How To Store Garden Seeds For Long-Lasting Growth Power
Knowing how to store garden seeds properly is essential for every gardener who wants healthy, thriving plants year after year. Proper seed storage preserves their viability and ensures a successful growing season.
In this guide, you’ll learn simple, practical tips and techniques to keep your seeds fresh, protected, and ready to sprout whenever you need them.
Let’s dive into the best ways to store garden seeds with confidence!
Seed Storage 101: Keep Your Garden Growing Year After Year
Saving seeds is an innovative and sustainable way to grow your garden season after season. With the proper storage methods, you can preserve seeds’ vitality and ensure vigorous, healthy plants for years to come. Let’s explore how to store garden seeds the right way for long-lasting growth power:
1. Choose The Right Seeds For Storage
Not all seeds are equally suitable for long-term storage. Open-pollinated and heirloom seeds are often preferred because they can be saved and replanted with reliable results.
Hybrid seeds, on the other hand, may not produce true-to-type plants. Also, only store mature, healthy seeds—those taken from disease-free plants and fully developed fruits or flowers. Damaged or underdeveloped seeds are more likely to fail during germination.
When selecting seeds for storage, prioritize high-quality varieties known for longevity and consistent performance. Taking care in the selection process ensures that your stored seeds have the best chance of sprouting in the future.
2. Allow Seeds To Fully Dry Before Storing
Proper drying is one of the most critical seed preservation procedures. Freshly harvested seeds often contain moisture, which can lead to mould or premature germination if not removed.
Spread the seeds out in a single layer on a paper towel, screen, or tray in a well-ventilated, dry area. Avoid direct sunlight, which can damage seeds. A few days to a few weeks may pass during the drying process, depending on the type of seed.
Ensure they are scorched before storing—biting one or using a moisture meter can help determine readiness. Thoroughly dried seeds store better and last longer.
3. Clean Seeds Before Storage
Knowing how to store garden seeds starts with proper cleaning to prevent mould, pests, and ensure long-term viability. Begin by removing plant debris, chaff, and any remaining fruit pulp from the seeds.
This can be done by hand, with sieves, or by winnowing, depending on the seed type. For wet seeds, such as tomatoes or cucumbers, fermentation might be necessary to remove the gel coating before drying. For dry seeds like beans or peas, gentle rubbing or screening is usually sufficient.
Clean seeds not only store better but are also easier to handle and sow later on. Cleanliness is a key factor in long-term seed preservation.
4. Label Seeds Clearly And Accurately
Labelling is crucial when storing multiple seed varieties. Include the plant name, variety, harvest date, and any relevant notes such as the source or special growing conditions.
Use waterproof labels or write directly on paper envelopes or containers with a permanent marker. For added organization, consider using a seed inventory spreadsheet to track what you have.
Good labelling prevents mix-ups and ensures you know exactly what you're planting in the next season. Accurate records are invaluable for managing crop rotation and succession planting strategies, making seed organization a time-saving investment for any gardener.
5. Choose The Right Containers
The choice of container plays a significant role in maintaining seed quality. Airtight containers are ideal for protecting seeds from humidity and pests.
Options include glass jars with tight-fitting lids, resealable plastic bags, and vacuum-sealed pouches. Paper envelopes can work well for short-term storage in a dry climate.
If using plastic bags, double-bagging or adding a desiccant packet can help control moisture. Reuse containers from old seed packets, or repurpose spice jars and pill bottles.
Whatever you choose, make sure it’s clean and scorched. The correct container will preserve the seed’s dormancy until you’re ready to plant.
6. Control Temperature And Humidity
A key part of learning how to store garden seeds is maintaining cool, dry, and stable conditions to maximize their longevity and viability.
Excellent storage conditions include temperatures between 32°F and 50°F (0°C and 10°C) and low relative humidity (less than 50%). A good rule of thumb is that the sum of temperature (°F) and humidity (%) should be less than 100.
Avoid storing seeds in warm or damp areas like basements or kitchens. For long-term storage, a refrigerator can be a great option, but avoid frequent temperature fluctuations.
To stop seeds from absorbing moisture, store them in airtight containers. Stable conditions slow seed aging and preserve germination potential, making climate control one of the most critical steps.
7. Use Desiccants To Keep Seeds Dry
Desiccants absorb moisture, helping to maintain a dry environment inside seed containers. Silica gel packets are commonly used and can be found in packaging for shoes or electronics.
You can also make your desiccants using powdered milk or rice wrapped in tissue or fabric. Place the desiccant in the container with the seeds, but keep it separated to avoid contact.
Monitor and replace desiccants if they become saturated. Using a desiccant adds an extra layer of protection against humidity, especially in climates prone to moisture. This small addition can make a big difference in seed longevity.

8. Avoid Exposure To Light
An important tip on how to store garden seeds is to keep them in complete darkness to preserve their dormancy and quality over time. Seeds are best stored in complete darkness.
Choose opaque containers or store clear containers in a dark cabinet, closet, or box. Avoid placing seed containers near windows or under grow lights. For added protection, store seed containers inside a larger opaque container like a metal tin or plastic box.
Keeping seeds in the dark helps maintain their dormant state, which is crucial for long-term viability. Just as with temperature and humidity, consistency in light exposure contributes significantly to successful seed storage and future germination.
9. Store In A Stable Environment
Fluctuating conditions can damage seed viability more than constant moderate conditions. Frequent changes in temperature or humidity can cause condensation, leading to mould or rot.
Choose a stable location such as a fabulous closet, drawer, or refrigerator drawer—not the freezer unless properly prepared. Avoid areas near heat vents or appliances.
For long-term storage, monitor conditions with a hygrometer or thermometer. Even if your space isn’t perfect, minimizing fluctuations can significantly extend a seed’s shelf life.
Consistency in the storage environment ensures your seeds are preserved in the best possible condition until it’s time to plant them.
10. Test Seed Viability Periodically
Over time, even properly stored seeds lose viability. Conduct a germination test every season to check quality. Place 10 seeds between damp paper towels and seal them in a plastic bag.
Keep them in a warm spot and check after a few days. Eight out of ten seeds sprouting indicates that the batch is 80% viable. Anything below 60% may result in spotty growth and should be replaced or sown thickly.
Testing saves time and disappointment in the garden. It helps you identify which seeds to use up soon and which still have strong potential for healthy growth.
11. Know Seed Shelf Life By Plant Type
Understanding seed longevity is essential when learning how to store garden seeds effectively and prioritize which ones to use first.
Onions and parsley often last only 1-2 years, while tomatoes, peppers, and carrots may remain viable for 3-5 years. Beans, peas, cucumbers, and lettuce can last even longer with proper care.
Create a seed rotation schedule based on expected viability to avoid storing seeds past their prime. This ensures you always plant strong, healthy seeds with high germination rates.
Familiarity with seed lifespan helps prioritize which seeds to use first and prevents wasted effort in sowing old or ineffective seed stock.
12. Organize Seeds For Easy Access
A good organization makes using stored seeds efficient and enjoyable. Sort them by plant type, season, or expiration date in labelled containers, boxes, or folders.
Photo storage boxes, recipe boxes, or small file drawers work well. Use dividers for quick navigation and inventory sheets to track what you have. Consider creating a digital database with notes on germination rates and harvest results.
Easy access to well-labelled seeds saves time when planning your garden. The organization also prevents duplicate purchases and helps keep older seeds in use before they lose viability.
13. Freeze Seeds For Long-Term Storage
Freezing is an option for long-term seed preservation but requires care. Only dehydrated freeze seeds or ice crystals can form and destroy the embryo.
Place seeds in airtight, moisture-proof containers like vacuum-sealed bags before freezing. To avoid condensation, allow seeds to reach room temperature before opening them after taking them out of the freezer.
Freezing is ideal for long-term seed banks or preserving rare varieties. While not necessary for everyday gardeners, it can extend seed life for several years when done correctly. Use this method when you want to keep seeds dormant for the long haul.
14. Use Stored Seeds To Save Money And Time
Reusing stored seeds can significantly reduce gardening costs. Rather than buying new packets every season, you can rely on your seed stash to start vegetables, herbs, or flowers.
Stored seeds also save time during planting season, since you’ll have them readily available. With proper labelling and organization, you’ll know exactly what you have and when to plant it.
Many gardeners find that growing from their seeds brings satisfaction and a deeper connection to the gardening process. Well-preserved seeds are a wise, sustainable investment in future gardens.

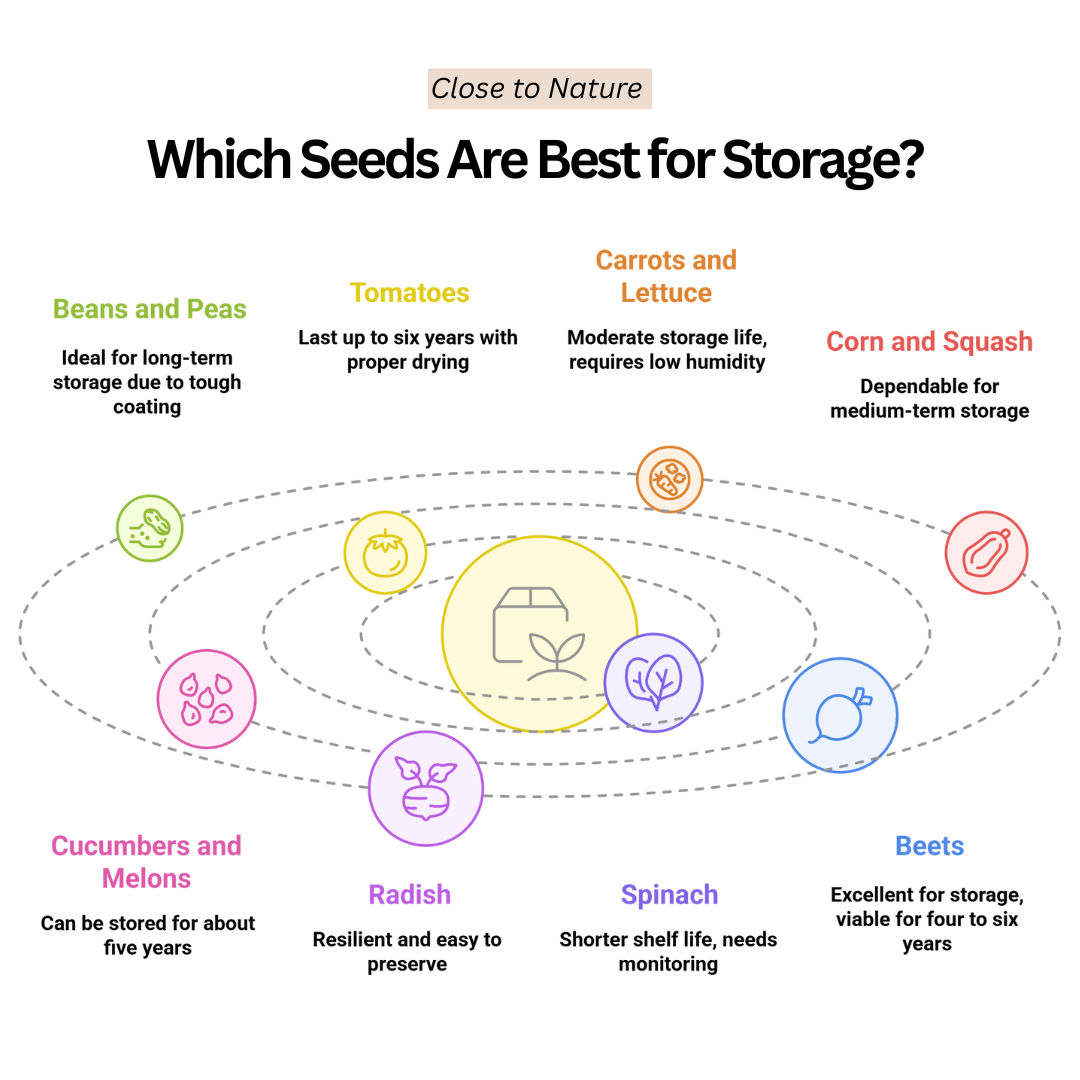
Which Seeds Are Best For Storage?
Knowing how to store garden seeds properly allows you to select varieties with long shelf lives for successful long-term gardening or emergency preparedness.
The following seeds store well and remain viable for years when kept in ideal conditions.
1. Beans And Peas
Beans and peas are ideal for seed storage due to their tough outer coating and low moisture content. They can remain viable for three to five years if kept in a cool, dry place.
These legumes are also easy to harvest and dry at home, making them excellent for long-term storage. Use airtight containers and store away from light for best results.
2. Tomatoes
Tomato seeds are a top choice for seed storage, lasting up to six years under ideal conditions. They require proper drying and should be stored in a low-humidity environment to maintain viability.
Heirloom or open-pollinated varieties are best for saving seeds. After fermentation and drying, store them in labelled envelopes or jars in a cool, dark place to ensure strong germination in future planting seasons.
3. Carrots And Lettuce
Carrot and lettuce seeds have a moderate storage life, typically lasting two to four years. They require low humidity and cool temperatures to remain viable. These seeds are small and delicate, so careful drying is essential before storing.
Use moisture-proof containers and keep them away from light and heat. Rotate stock every few years to maintain a reliable seed supply for your garden.
4. Corn And Squash
Corn and squash seeds are dependable for medium-term storage, lasting between two and five years when appropriately dried. Both types produce large seeds that are easy to clean and handle.
Store them in airtight containers at low humidity and temperatures around 40°F (4°C). Choose non-hybrid varieties if you plan to save seeds for replanting, as hybrids may not produce consistent offspring.
Turn Your Passion for Nature Into Income
🌿 Whether you love gardening, caring for animals, or exploring holistic living,
You can share your knowledge online and earn from it.
Discover how nature lovers are growing their passions into meaningful, income-generating blogs. 👇
5. Cucumbers And Melons
Cucumber and melon seeds can be stored for about five years if dried thoroughly and kept in optimal conditions. These seeds come from fruits that must be fully mature before harvesting the seeds.
After washing and drying, store them in sealed containers in a cool, dry, and dark location. To regulate moisture and prolong their shelf life, use desiccants such as silica gel packets.
6. Radishes
Radish seeds are a great example when learning how to store garden seeds, as they remain viable for years with proper drying and airtight storage. Their small size and low oil content make them easy to dry and preserve.
Harvest seeds once pods turn brown and dry thoroughly—clean and store in airtight containers away from moisture and heat. Radish seeds germinate quickly and are a staple for seed savers due to their reliability and long viability.
7. Spinach
Spinach seeds tend to last two to three years in storage. While their shelf life is shorter than some other vegetables, they remain viable when stored properly. Keep them dry and cool in sealed containers.
Choose open-pollinated varieties for future seed saving. Spinach seeds benefit from being stored with desiccants and monitored for mould or moisture, which can reduce germination rates over time.
8. Beets
Beet seeds are excellent for storage, remaining viable for four to six years under ideal conditions. These seeds are technically clusters containing multiple potential sprouts.
Ensure seeds are dehydrated before storing in moisture-proof containers. Keep them in a dark, cool space for long-lasting viability. Beet seeds are easy to save and are a great addition to your long-term seed storage plan.
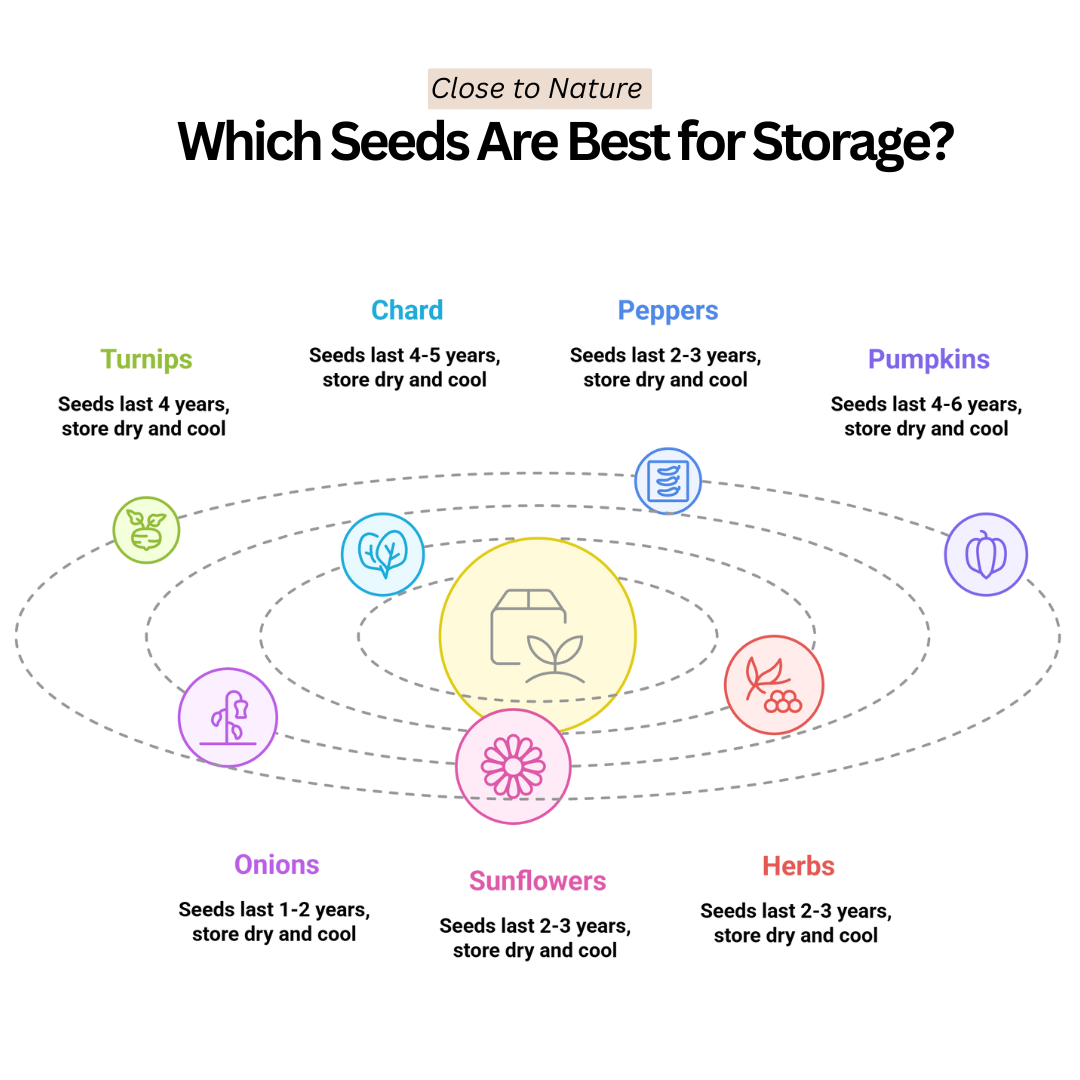
9. Turnips
Turnip seeds last around four years in storage and are a reliable root vegetable for seed savers. Allow plants to bolt and form seed pods, then harvest when dry and brittle. Store cleaned seeds in airtight containers away from heat and light.
Their low oil content supports longevity. Turnips proliferate and provide a nutritious food source, making them ideal for gardeners preparing for future seasons.
10. Chard (Swiss Chard)
Chard seeds have a long shelf life, often lasting four to five years. They are similar in appearance and structure to beet seeds and benefit from the same drying and storage techniques.
Keep seeds dry, calm, and sealed in moisture-resistant containers. Chard is a versatile and nutritious green, making its seeds an excellent investment for home gardeners interested in saving seeds for extended periods.
11. Peppers
Pepper seeds, especially from sweet and hot varieties, store well for about 2 to 3 years. They need to be thoroughly dried before storage to prevent mould.
Keep seeds in airtight containers away from light and humidity. Although their shelf life is shorter than some seeds, peppers are popular for seed saving because they’re easy to grow and produce flavorful fruits year after year.
12. Pumpkins
Pumpkin seeds have a solid storage life of about 4 to 6 years when properly dried. These large seeds are easy to clean and store.
They should be kept in cool, dark places inside sealed containers. Pumpkins are great for seed saving because heirloom varieties pass on their traits reliably, providing consistent crops season after season.
13. Onions
Onion seeds have a relatively short shelf life, usually about 1 to 2 years. They are high in oil content, which causes them to lose viability faster.
However, they can still be preserved for at least one season if they are allowed to air dry completely and kept in cool, dry conditions in sealed containers. Onions are essential for many gardens, making their seeds worth preserving carefully.
14. Sunflowers
Sunflower seeds can last 2 to 3 years in storage if kept dry and cool. These seeds are large and easy to handle, making them a favourite for seed saving.
Store in moisture-proof containers, and avoid temperature fluctuations to maintain germination rates. Sunflowers also produce edible seeds, adding extra value beyond planting.
15. Herbs (Basil, Dill, Parsley)
Many herb seeds like basil, dill, and parsley store well for 2 to 3 years when dried completely and kept in airtight containers.
These seeds are small and fragile, so proper drying and moisture control are vital. Herbs add flavour and nutrition to meals, so saving their seeds helps maintain a fresh herb supply year after year.
Conclusion
Mastering how to store garden seeds ensures your seeds stay healthy and ready for planting season after season. You may improve the quality and viability of your seeds and raise the chances that your garden will flourish by following these easy tips. Start applying these storage techniques today and enjoy a thriving, vibrant garden year after year!
I trust you enjoyed this article on How To Store Garden Seeds For Long-Lasting Growth Power. Please stay tuned for more inspiring guides, helpful tips, and ideas to help you live closer to nature every day.
Take care!
— JeannetteZ
💬 Your Opinion Is Important To Me
Do you have thoughts, ideas, or questions? I’d love to hear from you. Please leave your comments below or email me directly at Jeannette@Close-To-Nature.org.
📚 More Nature-Inspired Reads
Explore more ways to connect with nature, nurture your pets, and live in harmony with the world around you 🌿







