Don’t Let Lifestyle Diseases Control Your Life
As modern habits change toward convenience and sedentary living, lifestyle disorders, including obesity, diabetes, and heart disease, have become more prevalent.
These avoidable lifestyle diseases result from poor food choices, inactivity, and long-term stress. However, we can adopt healthier choices that protect our well-being by understanding how these diseases take root.
Here’s how to recognize the causes and take steps to prevent lifestyle diseases effectively.
What Are Lifestyle Diseases?
Diseases of Modern Living, also known as non-communicable diseases (NCDs), are conditions that develop primarily due to unhealthy lifestyle choices.
These diseases are largely preventable but can be chronic, affecting people over the long term. Some of the most common lifestyle diseases include:
- Heart disease, stroke, and other cardiovascular diseases
- Diabetes (especially Type 2 diabetes)
- Obesity
- Cancer (some types, including lung and colorectal cancer, have lifestyle links)
- Chronic Conditions of the Respiratory System (such as Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Syndrome)
What Causes Lifestyle Diseases?
Below, we'll review the five leading causes of lifestyle-related illnesses and how each contributes to these long-term health issues.
1. Poor Diet Choices
Our diets have transformed dramatically in recent decades, with processed foods, sugary drinks, and high-fat meals becoming the norm for many.
Unfortunately, diets prioritizing convenience over nutrition are often high in unhealthy fats, sugar, and sodium while lacking essential nutrients from fresh fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Poor food choices can lead to lifestyle-related illnesses in the following ways:
High Sugar Intake
Overindulging in sugar, especially from sodas, candy, and sweetened snacks, can raise blood glucose levels and cause obesity, both of which increase the risk of Type 2 diabetes over time.
Unhealthy Fats And Processed Foods
Processed meals are frequently high in saturated and trans fats, which can cause heart disease by clogging arteries with cholesterol. Additionally, these foods are low in fibre and essential nutrients, which the body requires for proper functioning.
Excess Salt
Many processed foods are high in salt, which can increase blood pressure, make the heart work harder, and raise the risk of heart disease and stroke.
Healthy eating is a vital preventive strategy emphasizing fresh, nutritious meals, including fruits, vegetables, lean meats, and whole grains. Maintaining a healthy diet can substantially reduce the risk of diseases associated with physical inactivity.

2. Physical Inactivity
Sedentary lifestyles are a hallmark of modern society, as many people work desk jobs, commute by car, and spend leisure time on screens. Obesity, heart disease, and diabetes are all significantly influenced by inactivity. Here’s how it affects health:
Reduced Caloric Expenditure
If energy intake surpasses expenditure, weight gain and obesity may result from the body burning fewer calories due to inactivity.
Increased Risk Of Hypertension
Regular physical activity helps keep blood pressure healthy. Physical inactivity, however, often results in elevated blood pressure, which strains the heart and arteries.
Impact On Blood Sugar And Insulin
Exercise is crucial for regulating blood sugar levels. Consistent physical activity helps keep blood glucose levels stable and lowers the risk of Type 2 diabetes by enhancing the body’s insulin sensitivity.
Participating in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week can reduce these risks and improve overall well-being.
Simple lifestyle adjustments, like using the stairs, walking during breaks, and dedicating time for physical activity, can effectively mitigate the effects of a sedentary lifestyle.
3. Smoking And Alcohol Consumption
Two of the most avoidable causes of lifestyle-related illnesses are excessive alcohol usage and tobacco use. Both behaviours are linked to some long-term medical disorders, such as cancer, liver disease, and heart disease.
Tobacco Use
Several malignancies, including those of the mouth, throat, and lungs, are significantly increased by smoking. Along with raising the risk of heart attacks and strokes, the chemicals in cigarettes also help to build up plaque in arteries. Smoking also causes lung damage, which results in long-term respiratory problems.
Alcohol Consumption
Moderate to heavy drinking is linked to a range of health problems. Alcohol can raise blood pressure, damage the liver, and weaken the immune system.
Heavy drinking is associated with liver diseases such as cirrhosis and liver cancer. Excessive alcohol also increases the risk of high blood pressure and some cancers.
These dangers can be considerably decreased by cutting back on alcohol and stopping smoking. There are also numerous support resources, including smoking cessation programs and counselling, to help individuals cut down or eliminate these habits.
4. Stress And Mental Health Issues
In today’s fast-paced, high-pressure environment, stress has become a shared experience. While short-term stress can be manageable, chronic stress has severe impacts on physical health, contributing to heart disease, high blood pressure, and even obesity.
Chronic Stress And Heart Health
When stress becomes chronic, it leads to prolonged heart rate and blood pressure increases, which puts undue strain on the cardiovascular system. Over time, this can damage arteries and increase the risk of heart attacks.
Stress And Sleep Disorders
Chronic stress often leads to poor sleep quality, which has a compounding effect on health. Sleep disorders are linked to obesity, Type 2 diabetes, and a weakened immune system, making individuals more susceptible to lifestyle diseases.
Unhealthy Coping Mechanisms
Mental health issues can lead to coping mechanisms such as overeating, smoking, or drinking alcohol, which contribute to lifestyle-related illnesses. Emotional eating, in particular, can lead to weight gain and elevate the risk of obesity and diabetes.
Stress-relieving practices like meditation, yoga, or regular exercise can reduce stress levels. Therapy and counselling are essential forms of mental health care that help manage stress and lower its health hazards.

5. Lack Of Sleep
A population with higher risks of obesity, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and even weakened immunity results from people's underestimation of the value of sleep for general health.
Sleep And Obesity
Poor sleep can lead to hormonal imbalances, affecting hunger hormones like ghrelin and leptin, which regulate appetite.
Impact On Insulin Sensitivity
Sleep deprivation negatively affects the body’s insulin sensitivity, making it harder to regulate blood sugar levels. This raises the chance of getting Type 2 diabetes.
Cardiovascular Health
Insufficient sleep strains the heart by increasing blood pressure and causing inflammation in blood vessels. This eventually leads to the emergence of cardiovascular disorders.
As an adult, strive to achieve 7 to 9 hours of restful sleep every night. Good sleep hygiene not only enhances sleep quality but also supports overall health. Examples are a regular sleep schedule, a calm resting environment, and avoiding devices right before bed.
How Stress Leads To Lifestyle Diseases
Understanding how stress leads to these diseases is essential for protecting our health and improving our quality of life.
1. The Physiology Of Stress: How It Affects The Body
When we experience stress, our body activates its “fight or flight” response, releasing stress hormones like cortisol and adrenaline.
These hormones give us the energy to react to danger by raising blood pressure, heart rate, and blood sugar levels. However, chronic stress keeps the body in a prolonged state of alertness, which can be damaging over time.
This constant activation of stress responses wears down the body’s systems, leading to inflammation, metabolic changes, and other effects that set the stage for lifestyle-related illnesses.
Key Points
- Stress sets off the “fight or flight” reaction, which releases adrenaline and cortisol.
- Blood pressure, blood sugar, and heart rate are all raised by stress hormones.
- Chronic stress keeps the body in a prolonged state of alertness, causing harm over time.
- Long-term stress leads to inflammation and metabolic changes and weakens body systems, paving the way for lifestyle diseases.
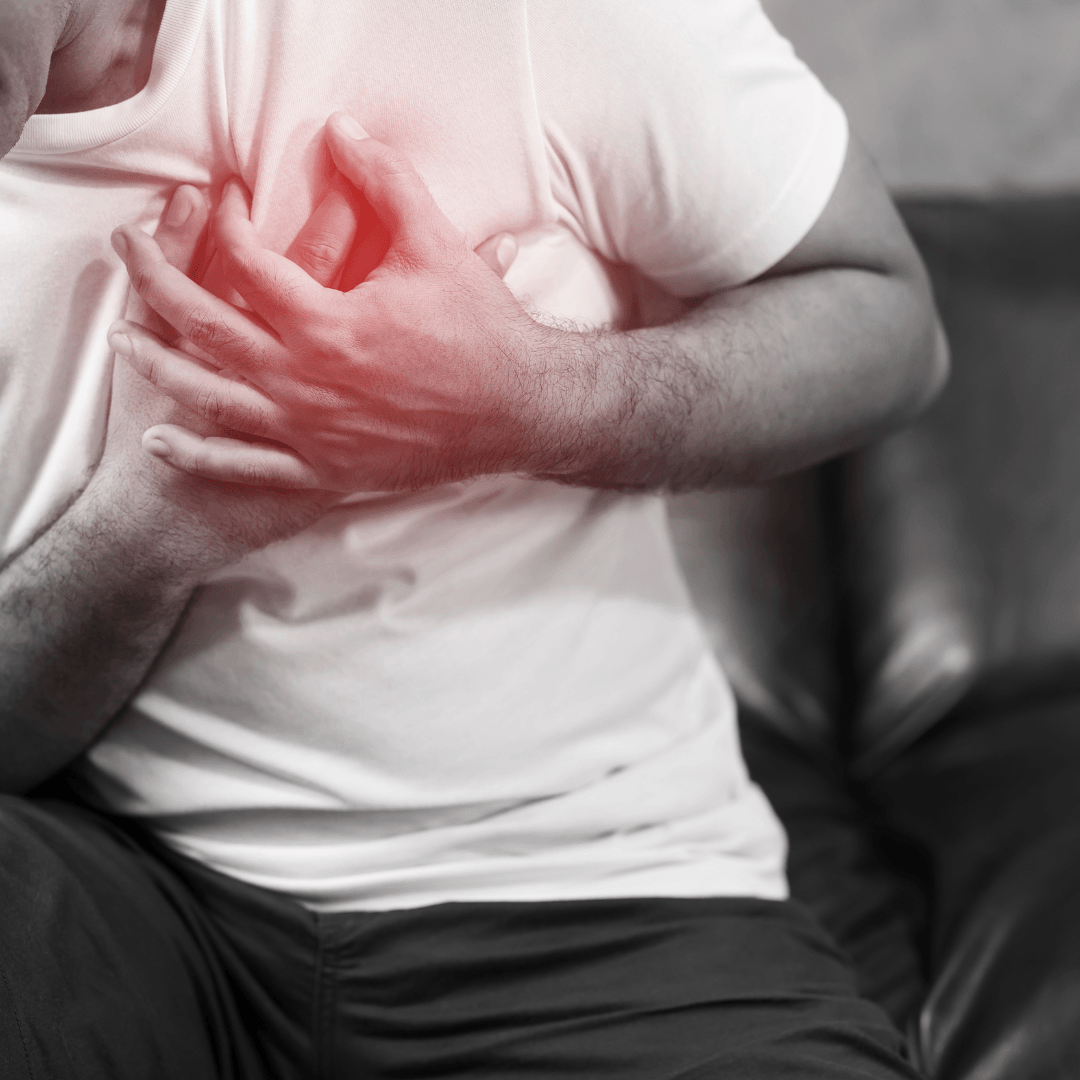

2. Heart Disease
Stress is a primary risk factor for heart disease. It increases blood pressure and forces the heart to work harder.
Over time, this strain can damage the cardiovascular system, leading to high blood pressure, atherosclerosis, and eventually heart disease.
Stress also contributes to unhealthy habits like smoking, overeating, and a sedentary lifestyle, which increase the risk of heart disease.
Key Points
- Stress raises blood pressure and heart rate.
- Chronic stress leads to inflammation, contributing to heart disease.
- Stress-related habits like smoking and poor diet further increase cardiovascular risk.
3. Stress And Diabetes: The Impact On Blood Sugar
Stress directly influences blood sugar levels, a significant factor in diabetes development. When stressed, the body releases glucose into the bloodstream to provide energy.
Ongoing stress, however, can lead to persistently high blood sugar, which can subsequently cause insulin resistance and Type 2 diabetes. Emotional eating brought on by stress also increases weight gain and the risk of diabetes.
Key Points
- Chronic stress affects blood sugar regulation.
- Insulin resistance brought on by ongoing stress can raise the risk of type 2 diabetes.
- Emotional eating under stress contributes to weight gain and diabetes.
4. Obesity: Stress And Weight Gain
Stress affects weight in several ways. First, elevated cortisol levels encourage the body to store fat, particularly around the abdomen.
Secondly, stress triggers cravings for high-sugar, high-fat “comfort” foods, leading to overeating and weight gain. Chronic stress also discourages physical activity, contributing to a sedentary lifestyle and an increase in body weight, which raises the risk of lifestyle-related illnesses like heart disease and diabetes.
Key Points
- Cortisol encourages abdominal fat storage.
- Stress leads to cravings for unhealthy foods, resulting in weight gain.
- Reduced physical activity under stress compounds obesity risk.
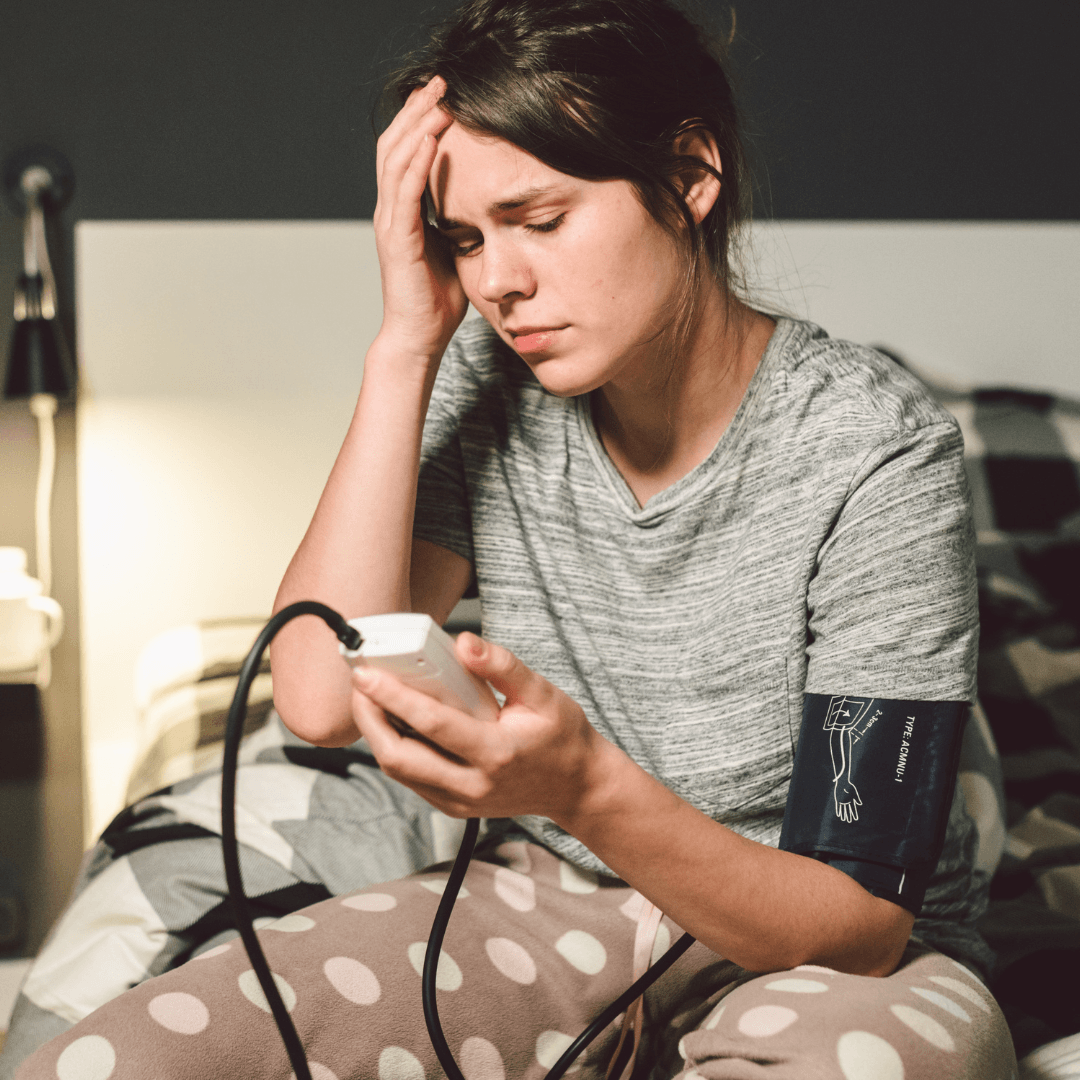

5. Hypertension: A Byproduct Of Chronic Stress
Stress is closely associated with hypertension or high blood pressure. When stressed, our blood vessels constrict, and blood flow increases.
Ongoing or recurring stress can keep blood pressure elevated, posing a significant risk for heart attacks, strokes, and various cardiovascular diseases.
Key Points
- Stress-induced blood pressure spikes can become chronic over time.
- The risk of heart disease and stroke is increased by chronic hypertension.
- Managing stress is essential to prevent long-term hypertension.
6. Mental Health Disorders: Anxiety And Depression
Chronic stress doesn’t only impact physical health; it also has severe implications for mental well-being. Long-term stress contributes to anxiety, depression, and other mental health conditions.
These conditions then raise the risk of lifestyle diseases by encouraging poor coping strategies like substance misuse, overeating, and a sedentary way of living.
Additionally, mental health challenges can make it harder to manage physical conditions, creating a cycle of stress and illness.
Key Points
- Stress is a significant contributor to the development of anxiety and depression.
- Poor mental health leads to behaviours that increase lifestyle disease risk.
- Addressing stress can improve both mental and physical health.
Create a Profitable Holistic Business That Transforms Lives
🌿 Discover inspiring holistic business ideas that blend nature, wellness, and purpose.
Learn how passionate nature lovers are building income streams while helping others live more balanced, mindful lives.
Read Profitable Holistic Business Ideas That Transform Lives
The Importance Of Prevention In Managing Lifestyle Diseases
Healthy habits can significantly reduce the risk of chronic conditions such as diabetes, high blood pressure, and heart disease. Here are some critical strategies for adopting a preventive lifestyle:
1. Adopt A Healthy Diet
One of the most effective strategies to prevent lifestyle-related illnesses is to maintain a well-balanced, nutrient-dense diet.
A diet emphasizing whole, unprocessed foods can provide the body with essential nutrients and lower the risk of health complications.
Prioritize Whole Foods
Incorporate fruits, vegetables, lean proteins (like fish, poultry, and legumes), and whole grains into your meals. These foods provide essential vitamins, minerals, and fiber, which support heart health, regulate blood sugar, and aid in weight management.
Limit Harmful Ingredients
Processed foods often contain high levels of sugar, salt, and unhealthy fats, risk factors for hypertension, diabetes, and obesity.
Reducing these ingredients can lower blood pressure, improve cholesterol levels, and help prevent excessive weight gain. A nutritious diet is the foundation of preventive care and can significantly influence the maintenance of long-term health.
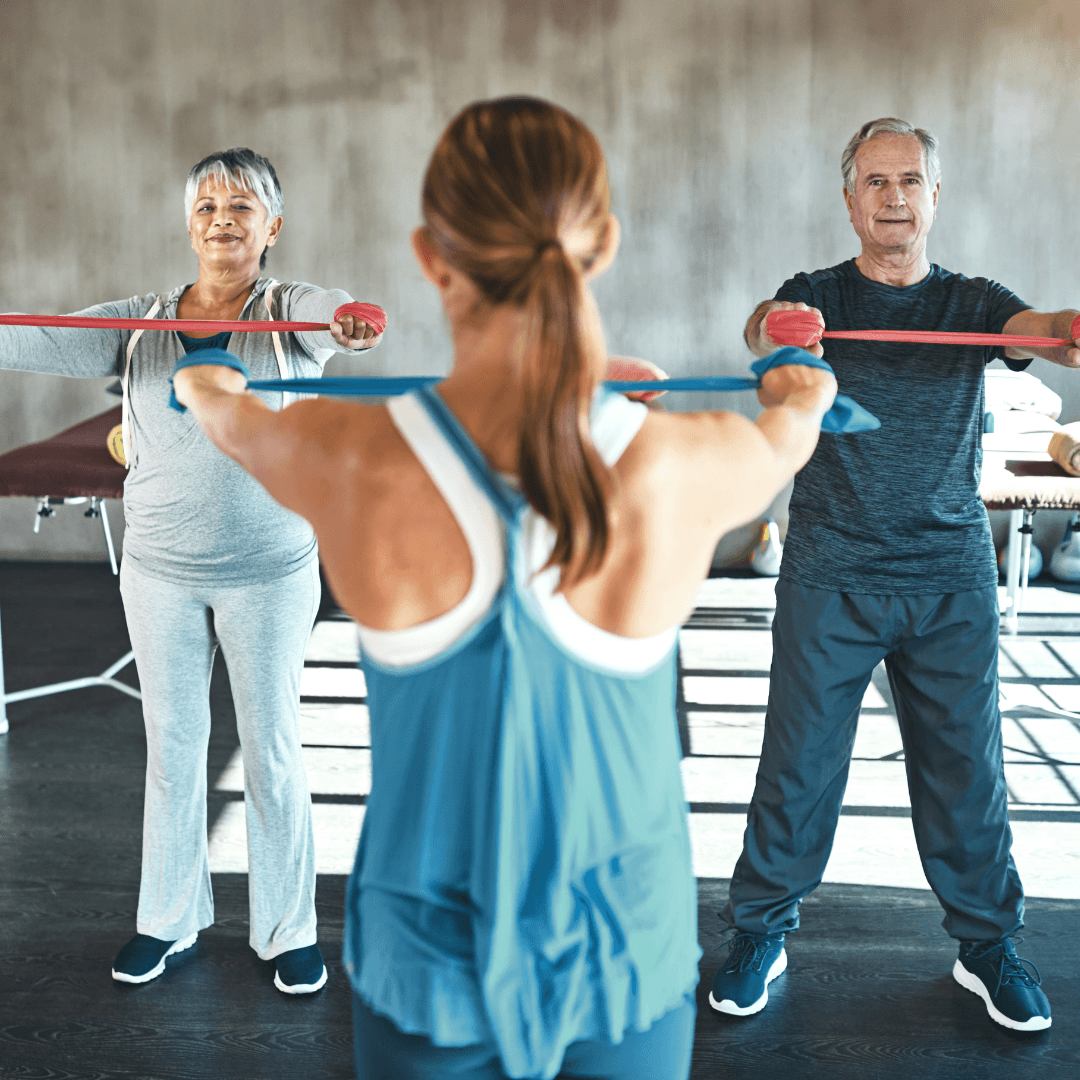

2. Engage In Regular Physical Activity
Regular exercise is critical to preventing lifestyle diseases. It helps with weight management, strengthens the cardiovascular system, improves mood, and reduces stress.
Aim For Consistent Exercise
Engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity weekly exercise. This could include brisk walking, cycling, swimming, or strength training. Seventy-five minutes of vigorous weekly exercise is also effective for those who prefer shorter sessions.
Benefits Beyond Weight Control
Exercise is essential for heart health. It improves circulation, lowers blood pressure, and supports stable blood sugar levels.
Endorphins, which are released after regular exercise, can also elevate mood and lessen the symptoms of depression and anxiety.
Whether it’s a walk around the neighbourhood or a workout at the gym, regular activity is an indispensable part of a healthy lifestyle.
3. Avoid Smoking And Limit Alcohol
Although they are mostly preventable, smoking and binge drinking are two of the leading causes of disease in the lifestyle.
Quit Smoking
A significant risk factor for cardiovascular problems, respiratory disorders, and malignancies is tobacco smoking. Quitting smoking, even later in life, can drastically reduce these health risks. Support groups, counselling, and smoking cessation programs can provide valuable assistance.
Limit Alcohol Consumption
Overindulgence in alcohol is linked to liver damage, high blood pressure, and some cancers. Moderation is key—one drink per day for women and up to two for men is recommended. Reducing alcohol intake supports liver health, reduces inflammation, and lowers the risk of chronic diseases.
Avoiding or moderating these habits is crucial for long-term health and preventing the onset of lifestyle-related illnesses.
4. Practice Stress Management Techniques
By increasing blood pressure, interfering with sleep, and inciting unhealthy coping strategies like smoking or overeating, chronic stress can exacerbate lifestyle illnesses.
Mindfulness And Relaxation
Breathing techniques, yoga, and mindfulness meditation can all support mental health and stress management.
Stay Connected And Engaged
Hobbies, quality time with loved ones, and regular breaks can help you recharge and reduce stress. Enjoyable hobbies and social relationships can boost resilience and mood, lessening the negative consequences of stress.
Stress management is essential not only for mental health but also for preventing physical complications related to lifestyle diseases.
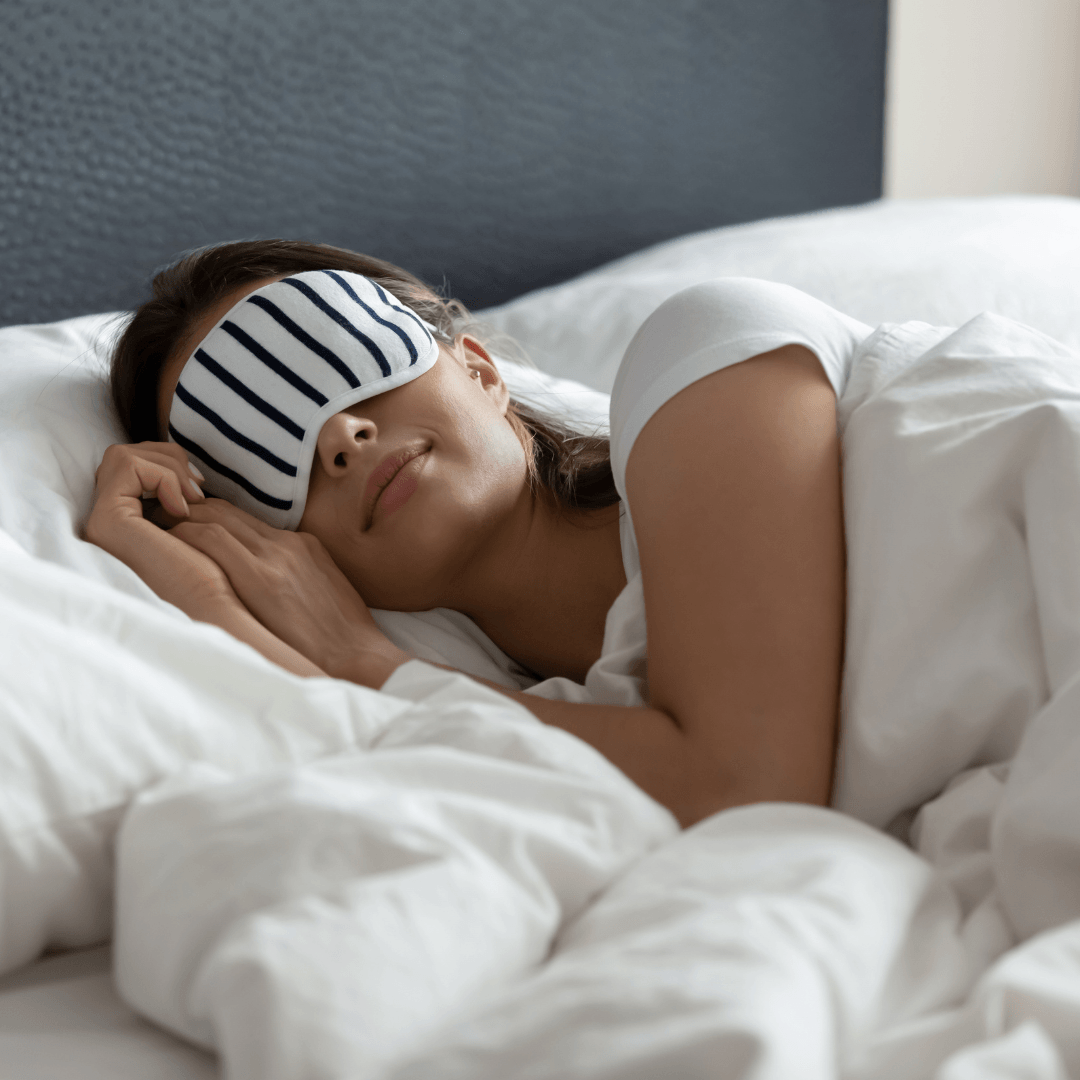

5. Prioritize Sleep
One important but frequently disregarded component in preventing lifestyle illnesses is sleep. Adequate sleep promotes a healthy immune system, maintains energy levels, and supports essential bodily functions.
Aim for 7-8 Hours Per Night
Adults should strive for a sleep pattern of 7-8 hours per night. Proper rest can improve concentration, emotional regulation, and physical health.
Practice Good Sleep Hygiene
Avoid screens before bed, keep your room dark and cool, and establish a relaxing bedtime routine. Good sleep hygiene supports deep, restful sleep, which is critical for repairing the body, managing weight, and reducing the risk of chronic disease. Sleep is essential for overall health because it supports the body and mind.
FAQs
Q1: Are Lifestyle Diseases Preventable?
Answer: Yes, most lifestyle-related illnesses are preventable by adopting healthier habits. Preventive factors for these diseases include a nutritious diet, regular exercise, stress reduction, abstaining from tobacco and excessive alcohol use, and prioritizing sleep.
Q2: How Soon Will I See Benefits After Making Lifestyle Changes?
Some benefits, like improved mood and energy levels, can be felt within a few weeks. Months and years of regular, healthy habits add to long-term health benefits like a lower chance of diabetes and heart disease.
Conclusion
In conclusion, lifestyle-related illnesses are mainly preventable by conscious choices and healthy habits. By prioritizing stress management, regular exercise, a balanced diet, and enough sleep, we can significantly reduce our risk of acquiring these conditions and enhance our quality of life.
We may take charge of our health by making little, regular changes that have long-lasting effects. Embracing preventive measures today lays a strong foundation for a healthier, longer future.
I trust you enjoyed this article on Don’t Let Lifestyle Diseases Control Your Life. Please stay tuned for more inspiring guides, helpful tips, and ideas to help you live closer to nature every day.
Take care!
— JeannetteZ🌿
💬 Your Opinion Is Important To Me
Do you have thoughts, ideas, or questions? I’d love to hear from you. Please leave your comments below or email me directly at Jeannette@Close-To-Nature.org.
📚 More Nature-Inspired Reads
Explore more ways to connect with nature, nurture your pets, and live in harmony with the world around you 🌿