustainable and innovative solutions for urban farming, gardening, and commercial agriculture.
Introducing The Types Of Hydroponic Systems
1. Wick System
The wick system is ideal for beginners, as it’s simple and requires minimal maintenance. A wick, often composed of absorbent materials like cotton or nylon, moves nutritional solution from a reservoir to the plant's roots.
Because it doesn't require electricity or sophisticated pumps, it's a low-tech, cost-effective option for small-scale hydroponic gardening.
How The Wick System Works
The wick in a wick system is a conduit transporting the nutrient solution from a reservoir to the growing medium. The plants absorb the solution through their roots, guaranteeing they get vital nutrients.
The system's passive design eliminates the need for electricity, pumps, or timers, making it simple to set up and low-maintenance—ideal for novices.
Advantages Of The Wick System
Low Cost And Easy Setup
The wick system is affordable and requires minimal equipment, making it ideal for beginners. The simple design ensures easy assembly and low ongoing maintenance costs.
No Need For Pumps Or Timers
Since the system works passively, there’s no need for electricity, pumps, or timers, reducing complexity and making it more energy-efficient and budget-friendly.
Ideal For Tiny Plants Such As Lettuce And Herbs
The wick system excels at growing smaller plants that don’t require intense nutrient uptake. It’s perfect for herbs, lettuce, and other small leafy greens.
Disadvantages Of The Wick System
Limited Nutrient Delivery
The wick system delivers nutrients more slowly than other hydroponic methods, potentially limiting plant growth and yield due to a slower nutrient absorption process.
Not Suitable For More Extensive Or Fast-Growing Plants
Larger or faster-growing plants need more nutrients and water than the wick system can provide, making it unsuitable for plants like tomatoes or cucumbers.
Overwatering Can Occur In Some Media
Some growing media may retain too much moisture, leading to overwatering.
The Wick System Is Best For
The wick system, ideal for beginners and small spaces, offers a simple, low-cost setup perfect for indoor gardening and hobbyists seeking easy maintenance for small plants.

2. Deep Water Culture (DWC)
Deep Water Culture (DWC) is a highly efficient hydroponic system where plants are suspended in nutrient-rich water. Their roots are submerged in the solution, ensuring constant access to water and nutrients.
Air pumps and stones provide oxygen to the roots, keeping them healthy. This system promotes rapid plant growth due to its steady nutrient supply and oxygenation.
How The Deep Water Culture (DWC) Works
In DWC, plants are placed in net pots, allowing their roots to hang directly in a nutrient-rich water solution. An air pump connected to air stones oxygenates the water, ensuring the roots receive sufficient oxygen.
The system provides continuous access to nutrients and water, ensuring plants grow rapidly and healthily. This setup requires regular monitoring to maintain water levels and nutrient balance.
Advantages Of The Deep Water Culture (DWC)
Continuous Nutrient Supply To Roots
DWC ensures a constant flow of nutrients to the roots, promoting healthy growth. Plants have easy access to water and nutrients, which supports rapid and consistent development.
Promotes Rapid Plant Growth
The system’s nutrient-rich, oxygenated solution allows plants to grow faster. The constant supply of nutrients and oxygen encourages robust root systems and quick plant development, which is ideal for high-yielding crops.
Minimal Maintenance
Once set up, DWC requires minimal maintenance. Regular monitoring of nutrient levels and pH is needed, but the system is relatively low-maintenance compared to other hydroponic setups, saving time and effort.
Disadvantages Of The Deep Water Culture (DWC)
Root Rot
If the water lacks sufficient oxygen, roots can suffocate, leading to rot. Proper oxygenation is essential to maintaining plant health and avoiding disease.
Requires Electricity For Pumps
DWC systems rely on air and water pumps to oxygenate the solution and circulate nutrients. A power outage or pump failure can negatively affect plant health and growth.
Not Suitable For All Plants
DWC works best for lightweight, fast-growing plants. Larger or more complex plants may not thrive in this system, requiring more space or different growing conditions.
The Deep Water Culture (DWC) Is Best For
DWC suits leafy greens and herbs like lettuce, spinach, and basil. It offers constant oxygen and nutrients for rapid growth, making it ideal for lightweight plants needing efficient nutrient delivery.
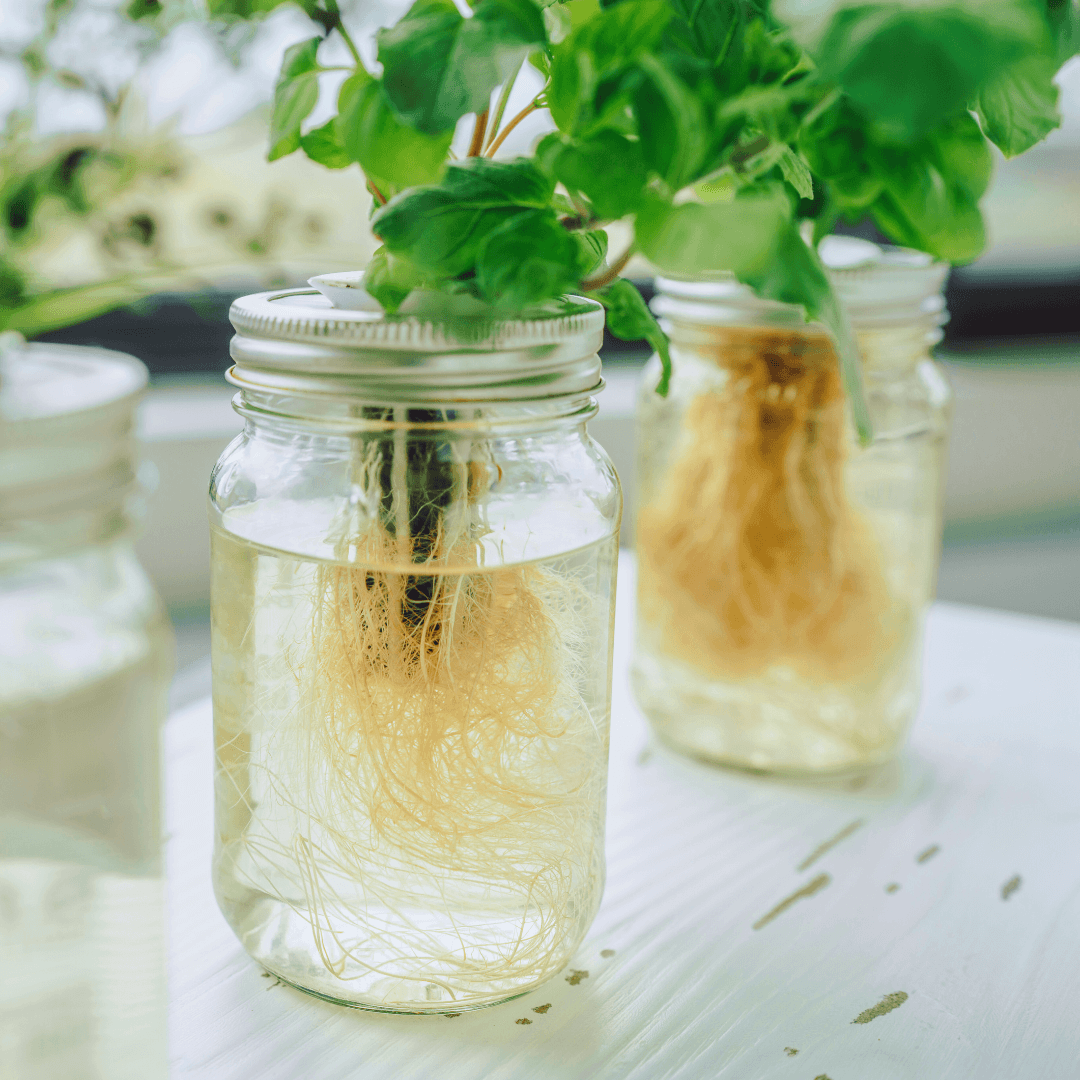

3. Nutrient Film Technique (NFT)
Commercial growers widely use the Nutrient Film Technique (NFT) for its scalability and efficiency. Plants are placed in channels that slope downward, allowing a thin layer of nutritional solution to run over the roots continuously.
This guarantees a steady flow of nutrients, oxygen, and water. The NFT system is perfect for high-density farming because it produces nutritious crops in a small space.
How The Nutrient Film Technique (NFT) Works
In NFT, plants are placed in shallow channels, allowing a thin film of nutrient solution to flow over their roots. The constant circulation of the solution ensures the roots stay moist and have access to both nutrients and oxygen.
The design allows excess solution to be collected and reused, making this system water-efficient. Proper oxygenation is crucial for preventing root diseases and promoting plant growth.
Advantages Of The Nutrient Film Technique (NFT)
Conserve Water And Nutrients
NFT recycles the nutrient solution, making it highly water-efficient. This reduces waste and ensures that plants receive just the right amount of nutrients, promoting sustainability in farming.
Highly Efficient For Fast-Growing Crops
The constant flow of nutrients and oxygen in the NFT system encourages rapid growth, making it perfect for fast-growing crops like leafy greens and herbs, which thrive in this environment.
Compact And Space-Saving
NFT’s design allows for high-density planting, using minimal space while maximizing crop yield. This makes it ideal for urban farming or commercial growers with limited space for large-scale crops.
Disadvantages Of The Nutrient Film Technique (NFT)
Requires Precise Setup And Monitoring
NFT systems need careful setup to ensure the proper slope, nutrient balance, and flow rate. Regular monitoring is essential to prevent clogs, imbalances, or inadequate oxygenation.
Pump Failure Can Lead To Rapid Crop Loss
If the pump fails, the continuous flow of nutrient solution is halted, which can quickly damage plants. Without the solution, plants’ roots dry out, causing rapid wilting or death.
Limited Support For Larger Plants
NFT is better suited for small, shallow-rooted plants. Larger plants or those with deeper root systems may not thrive due to limited root support and space for growth within the shallow channels.
The Nutrient Film Technique (NFT) Is Best For
NFT is ideal for small plants like lettuce and spinach, offering constant nutrients and oxygen for rapid growth but unsuitable for larger plants needing more root space.

4. Ebb and Flow (Flood and Drain) System
The ebb and flow system is known for its versatility and suitability for various plants. This method involves placing plants in a tray filled with a growing medium, like perlite or expanded clay.
The tray is periodically flooded with a nutrient solution, draining back into the reservoir. This cycle is automated using a timer, ensuring the plants receive nutrients and water regularly.
How The Ebb and Flow (Flood and Drain) System Works
In the ebb and flow system, nutrient solution floods the plant tray, soaking the growing medium and allowing the plant roots to absorb nutrients.
Once the flooding cycle ends, the solution drains back into the reservoir. This periodic flooding and draining cycle ensures the roots get the necessary nutrients while preventing waterlogging by allowing the medium to dry between cycles. It helps promote healthy root development.
Advantages Of The Ebb and Flow (Flood and Drain) System
Adaptable To Different Plant Sizes
The ebb and flow system can support small and large plants by adjusting the tray size and nutrient flow, making it suitable for various plant types.
Nutrients And Oxygen Are Delivered In Cycles, Promoting Root Health
The periodic flooding ensures that plants receive essential nutrients and oxygen regularly. This cycle lowers the danger of root rot by promoting healthy root development and avoiding water stagnation.
Relatively Low Maintenance
The ebb and flow system requires minimal daily intervention. As long as the timer and pumps are set up correctly, the system operates efficiently with little upkeep, making it convenient for growers.
Disadvantages Of The Ebb and Flow (Flood and Drain) System
Timer Or Pump Failure Can Harm Plants
If the timer or pump fails, the flooding and draining cycle is disrupted, potentially leading to nutrient deficiencies or overwatering, which can damage the plants or cause them to wilt.
Requires Careful Balancing Of Flood And Drain Cycles
The timing and draining cycle must be precisely managed to ensure plants don’t experience overwatering or underwatering. Incorrect cycles can affect plant health and growth.
The Growing Medium Can Be Heavy
Some growing media in the ebb and flow system, such as clay pellets or rock wool, can be heavy. This adds to the system's overall weight, making it more challenging to handle or move.
The Ebb and Flow (Flood and Drain) System Is Best For
The ebb-and-flow system suits fruits, vegetables, and flowering plants needing drying periods, promotes solid roots, and prevents root rot. It is ideal for crops like tomatoes, cucumbers, peppers, and flowers.
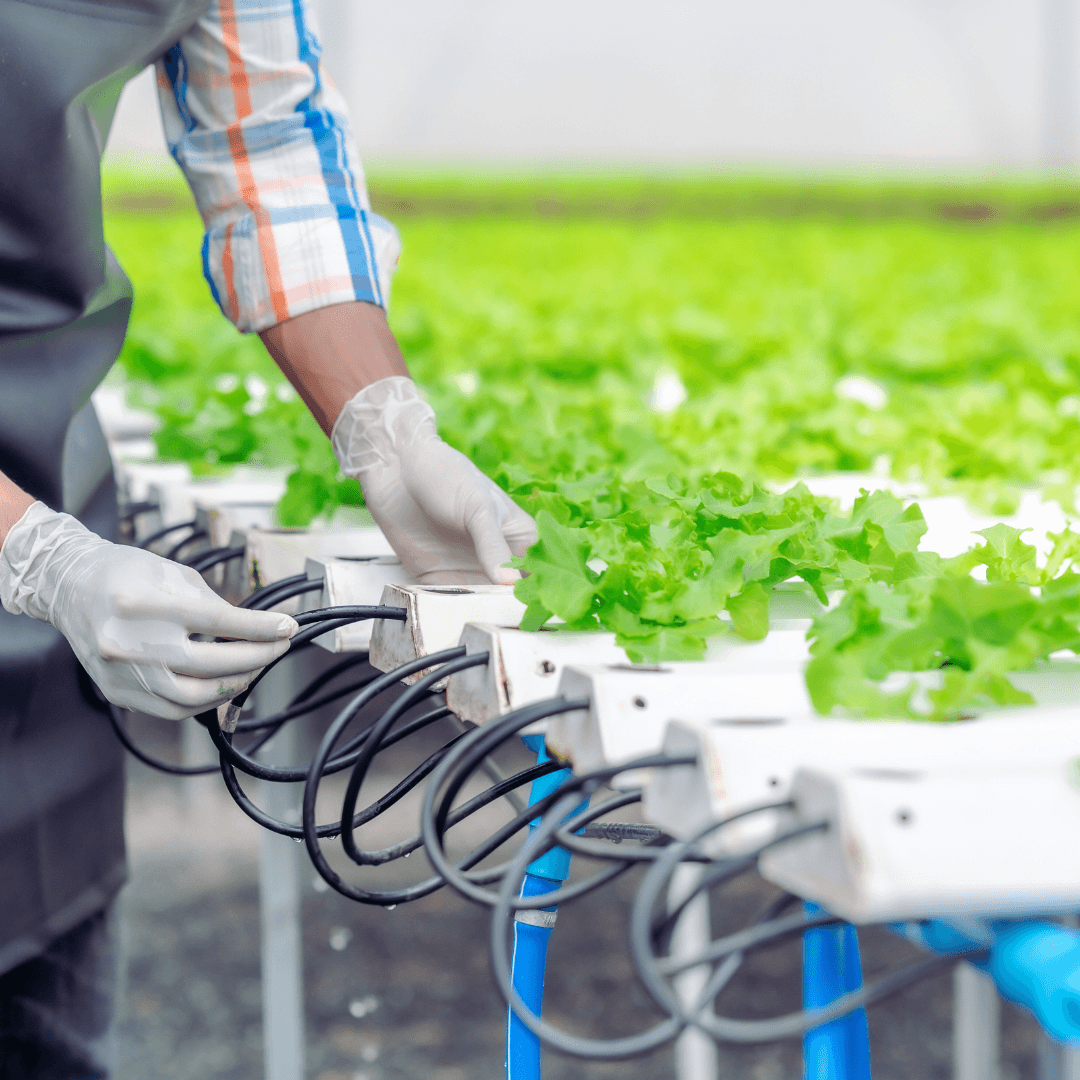

5. Drip System
Due to its efficiency and precision, the drip system is widely used in hydroponics, particularly in large-scale commercial operations.
It uses a tube network that delivers nutrient solution directly to each plant’s base through emitters. This technique makes the system vital for using nutrients in large plant varieties and scalable setups.
How The Drip System Works
The drip system is a hydroponic system that pumps nutrient solution through tubes to emitters, delivering controlled nutrients to plant roots for optimal growth.
These emitters regulate the amount of solution delivered to the plant roots. After the solution is absorbed, excess liquid drains back into the reservoir, where it is recirculated or disposed of. This system allows for controlled nutrient distribution, promoting healthy plant growth.
Advantages Of The Drip System
Precise Control Of Nutrient Delivery
The drip system accurately controls each plant's nutrient flow, ensuring optimal growth. This precision minimizes waste and promotes efficient nutrient uptake by plant roots.
Works For Various Plants
The drip system is a versatile crop option. It is one of the hydroponic systems that work for a diverse range of plants, from tiny herbs to larger fruiting plants.
Scalable And Customizable
The system can be readily extended or changed to accommodate additional plants or particular plant requirements. This scalability makes it ideal for both small and large commercial hydroponic operations.
Disadvantages Of The Drip System
Emitters Can Clog Easily
Nutrient solutions can contain particles that cause emitters to clog over time. Regular maintenance is required to clean or replace emitters to ensure consistent nutrient delivery.
Higher Initial Cost Compared To Simpler Systems
Drip systems require more equipment, such as pumps, emitters, and tubing, making the initial setup cost higher than simpler hydroponic systems like the Wick or Kratky methods.
May Require Regular Monitoring
While efficient, the drip system requires consistent monitoring to ensure proper nutrient levels, water pressure, and emitter function. Neglecting this can lead to uneven plant growth or system malfunctions.
The Drip System Is Best For
The drip system is suitable for large plants and commercial setups. It delivers precise nutrients to high-demand crops such as tomatoes and peppers, ensuring scalability, efficiency, and customization to optimize growth.
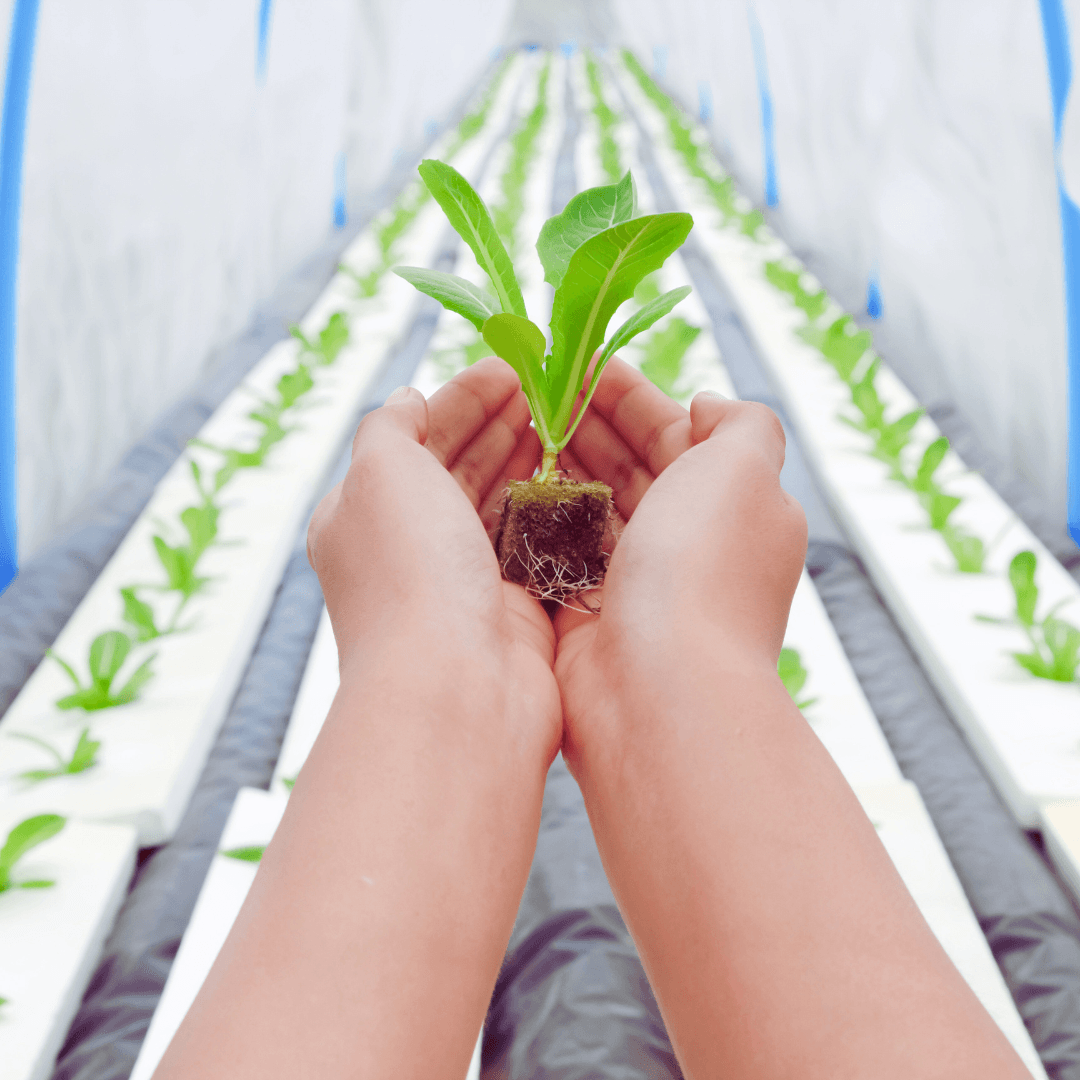

6. Aeroponics
Aeroponics is the most advanced hydroponic method, often used for research and space missions due to its precision and efficiency. In this system, plants are suspended in the air with their roots exposed.
This method provides maximum oxygenation and nutrient absorption, producing rapid, healthy plant growth with minimal water usage.
How Aeroponics Works
Aeroponics is a hydroponic system in which plants' roots are misted with a nutrient solution, promoting rapid growth and efficient nutrient absorption.
A misting system periodically sprays the roots with a nutrient solution, ensuring they stay moist and receive nutrients and oxygen.
The mist allows quick absorption and promotes faster growth than traditional soil-based methods. Excess solution is typically recirculated, making the system highly efficient.
Advantages Of Aeroponics
Maximizes Oxygen Exposure To Roots
Aeroponics delivers nutrients through a fine mist, providing roots with excellent oxygen exposure. This promotes faster root growth and overall plant health, enhancing nutrient uptake.
Uses Minimal Water And Nutrients
Aeroponics is highly water-efficient, as only a tiny mist delivers nutrients. This drastically reduces water and nutrient consumption compared to traditional farming methods.
Fast Growth Rates
With optimal oxygen and nutrient delivery, plants in aeroponics grow faster than in other hydroponic systems. The enhanced root development leads to accelerated plant growth and quicker harvest times.
Disadvantages Of Aeroponics
Expensive And Complex To Set Up
Aeroponics requires specialized equipment, such as misting systems and pumps, making the initial setup cost high. The system also requires careful design and planning to function correctly.
High Maintenance Requirements
The system requires frequent maintenance to ensure the misting equipment and pumps function properly. Clogged misting nozzles or pump failure can cause plants to suffer, so regular checks are essential.
Vulnerable To Power Outages
Since aeroponics relies on misting pumps and timers, power failures can quickly disrupt nutrient delivery, causing rapid damage to plants. Backup power systems are often necessary to prevent crop loss.
Aeroponics Is Best For
Aeroponics excels at growing high-value crops such as herbs and lettuce. It offers rapid growth and precision, making it ideal for research, controlled environments, and resource-limited spaces such as space stations.
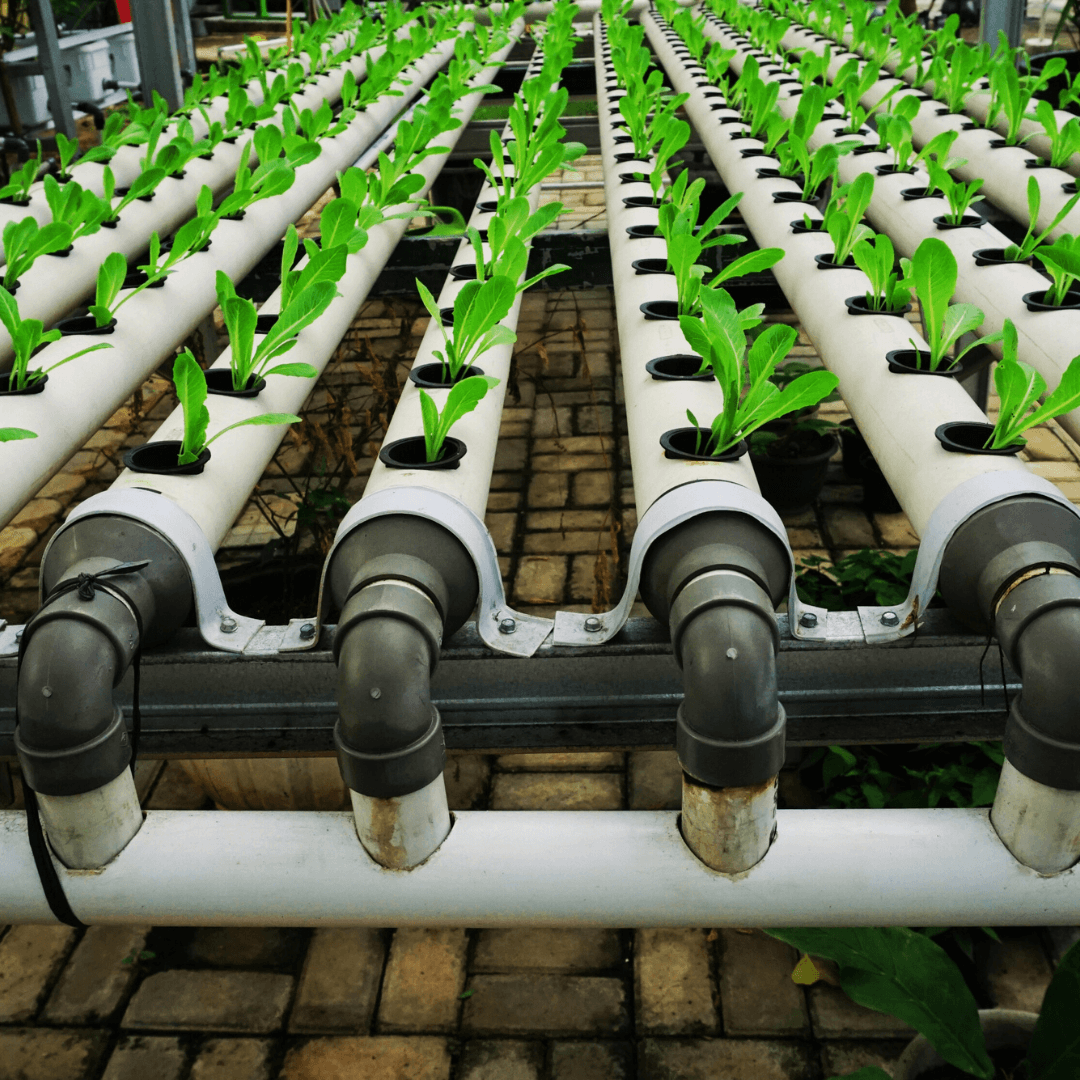

Factors To Consider When Choosing A Hydroponic System
1. Budget
Simple systems like the Wick system and DWC have lower initial costs, making them more affordable. In contrast, aeroponics requires advanced equipment, resulting in higher setup and maintenance costs.
2. Space
Compact systems like NFT and aeroponics are ideal for limited spaces, maximizing vertical growth. Ebb and flow, however, require more space due to their larger trays and flooding setup, limiting small-space use.
3. Plant Type
Different systems cater to specific plant needs. For example, fast-growing, small plants thrive in systems like NFT or DWC, while larger plants or flowering crops need more space, like drip systems.
4. Maintenance
Aeroponics requires intensive maintenance, including regular checks of misting systems and nutrient levels. Other systems, such as Wick or DWC, are more forgiving, requiring less frequent adjustments and simpler upkeep.
5. Scalability
The drip system is a hydroponic system that offers scalability. It allows you to expand and adjust the setup as your operation grows, easily accommodating increased plant numbers or larger crops.
FAQs
Q1: What Is The Most Straightforward Hydroponic System For Beginners?
The wick system is the easiest and most beginner-friendly. It requires no electricity and minimal maintenance, making it ideal for small-scale indoor gardening.
Q2: Which Hydroponic System Is Best For Fast-Growing Crops?
The Deep Water Culture (DWC) system is ideal for fast-growing crops like lettuce and herbs because it has constant access to nutrient-rich water and oxygen.
Q3: What Hydroponic System Is Most Suitable For Large Plants?
The drip system works well for larger plants, providing precise nutrient delivery and support for plants like tomatoes, cucumbers, and peppers.
Q4: Is Aeroponics Worth The Investment?
Aeroponics offers fast growth and minimal water use but requires a high initial investment and regular maintenance, making it best for high-value crops or research.
Q5: How Much Space Do I Need For An Ebb And Flow System?
Ebb-and-flow systems require more space than compact systems such as NFT or aeroponics because they use larger trays for periodic flooding and draining of the nutrient solution.
Q6: Can I Use Hydroponics For Fruits And Flowers?
Hydroponics is excellent for growing fruits, vegetables, and flowering plants. Systems like drip and aeroponics are especially suited for these high-value crops.
Conclusion
Hydroponics is a game-changing agricultural method, enabling growers to cultivate fresh, nutritious produce in virtually any environment.
Knowing the many kinds of hydroponic systems can help you choose the one that best suits your objectives, available space, and available funds.
Whether you're a hobbyist growing herbs in your kitchen or a commercial grower aiming for high yields, hydroponics offers a sustainable and efficient way to achieve your agricultural dreams.
I trust you enjoyed this article on the Types Of Hydroponic Systems. Please stay tuned for more inspiring guides, helpful tips, and ideas to help you live closer to nature every day.
Take care!
— JeannetteZ🌿
💬 Your Opinion Is Important To Me
Do you have thoughts, ideas, or questions? I’d love to hear from you. Please leave your comments below or email me directly at Jeannette@Close-To-Nature.org.
📚 More Nature-Inspired Reads
Explore more ways to connect with nature, nurture your pets, and live in harmony with the world around you 🌿