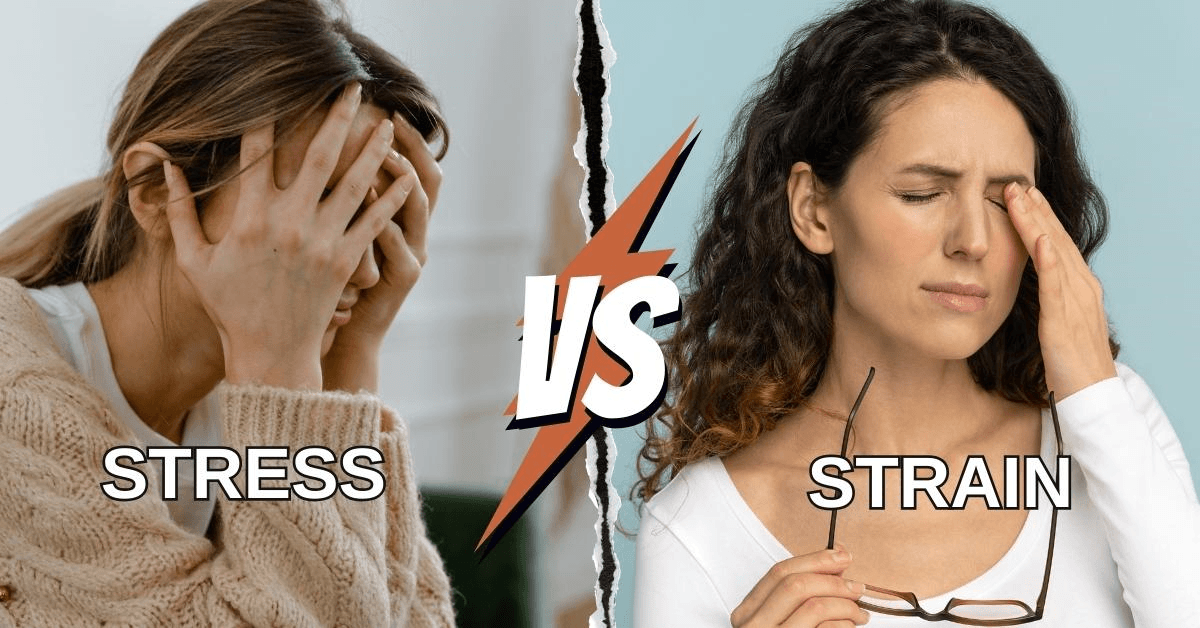
Understanding Stress vs Strain
Understanding Stress vs Strain: Keys To Better Mental Wellness
In the complex mental health landscape, stress and strain are pivotal markers influencing our well-being.
Understanding the nuanced interplay between these two factors is not just enlightening but imperative for cultivating resilience and fostering better mental wellness.
In this exploration, we delve into the intricate dynamics of stress versus strain, unravelling their definitions, manifestations, and impacts on the human psyche.
By clarifying these distinctions, we equip ourselves with invaluable insights to navigate life's challenges with greater efficacy and grace. Join us on this journey as we unlock the keys to unlocking better mental health through a deeper understanding of stress and strain.

What Is Stress?
Stress is the body's natural response to demands or pressures, whether physical, emotional, or psychological.
It manifests as a physiological and psychological reaction triggered by various stimuli, ranging from looming deadlines and financial worries to relationship conflicts and traumatic events.
When faced with stressors, the body activates its innate fight-or-flight response, releasing hormones like adrenaline and cortisol to prepare for action.
This heightened arousal can sharpen focus, boost energy levels, and mobilize resources to tackle the perceived threat.
Prolonged or chronic stress exposure, however, can be harmful to one's physical and emotional well-being.
Numerous symptoms may result from it, such as exhaustion, agitation, headaches, tense muscles, and trouble focusing.
Furthermore, several health issues, including anxiety disorders, depression, and cardiovascular disease, are associated with a higher chance of acquiring chronic stress.
Comprehending stress entails identifying its presence and appreciating its capacity to influence general welfare significantly.
This highlights the significance of implementing efficient coping mechanisms to regulate and alleviate its consequences.

What Is Strain?
Strain refers to the psychological, emotional, and physical toll experienced due to prolonged exposure to stress or pressure.
While stress is the external stimuli or demands placed on an individual, strain represents the internal response to those stressors.
It encompasses the wear and tear on the mind and body caused by continuous stress, which can lead to exhaustion, resource depletion, and diminished resilience.
Emotional and psychological symptoms such as worry, depression, and burnout can also be physical signs of stress, as can headaches, exhaustion, and tense muscles.
Unlike stress, which refers to external pressures or demands, strain reflects the wear and tear experienced by the mind and body due to enduring stressors.
It reflects the cumulative effect of enduring stressors over time, often resulting in decreased performance, impaired cognitive function, and compromised mental well-being.
Identifying and treating strain is crucial for maintaining general health and resiliency in adversity. People can better manage stress and safeguard psychological and physical health by recognizing strain symptoms and implementing useful coping methods.

Symptoms Of Stress
Stress may have many different physical and psychological effects. While it is natural occasionally, severe or chronic stress can cause symptoms affecting general health.

1. Physical Symptoms Of Stress
Stress manifests in various physical symptoms, including headaches, muscle tension, chest pain, fatigue, upset stomach, sleep disturbances, and fluctuations in sex drive.
These symptoms often indicate the body's response to heightened stress levels, affecting overall well-being.
Recognizing these signs is crucial for managing stress effectively, whether through relaxation techniques, exercise, or seeking professional support.
By swiftly treating these symptoms, people can reduce stress's negative effects on their physical health and improve their general quality of life.
2. Emotional Symptoms Of Stress
Emotional symptoms of stress include anxiety, restlessness, difficulty focusing or being motivated, feeling overwhelmed, impatience, and despair or sadness.
These emotional responses can significantly impact mental well-being and daily functioning. Recognizing these signs is essential for implementing coping strategies like mindfulness, seeking support from loved ones, or consulting with a mental health professional.
By addressing emotional symptoms of stress, individuals can better manage their mental health and foster resilience in the face of life's challenges.

3. Cognitive Symptoms Of Stress
Cognitive symptoms of stress include memory problems, difficulty concentrating, impaired judgment, and persistent worrying.
These symptoms can disrupt cognitive function, affecting decision-making and overall mental clarity.
Recognizing these signs is crucial for implementing mindfulness practices, cognitive-behavioural techniques, or seeking professional guidance.
By addressing cognitive symptoms of stress, individuals can enhance their mental resilience and better navigate challenges with clarity and confidence.
4. Behavioural Symptoms Of Stress
Behavioural symptoms of stress encompass changes in eating habits (eating more or less), disturbances in sleep patterns (oversleeping or insomnia), social withdrawal or isolation, procrastination, and neglecting responsibilities.
Additionally, individuals may turn to substances like alcohol, cigarettes, or drugs as coping mechanisms.
Recognizing these behaviours is crucial for implementing healthy coping strategies, seeking social support, and addressing underlying stressors.
By addressing behavioural symptoms of stress, individuals can cultivate healthier habits and effectively manage their stress levels for long-term well-being.

5. Relationship Symptoms Of Stress
Stress-related symptoms may include difficulties communicating or expressing emotions effectively, withdrawal from loved ones, and increased arguments or conflicts with others.
These symptoms can strain interpersonal relationships and impact overall social well-being. Recognizing these signs is vital for nurturing healthy connections, fostering open communication, and seeking support from loved ones or professionals.
By addressing relationship symptoms of stress, individuals can strengthen their relationships, enhance emotional bonds, and cultivate a supportive network during challenging times.
Here are the common symptoms of stress as manifested:
- Headaches
- Muscle tension
- Fatigue
- Sleep disturbances
- Gastrointestinal issues (e.g., stomachaches, cramps)
- Weakened immune system
- Anxiety
- Irritability
- Mood swings
- Difficulty concentrating
- Forgetfulness
- Depression
- Changes in appetite
- Social withdrawal
- Increased substance use
- Procrastination
- Restlessness
- Aggression

Symptoms Of Strain
The symptoms of strain reflect the cumulative impact of prolonged exposure to stress on an individual's mental, emotional, and physical well-being.

1. Physical Symptoms Of Strain
Physical symptoms of strain encompass headaches, muscle tension or pain, chest discomfort, fatigue, upset stomach, sleep disturbances, and fluctuations in sex drive.
These manifestations often indicate the body's response to stress and tension. Recognizing these signs is essential for implementing relaxation techniques, exercising, or seeking medical advice.
Treating the physical symptoms of strain can mitigate stress's detrimental impact on physical health and general well-being.
2. Emotional Symptoms Of Strain
Emotional symptoms of strain include heightened anxiety, restlessness, diminished motivation or focus, feelings of being overwhelmed, irritability, and bouts of sadness or depression.
These emotional responses often accompany periods of increased stress and pressure. Knowing what these symptoms mean will help you ask for support from loved ones, take care of yourself, or consult a professional.
Addressing the emotional symptoms of stress can help people become more resilient and have better mental health.
3. Cognitive Symptoms Of Strain
Cognitive strain symptoms include memory difficulties, decreased concentration ability, impaired judgment, and persistent worrying.
These mental challenges often arise during periods of heightened stress and pressure. Recognizing these signs is essential for implementing coping strategies such as mindfulness techniques, cognitive-behavioural therapy, or seeking professional support.
Treating the cognitive symptoms of strain can boost mental functioning, make better decisions, and lessen the negative effects of stress on general well-being.

4. Behavioural Symptoms Of Strain
Behavioural symptoms of strain encompass changes in eating patterns (eating more or less), disturbances in sleep duration (oversleeping or insomnia), social withdrawal or isolation, procrastination, neglecting responsibilities, and potentially turning to substances like alcohol, cigarettes, or drugs as coping mechanisms.
Recognizing these behaviours is crucial for implementing healthy coping strategies, seeking social support, and addressing underlying stressors.
By addressing behavioural symptoms of strain, individuals can cultivate healthier habits and effectively manage stress for long-term well-being.

5. Relationship Symptoms Of Strain
Relationship symptoms of strain may manifest as difficulties communicating or expressing emotions effectively, withdrawal from loved ones, and increased arguments or conflicts with others.
These symptoms can strain interpersonal relationships and impact overall social well-being. Recognizing these signs is vital for nurturing healthy connections, fostering open communication, and seeking support from loved ones or professionals.
By addressing relationship symptoms of strain, individuals can strengthen their relationships, enhance emotional bonds, and cultivate a supportive network during challenging times.
Here are the commonly observed symptoms of strain:
- Chronic fatigue
- Muscle tension and pain
- Frequent headaches
- Gastrointestinal issues (e.g., stomachaches, digestive disturbances)
- Compromised immune function
- Heightened anxiety
- Irritability
- Mood swings
- Difficulty concentrating
- Memory problems
- Impaired decision-making
- Development or worsening of mental health conditions (e.g., depression)
- Changes in appetite and sleep patterns
- Social withdrawal
- Increased substance use
- Procrastination
- Restlessness
- Aggression

Causes Of Stress
Individuals react differently to different stressors. Therefore, the causes of stress are diverse and can change significantly between people. But among the typical reasons for stress are:
1. Work-Related Stress
Work-related stress arises from a multitude of factors within the workplace. These include excessive workloads, looming deadlines, job security uncertainties, and interpersonal conflicts with colleagues or supervisors.
Moreover, stress is exacerbated by prolonged work hours, lack of autonomy in task management, and insufficient support from management.
This confluence of elements collectively fosters a stressful work environment, impacting individuals' mental and emotional well-being.
Promoting a more hospitable and healthy work environment requires an awareness of and response to these elements.

2. Financial Stress
Financial worries, such as debt, unemployment, or the inability to meet financial obligations, can be significant sources of stress for many individuals.
Financial stress refers to the strain experienced due to financial concerns such as debt and the inability to meet financial commitments.
These worries about paying bills, covering expenses, and securing future financial stability can lead to ongoing stress and anxiety.
Financial stress can adversely affect an individual's entire quality of life and capacity to do tasks, substantially impacting their mental and emotional health.
3. Relationship Stress
Relationship stress arises when individuals encounter difficulties within their connections, whether with family members, romantic partners, or friends.
This strain can stem from diverse factors, including miscommunication, disagreements, or the deterioration of relationships.
For instance, unresolved conflicts or frequent arguments can fuel tension and emotional distress. Furthermore, significant life events like breakups or losing friendships can exacerbate stress and strain within relationships.
Fostering better and more satisfying interpersonal connections requires acknowledging and addressing these issues.
4. Life Transitions
Life transitions, whether relocating, starting a new job, getting married, or becoming a parent, signify significant shifts in one's life trajectory.
While these changes may bring excitement and new opportunities, they also entail a degree of stress.
Stress and anxiety can arise from various situations, including adjusting to new surroundings, negotiating the uncertainties of these changes, and taking on new roles and duties.
People must be resilient and adaptable to deal with the difficulties and adjustments of significant life transitions.

5. Health-Related Stress
Health problems, chronic illnesses, or injuries not only bring about physical discomfort but also entail emotional distress as individuals grapple with their health challenges.
Coping with symptoms, managing treatments, and facing uncertainties about the future can all contribute to heightened stress levels.
Moreover, worries about the impact of illness on one's daily life, financial strain due to medical expenses, and concerns about the well-being of loved ones add further layers of stress.
Balancing physical and emotional well-being becomes paramount in navigating through health-related stressors.
6. Traumatic Events
Acute stress reactions can be brought on by stressful events, including natural disasters, violent crimes, losing a loved one, or accidents.
Responses like these can have significant psychological effects and frequently show up as strong emotional reactions like shock, worry, or dread.
People may have symptoms like nightmares, flashbacks, or avoidance behaviours as a way to cope with the fallout from such occurrences.
In several instances, individuals require professional intervention, such as counselling or therapy, to assist them in processing their experiences and creating coping mechanisms to handle the enduring psychological consequences of trauma.
7. Environmental Stressors
Environmental factors like noise pollution, overcrowding, and traffic congestion can significantly impact stress levels.
Constant exposure to these stressors can lead to heightened feelings of tension, anxiety, and irritability.
Living in such environments can gradually wear down an individual's overall well-being, making it harder to cope with other stressors in life.
Environmental stressors can also contribute to the development of new physical health issues and exacerbate pre-existing mental health disorders.
Thus, creating a more supportive and less stressful environment is essential for maintaining overall health and well-being.

8. Personal Stressors
Personal factors such as perfectionism, self-criticism, unrealistic expectations, or neglecting self-care can significantly increase stress levels.
Perfectionists often place immense pressure on themselves to meet unattainable standards, leading to chronic stress and dissatisfaction.
Similarly, self-criticism can fuel negative thought patterns and intensify feelings of inadequacy or failure.
Unrealistic expectations create tension between desired outcomes and reality, perpetuating a cycle of stress.
Furthermore, neglecting self-care, such as insufficient sleep or poor nutrition, diminishes resilience and exacerbates stress reactions.

Causes Of Strain
Causes of strain can vary widely depending on the context, whether physical, emotional, or relational. Here are some common causes of strain:

1. Communication Issues
Inadequate communication, marked by misunderstandings, lack of clarity, or ineffective expression of thoughts and feelings, can strain relationships.
When communication breaks down, conflicts remain unresolved, fostering frustration or resentment.
Fostering open, honest, and empathetic communication is essential to mitigate such strain. This involves active listening, clear articulation of needs and concerns, and a willingness to understand each other's perspectives.
Individuals can cultivate stronger, healthier relationships by addressing communication gaps and nurturing a mutual respect and understanding culture.
2. Conflicts And Disagreements
Divergent opinions, values, or expectations can spark relationship conflicts and disagreements. These conflicts can escalate when left unaddressed or unresolved, causing strain and tension between individuals.
By understanding and respecting each other's perspectives, individuals can navigate disagreements constructively, fostering empathy and strengthening their bond.
Moreover, embracing differences as opportunities for growth can lead to greater understanding and harmony within the relationship.

3. Trust Issues
Trust is a cornerstone in relationships and is pivotal for fostering intimacy and connection. However, when trust is eroded by dishonesty, betrayal, or past traumas, it can introduce substantial strain.
Trust issues may surface as feelings of insecurity, jealousy, or reluctance to be vulnerable, profoundly affecting the relationship's dynamics.
Rebuilding trust necessitates open communication, transparency, and consistent actions that demonstrate reliability and honesty.
Addressing trust issues with empathy and understanding is crucial for restoring stability and fostering a healthier, more resilient relationship.
4. Unmet Needs And Expectations
Strained relationships often stem from unmet needs, emotional, physical, or relational aspects, and unrealistic or unspoken expectations.
Unmet needs can breed frustration, resentment, and a sense of disconnection. At the same time, unclear expectations may evoke disappointment, blame, and confusion.
Openly communicating needs and expectations and a willingness to compromise fosters a foundation for building a robust and satisfying relationship.
This approach encourages mutual understanding, strengthens trust, and cultivates a supportive environment where both partners feel valued and fulfilled.
5. External Stressors
Even the strongest relationships can feel the weight of external pressures like financial strain, work burnout, health scares, or family drama.
These stressors act like uninvited guests, disrupting the delicate balance and making it harder to connect and be present with your partner.
To navigate these choppy waters, couples must be adept communicators, expressing their needs and frustrations openly.
But navigating these problems goes beyond just talking. It requires a commitment to mutual support and a willingness to be each other's cheerleaders and problem-solving partners.

6. Lack Of Boundaries
In relationships, unclear or nonexistent boundaries can pave the way for personal boundaries to be disregarded, fostering feelings of suffocation and resentment.
Imagine a room without designated spaces; things get cluttered, and resentment builds. Boundaries in relationships are similar.
Establishing and honouring boundaries is essential for fostering healthy and balanced relationships.
This practice promotes mutual respect, ensures individual autonomy, and helps prevent misunderstandings and conflicts.
By clearly defining boundaries, individuals can feel secure in expressing their needs and preferences, thus cultivating trust and harmony within the relationship.
7. Life Transitions
Major life changes, including relocation, career shifts, starting a family, or coping with loss, often disrupt the equilibrium of relationships.
Individuals must adapt to new roles, responsibilities, and circumstances, which can generate stress and strain within their relationships.
Adjusting to these changes requires effective communication, mutual support, and patience to navigate the challenges together.
This transition period can strengthen bonds or reveal underlying tensions, highlighting the importance of resilience and understanding in sustaining healthy relationships.
8. Unresolved Past Issues or Traumas
Another significant cause of strain in relationships is unresolved past issues or traumas. Relationships can suffer when people carry emotional baggage from past experiences, such as unsolved conflicts, childhood trauma, or past relationships.
These unresolved issues may surface during stress or conflict, leading to heightened tension and difficulty maintaining healthy communication and connection.
Addressing and processing these past traumas or unresolved problems through therapy or counselling can help individuals heal and strengthen their current relationships.

Tips To Reduce Stress
Recall that managing stress is a process, and it's acceptable to experiment with different approaches until you find the ones that work best for you.
When navigating through stressful situations, make self-care a priority and practice self-compassion. The following advice can be used to lessen stress:

1. Practice Relaxation Techniques
Including relaxation methods in your daily routine, such as progressive muscle relaxation, deep breathing, or meditation, can significantly soothe your body and mind.
Breathing deeply and slowly is necessary to trigger the body's relaxation response, which reduces stress chemicals and promotes calm.
By concentrating on awareness and mindfulness, meditation can help to calm racing thoughts and promote inner serenity.
2. Stay Active
Staying active through regular physical activity is a powerful way to reduce stress levels and boost overall well-being.
Exercise releases the brain's natural mood enhancers, or endorphins, promoting contentment and relaxation.
Exercise becomes more fun and consistent when you do it with activities you enjoy, like cycling or walking.
Whether it's a stroll in nature or an energetic dance session, finding activities that resonate with you can make staying active a rewarding and sustainable habit.
3. Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle
Enhancing resilience to stress requires maintaining a healthy lifestyle. A well-rounded diet abundant in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins supplies vital nutrients that promote overall health and wellness.
Consistent sleep schedules are a priority because they guarantee enough rest, which is necessary for stress reduction, mood control, and cognitive function.
Limiting caffeine and alcohol intake helps stabilize energy levels and promote better sleep quality.
Adopting these lifestyle habits can strengthen your body's ability to cope with stress, improving physical and mental health outcomes.

4. Set Realistic Goals
To reduce stress and boost productivity, you must set reasonable goals. Breaking tasks into smaller, manageable goals makes them more achievable and less daunting.
Prioritizing these goals helps you focus your time and energy on what's most important. Setting realistic expectations for yourself reduces the likelihood of feeling overwhelmed or discouraged.
Acknowledging and celebrating minor accomplishments throughout the journey can also enhance motivation and self-assurance.
5. Practice Time Management
Practicing effective time management is crucial for reducing stress and increasing productivity. To organize tasks and allocate time efficiently, use to-do lists, planners, or digital calendars.
Sort tasks into high- and low-priority categories according to their importance and due dates. You may prevent over-committing by evaluating your ability honestly and developing the ability to say no when required.
You may avoid burnout and preserve a good work-life balance by establishing boundaries and managing expectations.
Using good time management techniques, you may do more tasks in less time and reduce stress and overwhelm.
6. Seek Social Support
Seeking social support is vital for managing stress and maintaining emotional well-being. Connecting with loved ones, friends, or support groups offers a secure space for sharing emotions and experiences.
Talking to others can provide perspective, validation, and encouragement, helping you feel less isolated and overwhelmed.
Additionally, friends and loved ones can give practical advice and assistance in navigating challenges.
Whether through a heartfelt conversation, a listening ear, or a group setting, seeking social support fosters resilience and strengthens interpersonal connections, ultimately promoting mental and emotional health.
7. Take Breaks
Incorporating periodic breaks into your day is vital for preserving mental acuity, productivity, and holistic wellness.
Incorporate regular intervals to rest and recharge, stepping away from work or stressful situations. Use this time to relax and enjoy yourself by doing something you enjoy, such as taking a stroll, practicing mindfulness, or engaging in a favorite hobby.
Taking breaks allows your mind and body to reset, reducing fatigue and preventing burnout. By prioritizing self-care and allowing yourself to pause, you can better manage stress and sustain optimal performance throughout the day.

8. Limit Exposure to Stressors
Limiting exposure to stressors is key to managing stress effectively and maintaining well-being. Determine what aspects of your life—work, relationships, or personal responsibilities—are causing you stress.
This could be avoiding stressful situations or individuals, setting limits to safeguard your time and energy, or assigning responsibilities to others to reduce your workload.
Taking control of your environment and making intentional choices to reduce stress can cultivate a greater sense of calm and resilience in navigating life's challenges.

Tips To Reduce Strain
Reducing strain in life involves adopting strategies to alleviate stress and promote overall well-being.
Applying these techniques to your everyday life can reduce stress, build resilience, and enhance your general quality of life.

1. Practice Self-Care
Self-care involves consciously allocating time and resources to support your physical, mental, and emotional well-being.
It entails giving top priority to pursuits that advance general well-being and health. Exercise releases endorphins, improves mood, lowers stress levels, and improves mental and physical clarity.
Furthermore, relaxation methods, including yoga, meditation, and deep breathing, support relaxation and mental calmness.
Since interests and pursuits offer chances for creativity, expression, and renewal, pursuing them that make you happy and fulfilled is also crucial for self-care.
2. Manage Time Effectively
Effective time management involves utilizing tools like planners and calendars to prioritize tasks and set achievable goals while avoiding over-commitment.
Individuals can stay focused and accountable by breaking tasks into smaller, manageable goals and establishing realistic deadlines.
This approach prevents procrastination and ensures steady progress towards larger objectives.
Furthermore, understanding when and how to say no to extra tasks can help maintain a healthy work-life balance and avoid burnout.
Effective time management reduces stress, increases productivity, and promotes a sense of accomplishment and well-being.
3. Seek Social Support
Seeking social support is invaluable for maintaining mental and emotional well-being. Joining friends, family, or support groups allows people to express their emotions and experiences freely in a caring setting.
This exchange provides an opportunity to gain perspective, receive encouragement, and feel understood and validated.
Additionally, social support fosters a sense of belonging and reduces feelings of isolation and loneliness.
Through heartfelt conversations, group discussions, or shared activities, seeking social support strengthens interpersonal connections and promotes resilience in facing life's challenges.

4. Communicate Openly
Open communication is vital for nurturing healthy and thriving relationships. In an atmosphere of open communication, people can efficiently handle disagreements, establish boundaries, and communicate their requirements.
This entails paying attention to one another, being open to criticism, and honestly discussing views and feelings.
When conflicts arise, open communication allows for constructive dialogue and problem-solving, helping to resolve issues.
Setting boundaries through open communication ensures that each person's needs and preferences are respected, fostering mutual understanding and trust.
Overall, prioritizing open communication cultivates deeper connections and enhances intimacy.
5. Set Boundaries
Setting boundaries is essential for maintaining personal well-being and fostering healthy relationships.
By establishing clear and healthy boundaries, individuals protect their time, energy, and emotional health from excessive demands or negativity.
This involves identifying your limits and communicating them assertively to others. Whether it's saying no to additional responsibilities, limiting contact with toxic individuals, or scheduling time for self-care, setting boundaries empowers individuals to prioritize their needs and maintain balance in their lives.
Respecting and upholding boundaries fosters mutual respect and understanding in relationships.
6. Take Breaks
Taking breaks is crucial for maintaining mental clarity, preventing burnout, and sustaining productivity.
Regular intervals throughout your day to rest and recharge allow you to step away from tasks, reset your mind, and replenish your energy levels.
This can involve short breaks to stretch, walk around, or engage in relaxation techniques and longer breaks for meals or leisure activities.
By giving yourself permission to pause and take breaks, you can prevent exhaustion and maintain focus and efficiency throughout the day.
7. Practice Mindfulness
Intentionally focusing on the present moment while maintaining awareness and acceptance is a mindfulness practice.
Meditation, deep breathing techniques, and mindful movement routines like tai chi or yoga can all help develop mindfulness.
Regular participation in these practices can help people manage stress and improve their well-being.
Mindfulness helps quiet the mind, calm the nervous system, and cultivate inner peace and clarity. By staying present and non-judgmental, individuals can better manage challenging emotions and navigate life's ups and downs with greater ease and resilience.
8. Address Stressors
Addressing stressors involves taking proactive steps to identify and mitigate sources of stress in your life. Identify specific stressors from work, relationships, health concerns, etc.
Once identified, strategies to minimize exposure to these stressors should be considered. This may involve delegating tasks, setting boundaries, or avoiding triggers whenever possible.
Additionally, don't hesitate to seek professional help, whether therapy, counselling, or medical support.
By addressing stressors head-on, individuals can take control of their well-being and cultivate healthier, more balanced lives.

9. Seek Professional Help If Needed
Seeking professional help is crucial if stress becomes overwhelming or impacts your well-being. Counselors, therapists, and other medical experts are educated to offer people the support, direction, and resources they need to manage stress and enhance their mental well-being.
If you find it difficult to handle your stress alone, ask for assistance. Expert help can provide insightful information, coping mechanisms, and a secure environment to investigate and resolve underlying problems causing stress.
Recall that asking for aid shows strength and that putting your mental health first is crucial to your well-being.
Conclusion
Grasping the distinction between stress and strain is pivotal for fostering improved mental wellness.
By recognizing the triggers and manifestations of stress, individuals can proactively implement strategies to mitigate its effects and cultivate resilience.
Moreover, understanding the nuanced differences between stress and strain empowers individuals to adopt targeted approaches that promote well-being, such as stress-reduction techniques, self-care practices, and seeking support when needed.
Ultimately, by prioritizing mental well-being and implementing these principles into daily life, people may readily traverse obstacles and lead more balanced and meaningful lives.
I trust you enjoyed this article about Understanding Stress vs Strain: Keys To Better Mental Wellness. Please stay tuned for more blog posts soon.
JeannetteZ
>>>Please click here to read my all-inclusive article about Lessons That Will Teach You All About Stress<<<
>>>Are you interested in Natural Healing And Stress Relief through Herbs? Please click here for my #1 Recommendation<<<
Your Opinion Is Important To Me
Do you have thoughts, ideas, or questions? I would love to hear from you. Please leave me your questions, experiences, and remarks about this Understanding Stress vs Strain: Keys To Better Mental Wellness article in the comments section below. You can also email me at Jeannette@Close-To-Nature.org.
Disclosure
This post may contain affiliate links. I earn from qualifying purchases as an Amazon Associate and other affiliate programs. Please read my full affiliate disclosure.
You might also enjoy these blog posts:
Why Do Cats Get Stressed And How Can We Help?
Why Is My Dog Stressed And How To Relieve It?
15 Best Ways To Reduce Stress In Kids
15 Best Tips On How To Reduce Eye Stress
17 Best Tips On How To Reduce College Stress