Aquaponics vs Hydroponics: Which Sustainable System Wins
In the ever-evolving world of sustainable agriculture, soilless farming systems have risen to the forefront as practical, efficient, and eco-friendly ways to grow fresh produce. Two of the most popular methods are aquaponics and hydroponics.
This article will explore the key differences and advantages of aquaponics vs hydroponics to help you decide which method suits your growing needs best.
If you’ve been wondering which one might be right for your urban garden, greenhouse, or commercial venture, this in-depth guide will help you understand how each system works, its unique benefits and drawbacks, and how to choose the one that best aligns with your goals.
What Is Hydroponics & How Does It Work?
With hydroponics, vital minerals are delivered straight to plant roots via a nutrient-rich water solution, eliminating the need for soil in plant growth.
Instead of pulling nutrients from the soil, plants grow in a controlled environment where their roots are suspended in water or supported by an inert growing medium like coco coir, perlite, or rock wool.
This soilless farming method isn’t new — ancient civilizations used early versions — but it has become far more popular in recent decades.
Innovations in greenhouse technology, urban agriculture, and sustainability have helped hydroponics gain traction with both hobbyists and commercial growers worldwide.
How Does Hydroponics Work?
A basic hydroponic system includes several key components:
- A reservoir to hold water mixed with precise mineral nutrient solutions.
- A growing tray or series of pipes where plants sit securely.
- An air pump to keep the water oxygenated for healthy root systems.
- Water pumps circulate the nutrient solution to the plants.
- Optional grow lights to supplement or entirely replace sunlight, enabling year-round indoor cultivation.
Several hydroponic techniques exist, such as Deep Water Culture (DWC), Nutrient Film Technique (NFT), Ebb and Flow (Flood and Drain), Wick systems, and even Aeroponics — where roots are misted with nutrients instead of submerged.
The core idea behind hydroponics is simple yet powerful: by giving plants direct, balanced access to water, nutrients, and oxygen, they can grow faster, use less space, and produce higher yields than conventional soil-based gardening.
What Is Aquaponics & How Does It Work?
Aquaponics is an innovative farming method that merges hydroponics (soilless plant cultivation) with aquaculture (raising fish or other aquatic animals).
This unique system creates a balanced, closed-loop ecosystem where plants and fish support each other naturally.
In aquaponics, fish waste becomes a valuable resource rather than pollution. Fish kept in tanks produce waste, mainly ammonia, which would be toxic if it built up.
Beneficial nitrifying bacteria, which transform ammonia into nitrites and subsequently into nitrates—two vital nutrients for plants—come to the rescue.
From the fish tank, this nutrient-rich water is piped to the growing beds for the plants. The plants absorb the nitrates, effectively filtering and purifying the water.
Once cleaned, the water cycles back to the fish tank, creating a self-sustaining loop that uses significantly less water than conventional farming and eliminates the need for chemical fertilizers.
How Does Aquaponics Work?
- A fish tank to house species like tilapia, catfish, trout, or ornamental fish such as koi or goldfish.
- Biofilters are where bacteria thrive and carry out the nitrogen conversion process.
- Grow beds or pipes where plants like leafy greens, herbs, or some fruiting crops are cultivated.
- Pumps and pipes that circulate water throughout the system.
By mimicking natural ecosystems, aquaponics offers a sustainable, efficient, and organic way to raise both fresh fish and healthy produce simultaneously, making it increasingly popular for home gardeners, schools, and commercial growers alike.
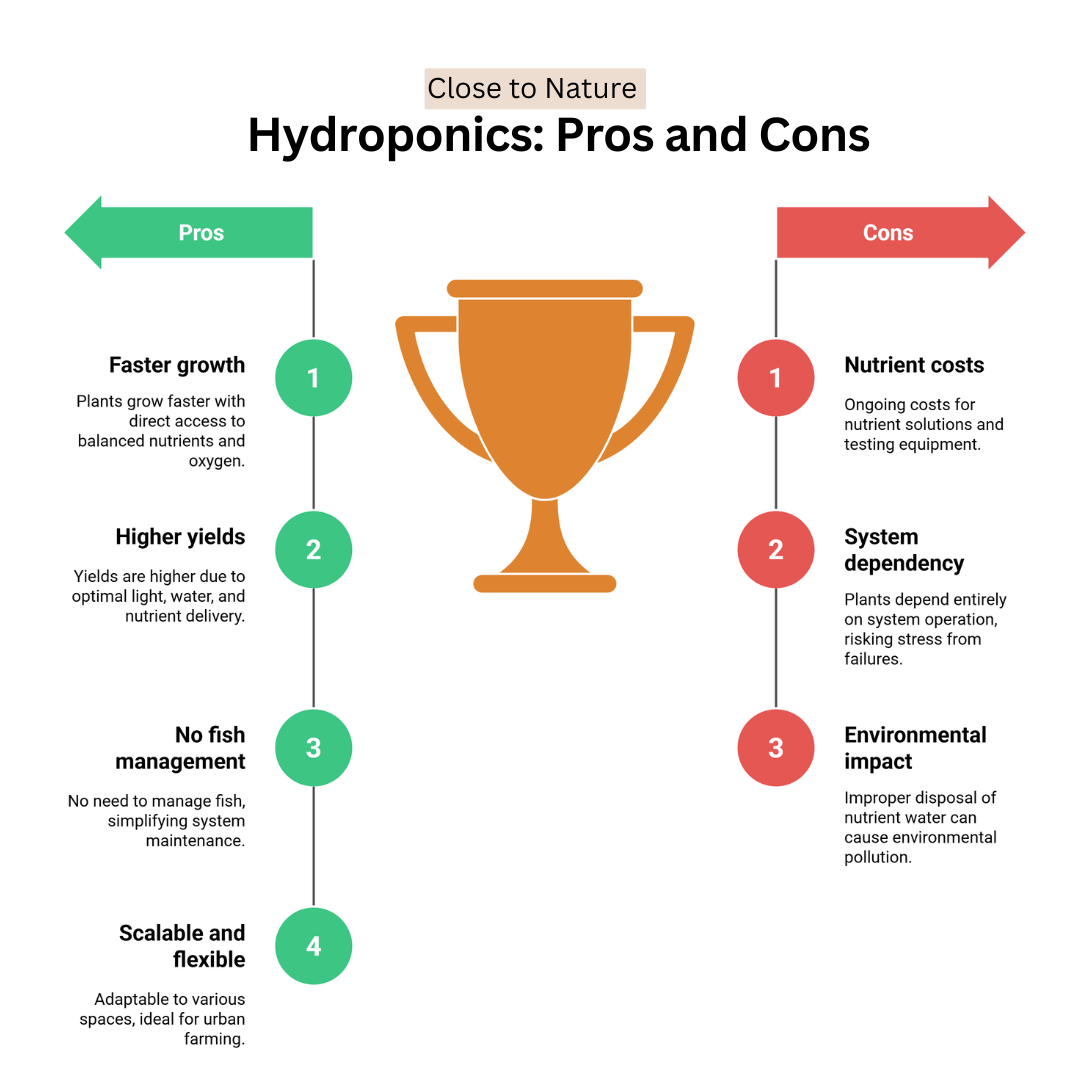
Hydroponics: Pros And Cons
Hydroponics is a popular soilless growing method that uses nutrient-rich water to cultivate plants efficiently. While it offers many advantages, like faster growth and higher yields, it also comes with specific challenges.
Here’s a quick look at the pros and cons of hydroponics.
Pros Of Hydroponics
1. Faster Plant Growth
The pace at which plants develop is one of the most significant benefits of hydroponics. In a hydroponic system, plants have direct and constant access to perfectly balanced nutrients, oxygen, and water, which are all critical for rapid development.
Unlike soil gardening, where roots must search through the soil for these elements, hydroponic roots can focus solely on growth.
This means vegetables and herbs reach harvest size much faster, allowing growers to enjoy more frequent planting and harvesting cycles throughout the year.
2. Higher Yields
When it comes to yields, hydroponic systems are known to yield much more than conventional soil-based farming. Since plants always receive the right amount of light, water, and nutrients, they may focus more of their energy on developing into robust, healthy plants.
Additionally, because hydroponics eliminates competition from weeds and reduces pest issues, crops can flourish without unnecessary stress.
This translates into more produce per square foot, which is especially valuable for commercial growers looking to maximize profits and efficiency within limited spaces.
3. No Fish Management
Unlike aquaponics, hydroponic gardening doesn’t require you to raise fish alongside your plants. This makes the system easier to manage, especially for beginners who may feel overwhelmed by balancing two living systems.
Without fish, there’s no need to monitor water toxicity, feed schedules, or fish health, which can add layers of complexity. You can focus solely on adjusting nutrient levels and maintaining equipment.
This simplicity lets growers concentrate on optimizing plant growth without worrying about an entirely separate aquaculture component.
4. Scalable And Flexible
Hydroponic setups are incredibly adaptable, making them ideal for a wide range of spaces and goals. Whether you want a small herb garden on your kitchen counter or a commercial greenhouse producing thousands of heads of lettuce, hydroponics can be scaled up or down with ease.
Hydroponic systems can be customized to fit rooftops, basements, shipping containers, or vertical racks. This flexibility means urban farmers and hobbyists alike can make the most of limited space and grow fresh produce year-round, regardless of climate.
Cons Of Hydroponics
1. Nutrient Cost
One downside of hydroponics is the ongoing cost of nutrient solutions. Unlike aquaponics, which relies on natural fish waste, hydroponic systems need commercially prepared fertilizers to provide essential minerals.
These nutrient solutions must be replenished regularly and carefully balanced to meet each crop’s needs. This means you’ll need to invest in quality nutrients and testing equipment to monitor levels.
These expenses can mount up quickly for commercial operations, so you should account for them in your overall budget and profit margins.
2. System Dependency
Hydroponic plants are entirely dependent on the system’s continuous operation. If there’s a power outage, pump failure, or blockage in the system, plants can quickly become stressed because their roots don’t have soil to fall back on for moisture or nutrients.
Even a few hours without oxygenated water flow can cause root damage or plant loss. This makes backup power sources, reliable equipment, and regular maintenance crucial for anyone running a hydroponic setup to prevent unexpected system breakdowns.
3. Environmental Impact
While hydroponics is efficient in water use, improper disposal of nutrient-rich water can pose environmental risks. If growers flush nutrient solutions directly into storm drains or waterways, the excess chemicals can contribute to nutrient pollution, leading to harmful algal blooms and damage to aquatic ecosystems.
Responsible hydroponic growers must manage waste carefully by reusing or properly disposing of nutrient solutions. It’s essential to consider this aspect when choosing hydroponics, primarily if you aim to run a truly sustainable operation.
Aquaponics: Pros And Cons
Using a symbiotic relationship between growing plants and raising fish, aquaponics is a sustainable agricultural technique.
It offers unique benefits like organic fertilization and dual food production, but also presents some challenges. Here is a quick summary of aquaponics' benefits and drawbacks:
Pros Of Aquaponics
1. Organic Fertilizer
In aquaponics, the fish waste produced in the system serves as a constant organic fertilizer for your plants. As fish excrete ammonia, naturally occurring beneficial bacteria convert it into nitrates, which plants absorb as nutrients.
This creates a renewable and sustainable nutrient source that eliminates the need for synthetic fertilizers.
This organic approach not only lowers input costs over time but also aligns with eco-friendly and organic growing practices, making your harvest more appealing to environmentally conscious consumers.
2. Dual Income Stream
Aquaponics provides growers with the unique advantage of producing two marketable products at once: fresh vegetables and fish.
While your plants thrive on nutrients from fish waste, the fish themselves can be harvested and sold for food, or in the case of ornamental species like koi or goldfish, for decorative ponds and aquariums.
This dual income potential can make aquaponics more profitable than hydroponics alone, especially for small farms seeking diversified revenue streams and resilience against market fluctuations.
3. Sustainable Ecosystem
One of aquaponics’ greatest strengths is that it mimics nature by creating a balanced, closed-loop ecosystem. Plants use the waste that fish make as a resource, and the plants clean the water for the fish.
This efficient cycle minimizes waste and uses significantly less water than traditional agriculture. By integrating aquaculture and hydroponics, aquaponics reduces the need for chemical inputs.
It lowers environmental impact, making it an excellent choice for growers who prioritize sustainability and ecological responsibility in their farming practices.
4. No Chemical Fertilizers
Aquaponics naturally eliminates the need for synthetic fertilizers because fish waste provides all the nutrients plants need to grow.
This is beneficial for the environment and for anyone who wants to grow food organically because it means you're not buying or handling potentially harsh chemicals.
As a result, aquaponic produce can appeal to health-conscious consumers and local markets seeking chemical-free vegetables.
The absence of chemical fertilizers also reduces the risk of runoff pollution, supporting a cleaner, greener approach to agriculture.
Cons Of Aquaponics
1. Complexity
One of the main challenges with aquaponics is its higher level of complexity compared to hydroponics. Maintaining a healthy fish population and a balanced bacterial ecosystem is equally as important as caring for plants.
Water quality, pH, and temperature must remain within tight ranges that keep both fish and plants healthy. If one part of the system fails, it can affect the entire cycle. This requires careful monitoring and a good understanding of aquaculture and plant care together.
2. Higher Startup Cost
Starting an aquaponics system typically requires a bigger upfront investment than a basic hydroponic setup. In addition to the usual pumps, grow beds, and plumbing, you’ll need fish tanks, biofilters, and often more robust water circulation equipment to handle waste and maintain water quality.
These added components mean higher material and installation costs. Beginners should plan for this extra expense and be prepared to invest in quality equipment to ensure the system runs smoothly and sustainably from the start.
3. Fish Care Required
Running an aquaponics system means you’re responsible for the well-being of live fish in addition to your plants. This includes feeding them the right amount of quality food, monitoring water temperature, oxygen levels, and ammonia buildup, and watching for signs of stress or disease.
Fish health issues can disrupt the nutrient cycle and harm your plants. For those unfamiliar with aquaculture, learning fish care can be an extra layer of responsibility and time commitment that shouldn’t be underestimated.

Cost Comparison: Aquaponics vs Hydroponics
When comparing aquaponic vs hydroponic systems, understanding their initial and ongoing costs is essential to choosing the best fit for your needs.
Both systems require investments but differ in setup complexity and expenses. Here’s a brief comparison of the costs involved in each method.
Initial Investment
Hydroponics
Generally, it is less expensive to set up initially because you only need basic equipment like reservoirs, pumps, and grow trays.
Small home systems can start around $200–$500, while larger commercial hydroponic farms may require a higher investment for automation and advanced lighting.
Aquaponics
More costly upfront since you need additional components like fish tanks, biofilters, and plumbing to support both plants and fish.
A simple backyard aquaponics system often starts around $1,000–$5,000, depending on size, materials, and whether you’re building it yourself.
Turn Your Passion for Nature Into Income
🌿 Whether you love gardening, caring for animals, or exploring holistic living,
You can share your knowledge online and earn from it.
Discover how nature lovers are growing their passions into meaningful, income-generating blogs. 👇
Operating Costs
Hydroponics
Hydroponics requires ongoing purchases of nutrient solutions to feed plants since there’s no natural nutrient source like fish waste.
These solutions must be monitored and replenished regularly, which adds to your operating costs and makes careful management essential for healthy plant growth.
Aquaponics
Aquaponics relies on fish food to keep the fish healthy and produce waste for plant nutrients. You’ll also have electricity costs for pumps and aeration, plus occasional restocking if fish are harvested or lost. These recurring costs should be budgeted upfront.
Labour
Hydroponics
Hydroponics may require daily checks of pH and nutrient strength to keep plants healthy and prevent deficiencies or toxic buildup.
Consistent monitoring helps ensure optimal growth conditions, but it does demand time and attention to detail from the grower.
Aquaponics
Aquaponics needs the same water quality checks, plus daily fish feeding, cleaning tanks to remove debris, and managing biofilters to keep beneficial bacteria thriving. This adds more daily tasks, so aquaponics growers must balance the needs of both plants and fish consistently.
Which One Should You Choose?
Deciding between aquaponic and hydroponic systems ultimately depends on your goals, available resources, and how much time you’re willing to commit.
Reasons To Choose Hydroponics
1. Straightforward & Controlled System
Hydroponics is a straightforward, controlled system because it allows precise management of nutrients, water, and the environment without the added complexity of caring for fish. This makes it easier to focus solely on optimizing plant growth for consistent results.
2. Easy To Scale
The hydroponics system is easy to scale since it can be expanded from small home setups to large commercial farms by simply adding more growing units or upgrading equipment without significant changes in system design.
3. No Fish Management
Hydroponics is ideal if you don't want to manage fish. It eliminates the responsibility of feeding, monitoring, and maintaining aquatic animals. This reduces workload and removes the risks associated with fish health and water quality management.
4. Flexible In Growing Various Plant Types
You may want to choose hydroponics if you plan to grow a wide variety of crops because hydroponics supports many plant types, including leafy greens, herbs, fruits, and vegetables. It offers flexibility to adjust nutrient solutions and system setups to meet the diverse needs of different crops.
Reasons To Choose Aquaponics
1. Sustainability And Organic Methods
In aquaponics, sustainability and organic methods are top priorities because aquaponics uses natural fish waste to fertilize plants, eliminating synthetic chemicals.
This creates an eco-friendly, closed-loop system that conserves water and reduces environmental impact, aligning with sustainable and organic growing goals.
2. Enjoyment Of Raising Fish
Choose aquaponics if iou love the idea of raising fish, as it adds another dimension to your gardening experience. Caring for fish provides a rewarding connection to nature, and harvesting both plants and fish offers a unique, productive way to grow food sustainably.
3. Self-Sustaining Ecosystem
Aquaponics is an excellent choice if you want a fascinating, self-sustaining ecosystem because aquaponics mimics natural cycles where fish, bacteria, and plants coexist and support each other. This dynamic balance creates an engaging, living system that continuously recycles nutrients and water efficiently.
4. Skills To Maintain Balance Between Plants & Fish
Choose aquaponics if you have the time and skill to manage the balance between plants and fish, since maintaining aquaponics requires monitoring water quality, feeding fish, and ensuring both species thrive. It demands knowledge, attention, and commitment to keep the ecosystem healthy and productive.

Conclusion
When considering aquaponics vs hydroponics, both systems offer unique benefits and challenges that depend on your goals, resources, and desired level of care.
Hydroponics provides faster growth, simpler management, and scalability, ideal for growers focusing solely on plants. Aquaponics creates a sustainable, natural ecosystem producing both fish and crops, but requires more complex care.
What you decide to do will rely on your objectives, available resources, and fish management readiness. Both systems represent exciting steps toward sustainable, high-yield food production for the future.
I trust you enjoyed this article on Aquaponics vs Hydroponics: Which Sustainable System Wins. Please stay tuned for more inspiring guides, helpful tips, and ideas to help you live closer to nature every day.
Take care!
— JeannetteZ
💬 Your Opinion Is Important To Me
Do you have thoughts, ideas, or questions? I’d love to hear from you. Please leave your comments below or email me directly at Jeannette@Close-To-Nature.org.
📚 More Nature-Inspired Reads
Explore more ways to connect with nature, nurture your pets, and live in harmony with the world around you 🌿