Unveiling The Negative Side Effects Of Stress
Unveiling The Negative Side Effects Of Stress
Stress is now an inevitable part of life for many people in today's fast-paced society. The negative effects of stress cannot be ignored, even though it can occasionally inspire people to meet deadlines and accomplish their goals.
Particularly, long-term stress can have a large negative impact on one's physical and mental health and have a variety of negative effects.
Furthermore, stress can impair immunity, making people more vulnerable to infections and disease.
It can worsen pre-existing medical disorders like anxiety, depression, and sleeplessness, which lowers quality of life overall.
In this article, we will delve into the negative side effects of stress, exploring its impact on various facets of health and well-being.
By understanding these effects, individuals can take proactive steps to manage stress and mitigate its harmful consequences, ultimately striving towards a healthier and more balanced lifestyle.
What Is Stress?
Stress is, at its most basic, the body's natural reaction to any demand or challenge, whether it be psychological, emotional, or physical.
The “fight or flight” response, deeply rooted in our evolutionary past, is a complex physiological reaction that releases hormones such as cortisol and adrenaline, priming the body to confront or flee a perceived threat.
While this acute stress response is essential for survival in immediate danger, the modern human experience often involves chronic stressors that extend beyond momentary threats.
Chronic stress, stemming from ongoing challenges like work pressures, financial worries, or relationship issues, can have profound effects on physical and mental well-being.
Over time, the body may struggle to return to equilibrium, leading to various negative consequences.
Stress manifests not only in palpable physical symptoms like increased heart rate and muscle tension but also in emotional and cognitive challenges, such as anxiety, irritability, and impaired concentration.
It is crucial to recognize that stress is a natural part of life, but it can significantly impact health when unmanaged or chronic.
Understanding the mechanisms and effects of stress is a key step in developing effective coping strategies to navigate life's demands and maintain overall well-being.
What Are Signs That You Are Stressed?
Stress can manifest in various ways, affecting the body and the mind. Recognizing the symptoms is crucial for timely intervention and stress management. Common symptoms of anxiety include:
1. Physical Symptoms Of Stress
- Headaches: Stress often contributes to tension headaches or migraines.
- Muscle Tension: Persistent stress can lead to tightness and discomfort in muscles.
- Fatigue: Chronic stress may result in persistent fatigue and low energy levels.
- Sleep Disturbances: Stress may cause trouble sleeping or staying asleep.
2. Emotional Symptoms Of Stress
- Anxiety: Excessive worry, restlessness, and a sense of unease are common signs of stress.
- Depression: Prolonged stress can contribute to feelings of sadness and hopelessness.
- Irritability: Increased irritability and frustration are emotional responses to stressors.
3. Cognitive Symptoms Of Stress
- Poor Concentration: Stress can impair concentration and memory.
- Forgetfulness: Difficulty remembering details or tasks may be stress-related.
- Negative Thinking: Chronic stress often leads to negative thought patterns.
4. Behavioural Symptoms Of Stress
- Changes in Eating Habits: Stress may result in overeating or loss of appetite.
- Increased Substance Use: Some individuals may turn to substances like alcohol or drugs to cope.
- Social Withdrawal: Avoiding social activities and isolating oneself are common responses to stress.
5. Digestive Issues
- Upset Stomach: Stress can contribute to digestive problems, including indigestion and nausea.
- Changes In Bowel Habits: Diarrhea or constipation may occur under stress.
6. Cardiovascular Symptoms Of Stress
- Increased Heart Rate: Stress triggers the release of stress hormones, elevating heart rate.
- High Blood Pressure: Chronic stress is linked to elevated blood pressure levels.
7. Skin Issues
- Acne or Eczema Flare-Ups: Stress can exacerbate skin conditions.
- Hair Loss: Prolonged stress may contribute to hair loss in some individuals.
8. Sexual Dysfunction
- Decreased Libido: Stress can affect sexual desire and function.
Notably, the severity of these symptoms can vary, and some people may experience a combination of them.
If stress symptoms persist or significantly impact daily life, seeking support from healthcare professionals or mental health experts to develop effective coping strategies is advisable.
Exploring The Negative Side Effects Of Stress
Stress can have a range of negative effects on both your physical and mental well-being. Here are some common negative side effects of stress:

1. Physical Health Issues
Prolonged stress affects the body's immune system, significantly increasing vulnerability to illnesses like colds and infections.
The persistent initiation of the body's stress response results in the discharge of stress hormones, including cortisol, which have the potential to impede the immune system's capacity to combat infections effectively.
This weakened immune response heightens susceptibility to common illnesses and exacerbates pre-existing health conditions.
For individuals with asthma, stress-induced inflammation can trigger or worsen respiratory symptoms, leading to more frequent and severe asthma attacks.
Similarly, chronic stress can exacerbate cardiovascular disease by raising blood pressure, increasing heart rate, and promoting inflammation within the cardiovascular system.
Furthermore, altered gut flora brought on by stress can worsen digestive issues like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) or inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), exacerbating symptoms like diarrhea, constipation, or abdominal pain.
Maintaining a strong immune system and reducing the aggravation of underlying medical conditions depend on efficient stress management.

2. Mental Health Issues
Chronic stress has profound implications for mental health, significantly elevating the risk of developing debilitating disorders such as anxiety, depression, and PTSD.
The body's chronic stress response system activation can throw off the neurotransmitter balance in the brain, altering mood regulation and emotion processing.
Individuals exposed to chronic stress may experience persistent feelings of worry, apprehension, and dread characteristic of anxiety disorders.
Similarly, the prolonged release of stress hormones like cortisol can dampen mood, deplete serotonin levels, and impair neural plasticity, contributing to the onset or exacerbation of depression.
Moreover, traumatic experiences accompanied by chronic stress can overwhelm the brain's coping mechanisms, increasing susceptibility to PTSD—a debilitating condition characterized by intrusive memories, hypervigilance, and emotional numbness.
For individuals already grappling with these mental health challenges, chronic stress can exacerbate symptoms, intensify emotional distress, and impair coping abilities, further perpetuating a cycle of psychological suffering.
Thus, prioritizing stress management strategies and seeking appropriate support are essential for safeguarding mental well-being and mitigating the risk of developing or exacerbating these mental health disorders.
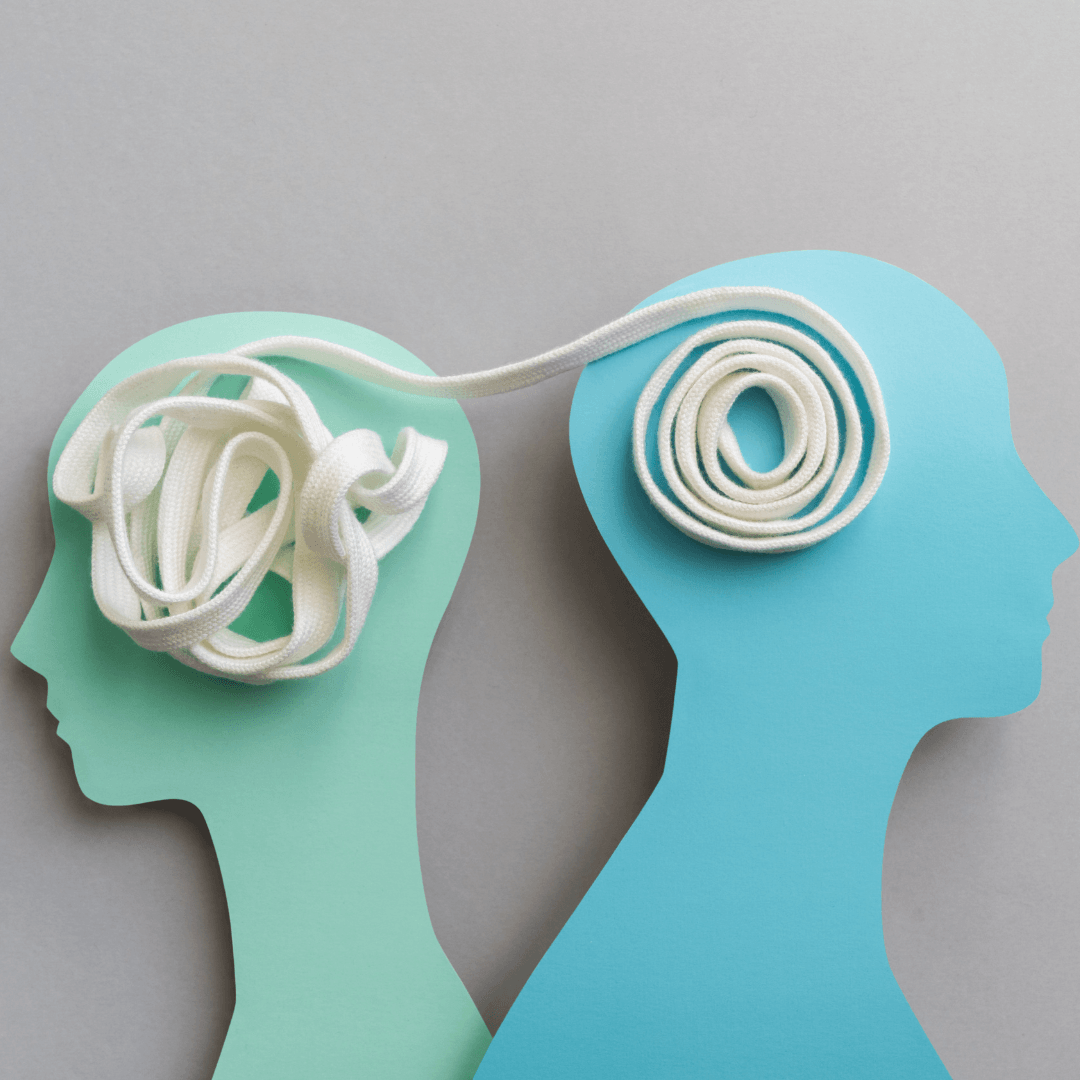

3. Cognitive Impairment
Chronic stress harms cognitive function, manifesting in various domains such as memory, concentration, and decision-making abilities.
The prolonged release of stress hormones, particularly cortisol, can disrupt neural networks involved in cognitive processes, impairing the encoding and retrieval of information in memory.
The negative side effects of stress on cognitive function include impaired memory, decreased concentration, and compromised decision-making abilities due to disrupted neural networks by prolonged cortisol release.
Moreover, stress-induced alterations in the prefrontal cortex, hippocampus, and amygdala—the brain regions crucial for executive function and emotional regulation—can compromise decision-making abilities and increase impulsivity.
Prolonged exposure to chronic stress has also been associated with a reduction in general cognitive function, which may hasten age-related cognitive decline and raise the chance of neurodegenerative diseases like dementia in later life.
Therefore, effective stress management techniques, including mindfulness and relaxation, are essential to preserving cognitive function and reducing the risk of cognitive impairment associated with prolonged stress.
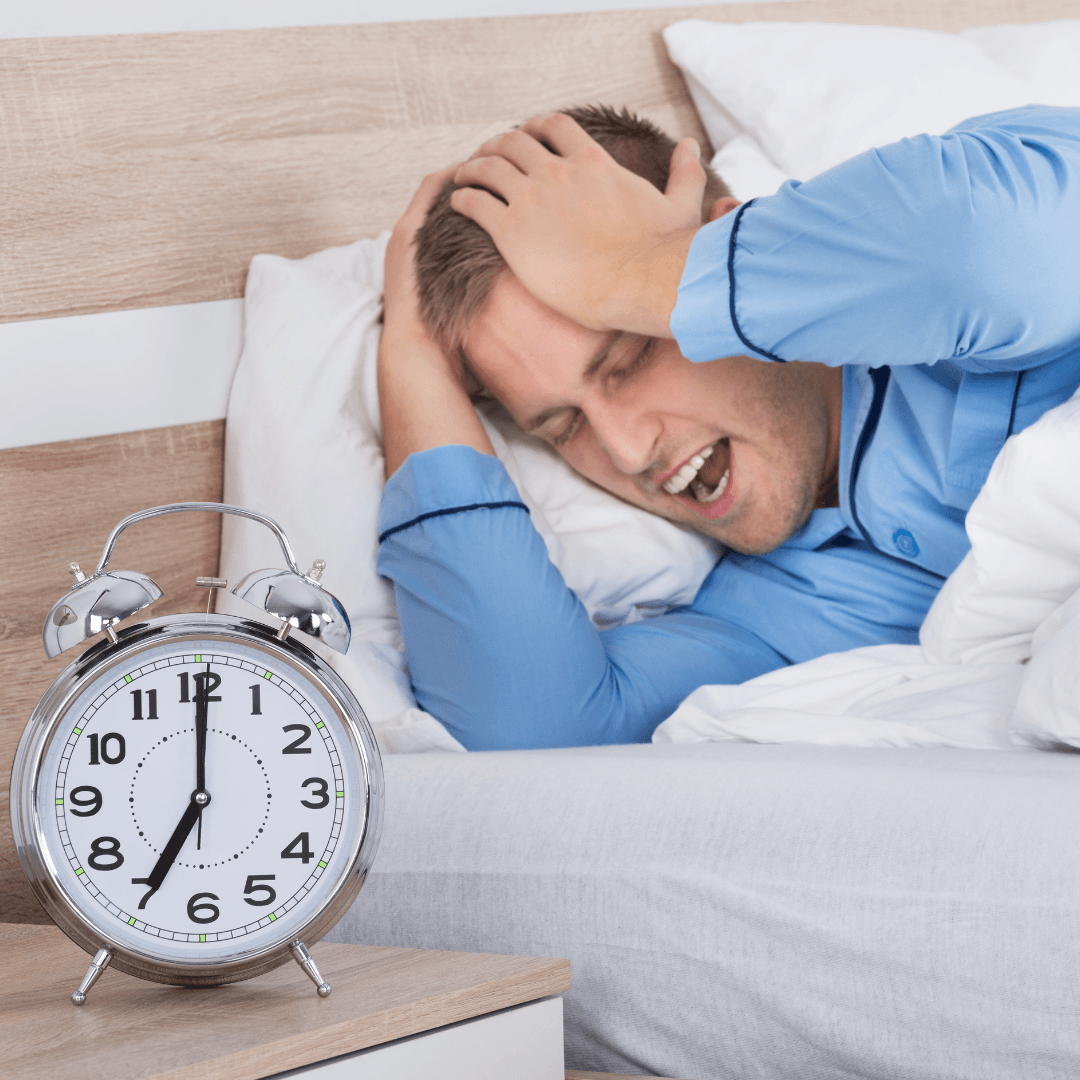

4. Sleep Disturbances
Stress disrupts the delicate balance necessary for healthy sleep patterns, often leading to various sleep disturbances.
Individuals experiencing stress may find it challenging to fall asleep due to racing thoughts, worries, or physical tension.
Once asleep, stress can contribute to frequent awakenings throughout the night, disrupting sleep continuity and reducing overall sleep quality.
Even when individuals manage to sleep, it may be shallow or fragmented, preventing them from reaching deeper, restorative stages.
Consequently, they wake up feeling unrefreshed, tired, and irritable, with decreased daytime functioning.
Chronic sleep disturbances resulting from stress can further exacerbate feelings of stress and anxiety, creating a vicious cycle that perpetuates sleep problems.
Stress must be addressed through relaxation methods, stress management strategies, and the creation of restful nighttime routines, consistent sleep schedules, and healthy sleep habits to restore regular sleep patterns and enhance general well-being.
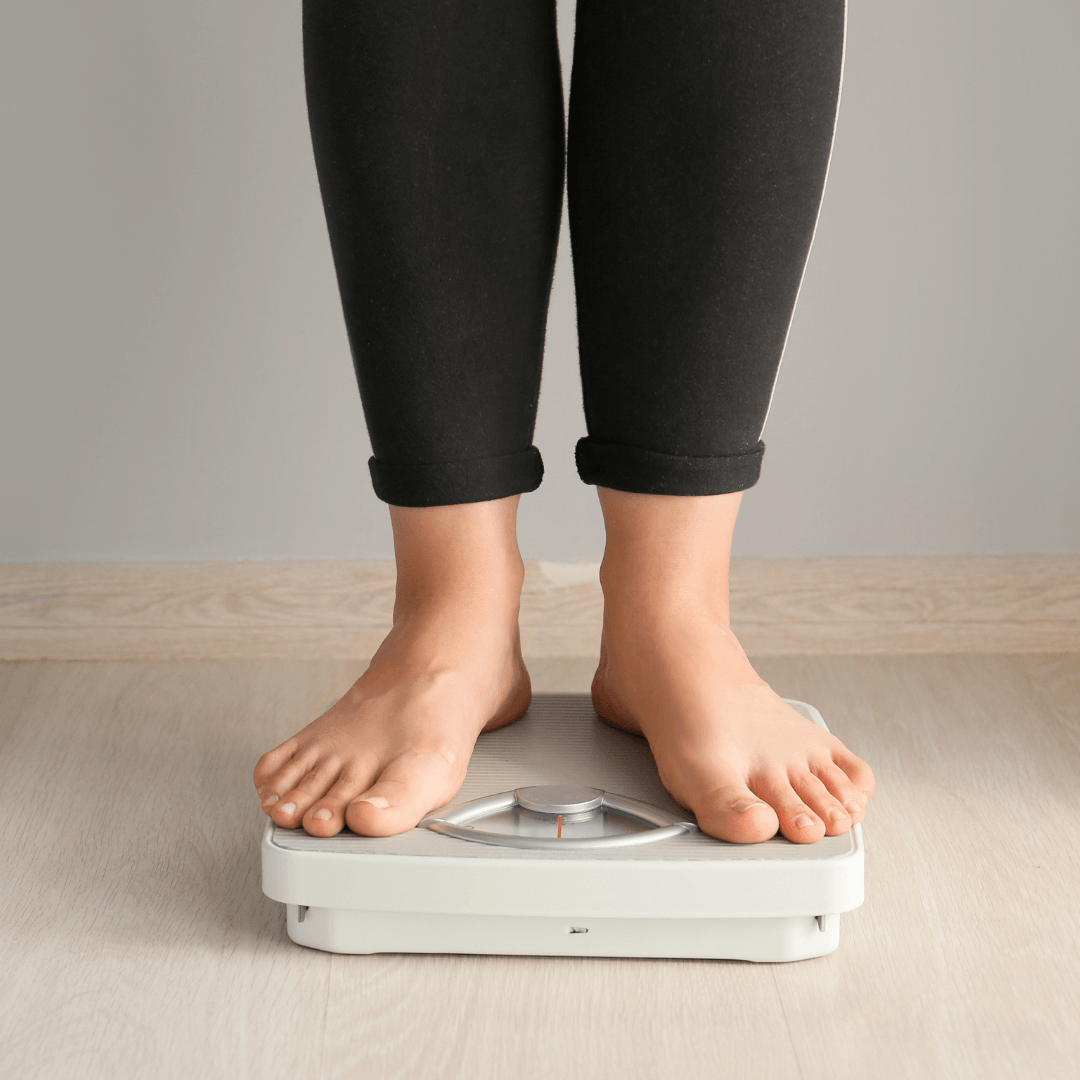

5. Weight Gain Or Loss
Stress can significantly impact eating habits and body weight, often leading to either weight gain or loss.
For some individuals, stress triggers an increase in appetite and cravings for high-calorie, comfort foods rich in sugar, fat, and carbohydrates.
This emotional eating serves as a coping mechanism, providing temporary relief from stress and anxiety.
Consequently, individuals may consume excessive calories, leading to weight gain over time.
Conversely, others may experience a loss of appetite when under stress, as heightened cortisol levels suppress hunger signals and disrupt normal appetite regulation.
Additionally, stress-induced changes in metabolism can further contribute to fluctuations in body weight.
Whether stress leads to overeating or undereating, these disruptions in eating habits can have significant implications for overall health and well-being.
Adopting healthy coping mechanisms, like mindfulness exercises, regular exercise, and getting support from friends, family, or mental health specialists, can help lessen the negative effects of stress on eating habits and encourage a well-rounded nutritional approach.

6. Increased Risk Of Substance Abuse
High levels of stress can drive individuals to seek solace in substances like alcohol, tobacco, or drugs as a coping mechanism, which can quickly escalate into substance abuse and addiction.
For many, these substances offer a temporary escape from the overwhelming feelings of stress, anxiety, or depression.
However, relying on substances to manage stress is not only ineffective but also dangerous, as it can lead to a vicious cycle of dependency and worsening mental health problems.
Substance abuse further compounds the negative effects of stress on physical health, increasing the risk of liver disease, cardiovascular problems, respiratory issues, and other serious medical conditions.
Among the negative side effects of stress, substance abuse stands out as it can worsen mental health disorders like depression and anxiety, necessitating a holistic treatment approach to break the cycle.
Breaking the cycle of substance abuse often requires comprehensive treatment that addresses both the underlying stressors and the addiction itself, emphasizing healthy coping mechanisms and holistic approaches to recovery.
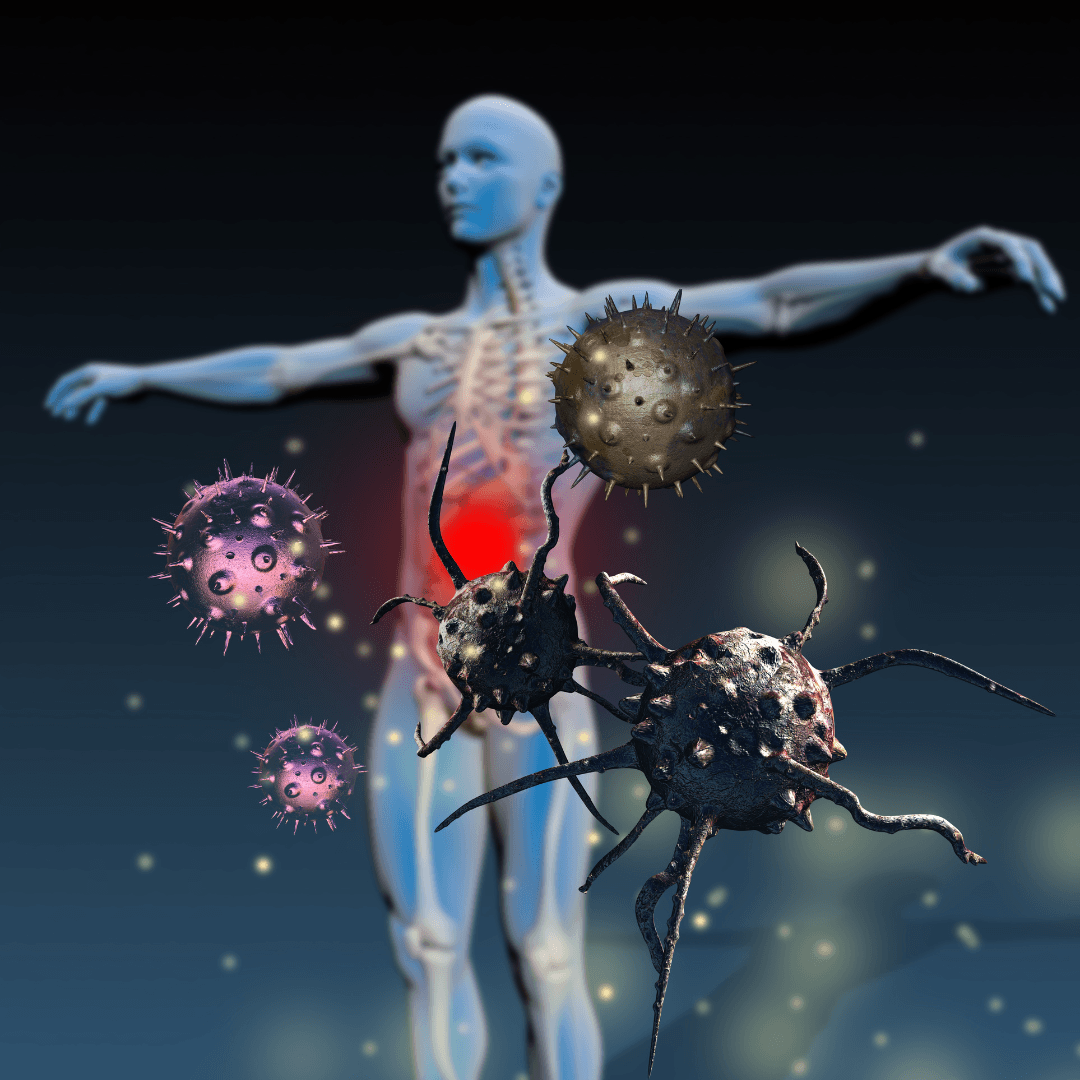
7. Immune System Suppression
Stress can significantly compromise the immune system, reducing the ability to fend off infections and prolong illness recovery.
This suppression occurs as the body's stress response diverts resources from the immune system to deal with perceived immediate threats, lowering defences.
Chronic stress, in particular, leads to elevated levels of cortisol and adrenaline, hormones that, over time, can diminish the effectiveness of immune responses.
The result is an increased susceptibility to colds, flu, and other infections and a slower healing process when one falls ill.
This weakened immune function under stress underscores the importance of managing stress through healthy lifestyle choices, relaxation techniques, and, when necessary, seeking professional guidance.
By addressing stress, individuals can help bolster their immune system's resilience, ensuring a more robust defence against pathogens and a swifter return to health following sickness.
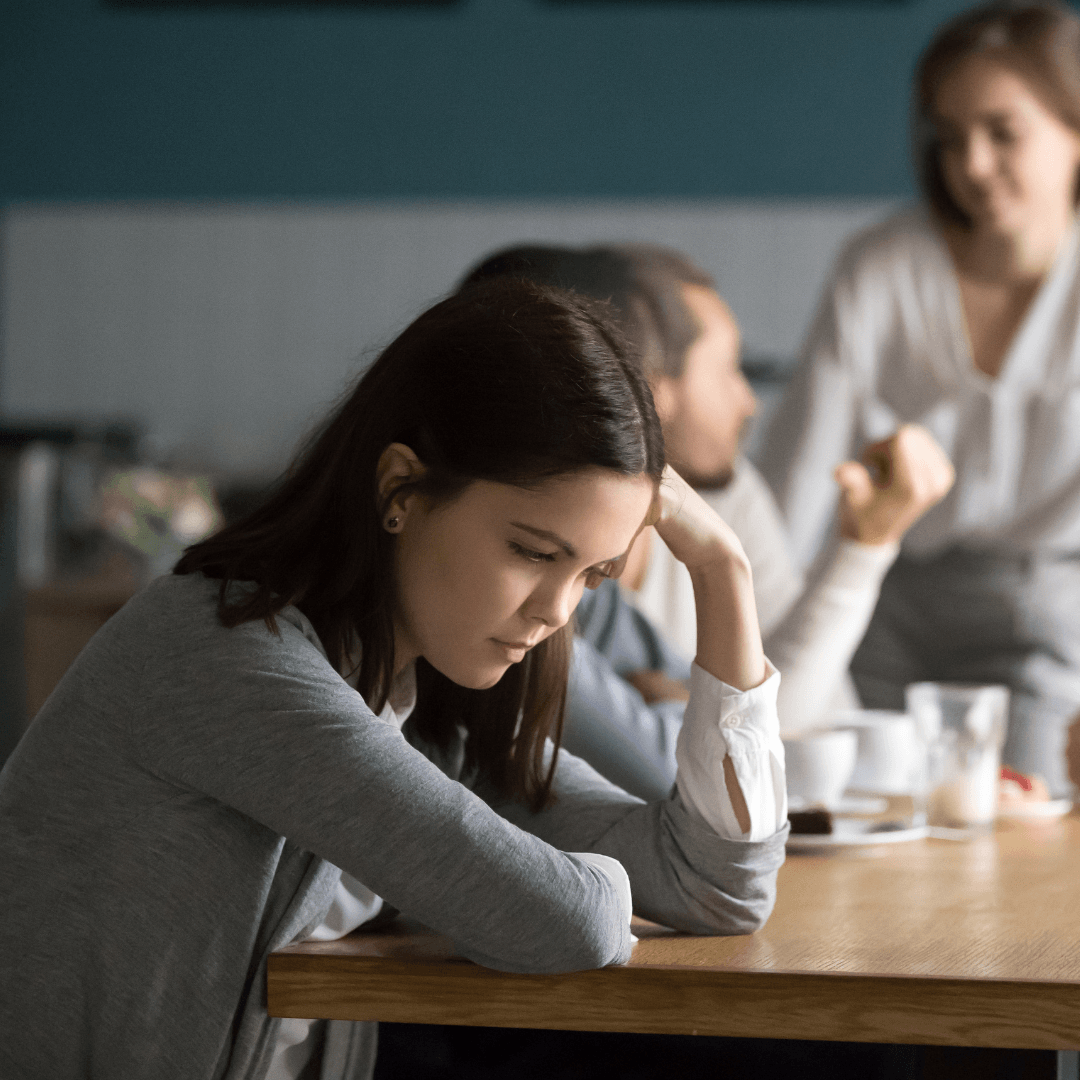

8. Social Withdrawal
Social withdrawal is a common consequence of prolonged stress, characterized by a retreat from social activities and networks that were once sources of pleasure and support.
This behaviour often emerges as individuals feel overwhelmed by their stressors, leading them to isolate themselves in an attempt to manage their feelings or because they perceive themselves as unable to meet the demands of social interaction.
The irony of social withdrawal is that while it may offer a reprieve from stress, over time, it can exacerbate feelings of loneliness and depression, further entrenching the cycle of stress.
Social connections are vital for emotional support and resilience against life’s challenges, and by withdrawing, individuals deprive themselves of these essential resources.
The loss of social support can also make it more difficult to cope with stress, creating a feedback loop that can be hard to break.
Recognizing the signs of social withdrawal and addressing the underlying stress through supportive relationships, professional help, or stress management techniques is crucial for reversing this trend and promoting overall well-being.
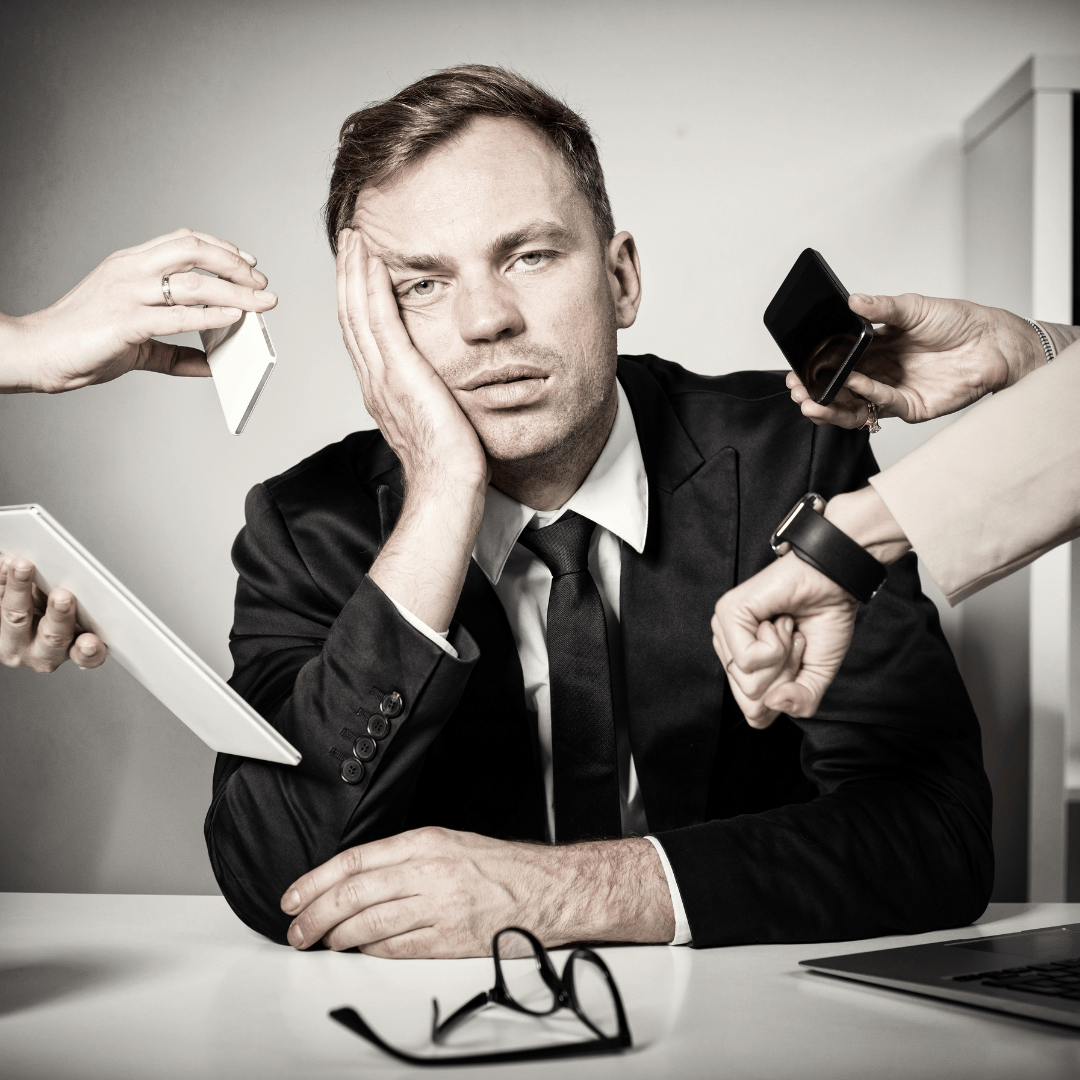

9. Neglect Of Responsibilities
When individuals are under significant stress, their ability to manage and prioritize various aspects of life can be severely compromised, leading to neglecting professional, social, or personal responsibilities.
Neglect of duties is a significant negative side effect of stress, leading to missed deadlines, withdrawal from social activities, and neglect of self-care routines.
This might manifest as missed deadlines, poor work quality, or absenteeism in a professional context.
Socially stressed individuals might withdraw from friendships, family gatherings, or community activities, neglecting the relationships that could otherwise offer support and relief from stress.
On a personal level, self-care routines and health management may fall by the wayside, exacerbating the physical and mental effects of stress.
The cycle of neglect and its negative side effects of stress can perpetuate a downward spiral, necessitating targeted strategies to break this cycle and restore well-being.
Breaking this cycle often requires conscious effort to address the underlying stress, involving time management strategies, seeking support from friends, family, or professionals, and prioritizing self-care and well-being.
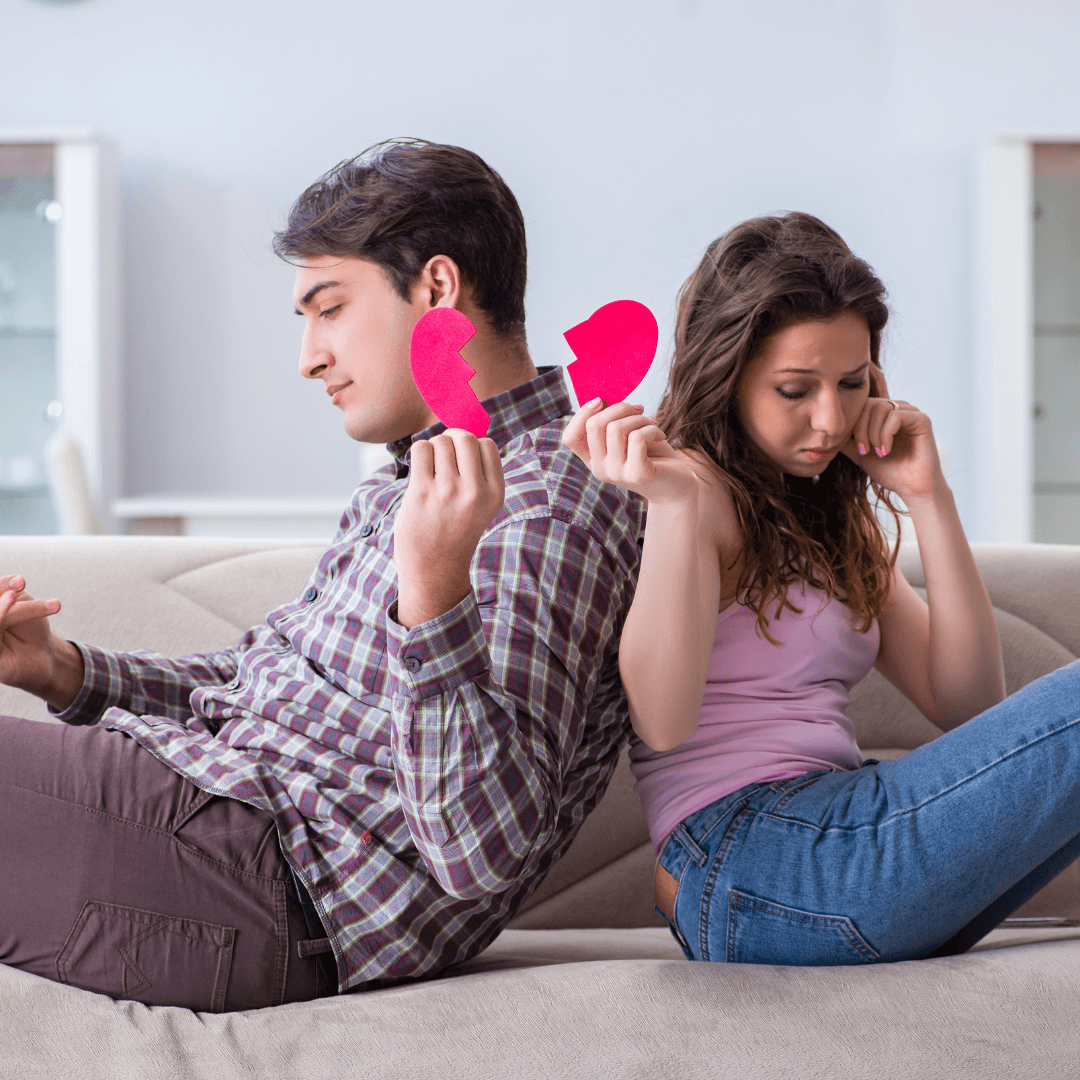

10. Conflict In Relationships
Stress is a significant catalyst for conflict in personal and professional relationships, often intensifying existing issues or creating new tensions.
When stressed, their patience diminishes, and their tolerance for misunderstandings or disagreements lowers, making them more reactive or defensive.
This heightened emotional state can lead to miscommunications, where parties involved may interpret actions, words, or intentions differently, further fueling disputes.
In personal relationships, this might manifest as arguments over seemingly minor issues, while in professional settings, stress can lead to conflicts over workload, deadlines, or project directions.
Moreover, stress can impair communication, making it challenging to express thoughts and feelings constructively.
As these conflicts escalate, they can strain relationships, potentially leading to a breakdown in communication.
The key to mitigating stress-induced conflicts is recognizing stress's role in these dynamics and actively working towards stress management techniques, fostering open and empathetic communication, and seeking compromise and understanding in interactions. Thus, relationships can be preserved and strengthened amidst stress.

11. Skin Conditions
Stress is known to profoundly impact the skin, exacerbating conditions like acne, eczema, and psoriasis.
This occurs because stress triggers the body to release cortisol, which can increase oil production in the skin's sebaceous glands, leading to acne flare-ups.
Stress can exacerbate the symptoms of psoriasis and eczema by weakening the immune system, making it more difficult for the body to fight inflammation, and making the skin react more sensitively.
The skin, the body's largest organ and a primary barrier against external threats, often reflects internal emotional states.
Therefore, when under stress, individuals might experience more frequent outbreaks, increased redness, and irritation.
Stress can also impair the skin's ability to function as a barrier, causing moisture loss and increasing the skin's sensitivity to allergens and irritants.
Managing stress through lifestyle changes, mindfulness practices, and, in some cases, professional help can significantly mitigate its negative effects on skin health.
It's also important for individuals with chronic skin conditions to have a tailored skincare routine to help manage symptoms during periods of high stress.
Understanding these negative effects is the first step in creating workable stress-reduction strategies, such as mindfulness training, physical exercise, social support, and, when necessary, medical consultation.
FAQ
Can Stress Affect You Physically?
Yes, stress can affect you physically. It might cause headaches, tense muscles, exhaustion, appetite swings, and sleep difficulties. Stress can also affect the immune system and worsen pre-existing medical issues.
Can Stress Influence Your Period?
Yes, stress can influence your menstrual cycle. It can cause irregularities such as missed periods, more frequent periods, or heavier or lighter bleeding.
Stress affects the body's hormone levels, which can disrupt the regularity of the menstrual cycle.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the negative side effects of stress underscore the critical importance of managing stress levels to maintain physical and mental health.
Recognizing these signs and taking proactive steps toward stress management can significantly mitigate its harmful effects.
The insidious nature of stress underscores the importance of adopting effective management strategies.
Ultimately, understanding the comprehensive impact of stress is the first step towards empowering individuals to take proactive measures, ensuring a healthier, more balanced life.
Techniques like getting regular exercise, meditating and practicing mindfulness, eating a balanced diet, and asking friends, family, or experts for support are very important.
It is vital to acknowledge that stress is inevitable; however, its impact can be minimized through conscious effort and lifestyle adjustments.
Addressing stress is about avoiding its negative side effects and enhancing overall quality of life and well-being.
I trust you enjoyed this article about Unveiling The Negative Side Effects Of Stress. Please stay tuned for more blog posts to come shortly.
JeannetteZ
>>>Please click here to read my all-inclusive article about Lessons That Will Teach You All About Stress<<<
>>>Are you interested in Natural Healing And Stress Relief through Herbs? Please click here for my #1 Recommendation<<<
Your Opinion Is Important To Me
Do you have thoughts, ideas, or questions? I would love to hear from you. Please leave me your questions, experiences, and remarks about Unveiling The Negative Side Effects Of Stress in the comments section below. You can also email me at Jeannette@Close-To-Nature.org.
Disclosure
This post may contain affiliate links. I earn from qualifying purchases as an Amazon Associate and other affiliate programs. Please read my full affiliate disclosure.
You might also enjoy these blog posts:
Is Yoga Good For Stress Relief?
10 Best Stress-Relieving Plants For Your Office
10 Best Stress-Relieving Plants For Your Home
Spirituality And Stress Relief
Stress Relief Activities For Kids